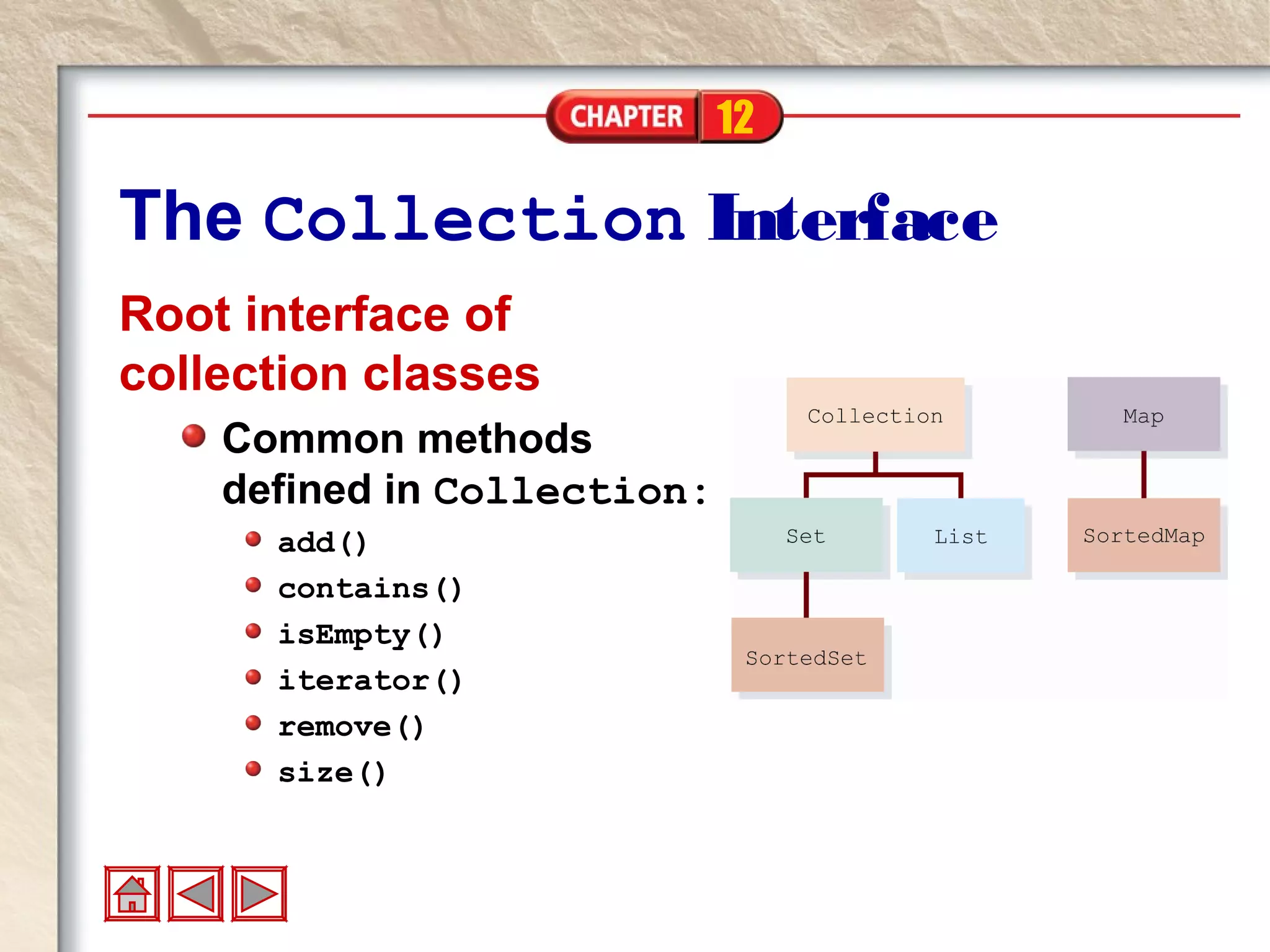
The document discusses Java collection frameworks. It describes different types of collections like sets, lists, and maps. It explains that collections are groups of objects known as elements. The document also outlines the Collection interface, ArrayList class, and methods for adding, removing, replacing, and controlling the size of elements in an ArrayList.