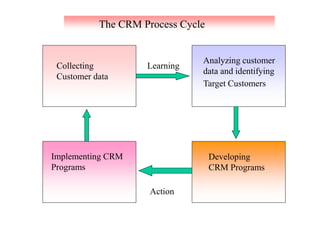
The document discusses the significance of Customer Relationship Management (CRM) in enhancing customer loyalty and profitability for retailers. It highlights how retailers are shifting from generic promotional strategies to targeted efforts that focus on building emotional connections with valued customers through personalized experiences. The CRM process involves collecting and analyzing customer data to develop strategies that foster loyalty and repeat business, ultimately leading to increased profits.