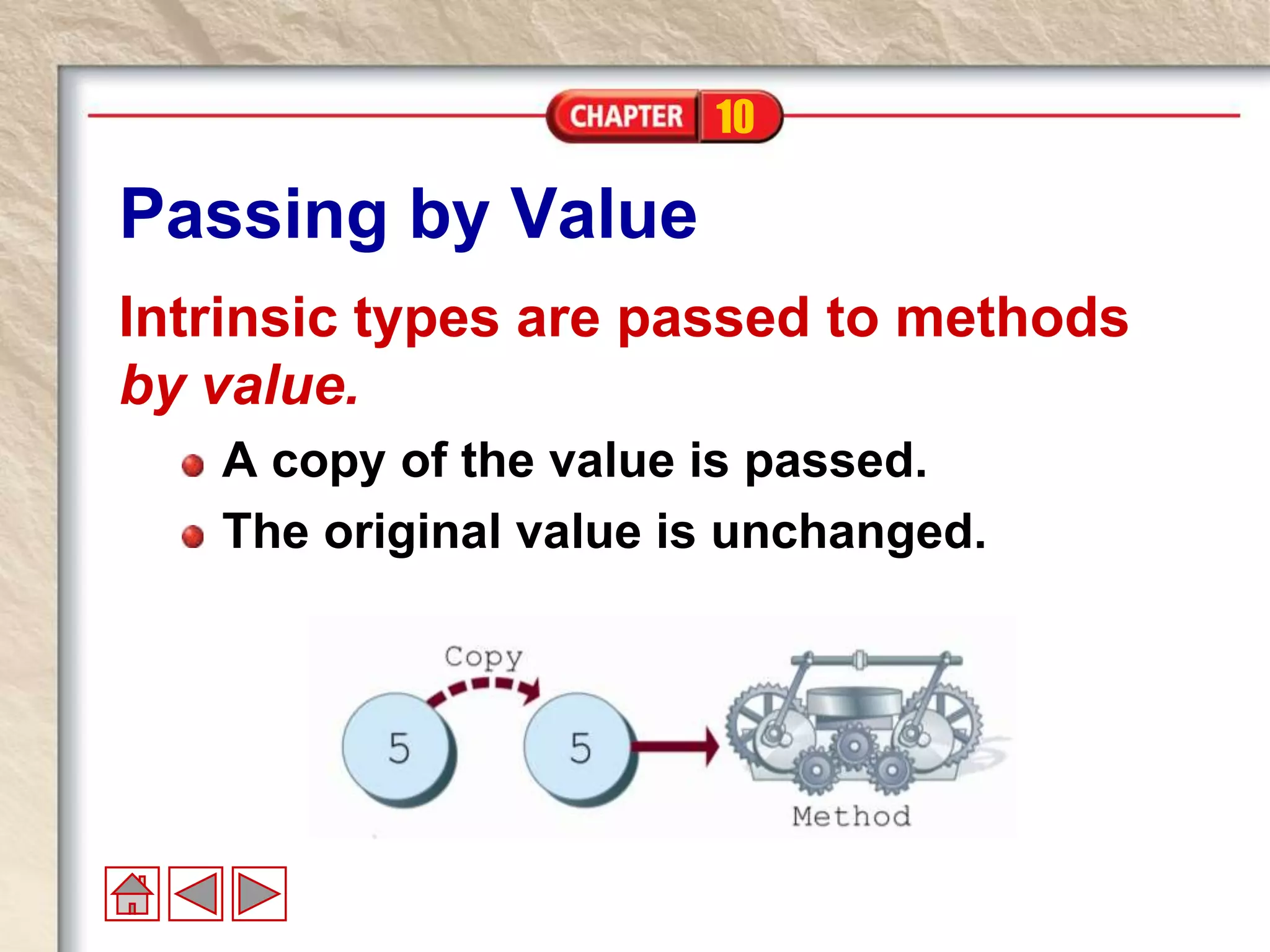
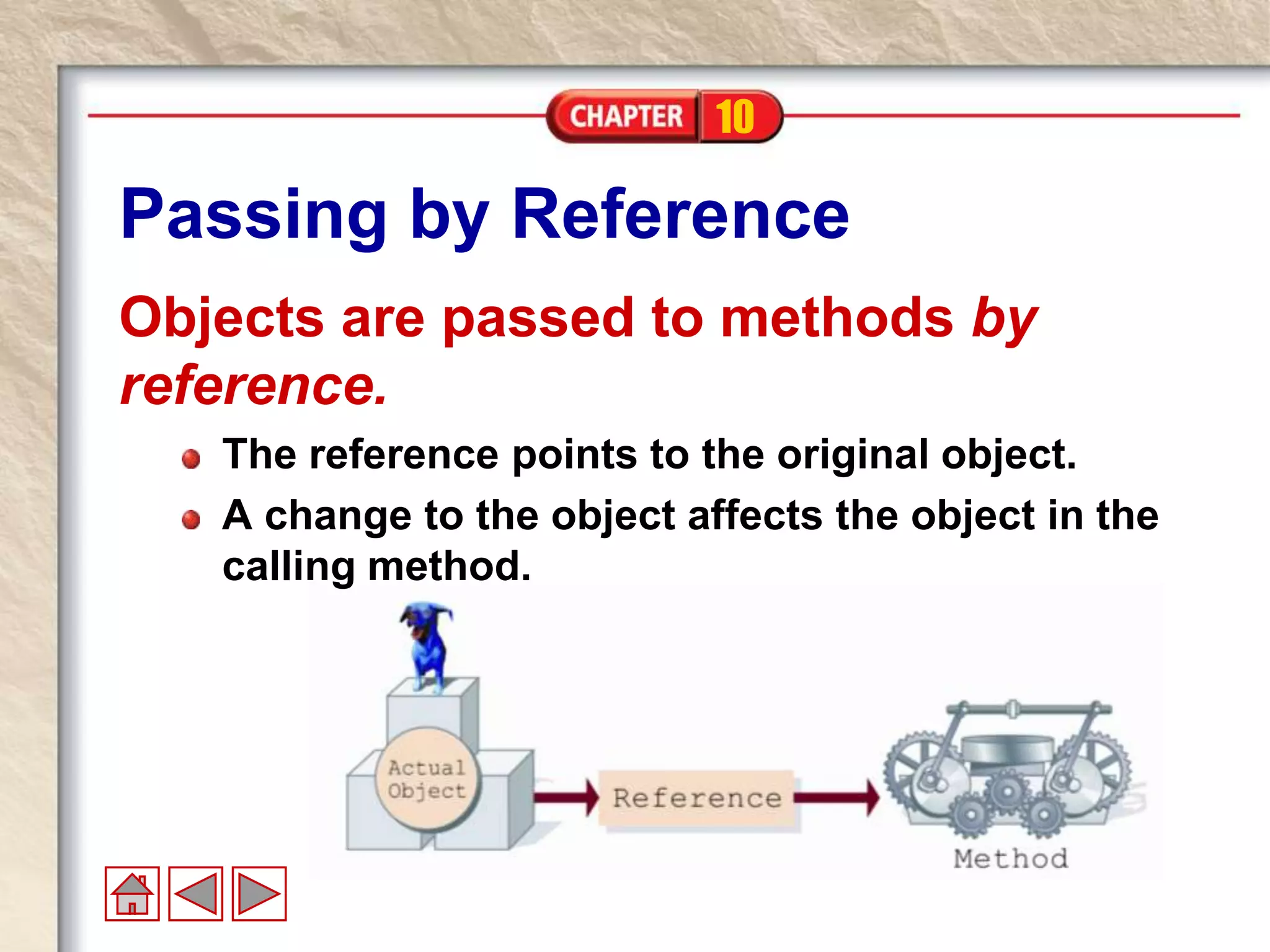
An array is an ordered collection that stores elements of the same type within a single variable name. Elements are accessed via an index number that starts at 0. Arrays can be declared with a type and size, then instantiated using new. Values are assigned using the index operator. The length property returns the number of elements in the array. Arrays are objects that are passed by reference, but intrinsic element types within arrays are passed by value.


![10
Declaring Arrays
Identify type of array
Use square brackets
int[] myArray;
Declares an array of int values](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter10-140413041707-phpapp02/75/Chapter-10-3-2048.jpg)
![10
Instantiating Arrays
Use the new keyword
Identify number of elements
myArray = new int[1000];
Instantiates myArray with 1000 elements
You can declare and instantiate in one
line
int[] myArray = new int[1000];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter10-140413041707-phpapp02/75/Chapter-10-4-2048.jpg)
![10
Putting Values in the Array
Use the index operator to assign a
value at a particular place in the array.
myArray[10] = 100;
Assigns the value 100 to the 10th element
in the array
Most programs use a for loop to
iterate the array.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter10-140413041707-phpapp02/75/Chapter-10-5-2048.jpg)
![10
Initializing the Array
You can initialize the array with values
at the same time the array is created.
int[] myArray = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter10-140413041707-phpapp02/75/Chapter-10-6-2048.jpg)