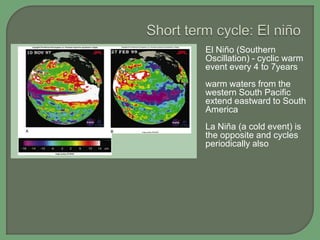
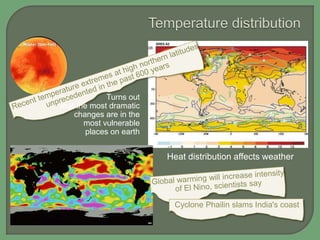
- Climate varies naturally due to regular orbital cycles that influence sunlight and atmospheric greenhouse gases, but is also influenced by human activities that are increasing global temperatures
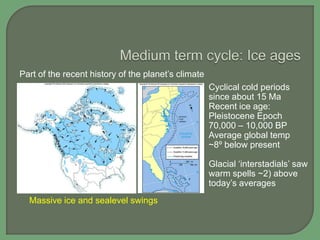
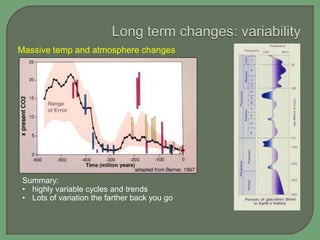
- Both natural cycles and human-caused trends affect global climate over time, with temperatures and climates highly variable the farther back in history
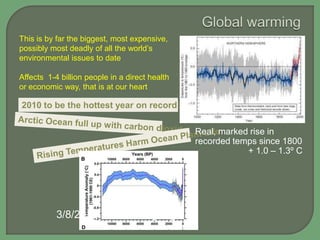
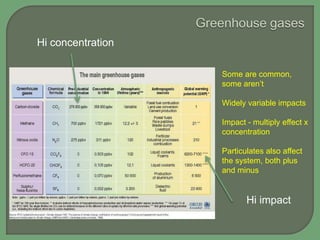
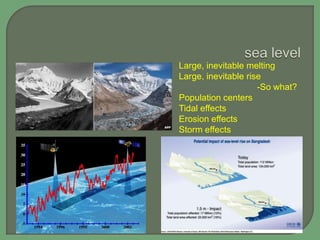
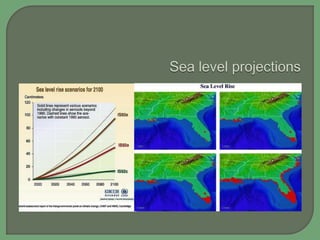
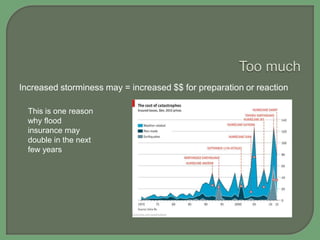
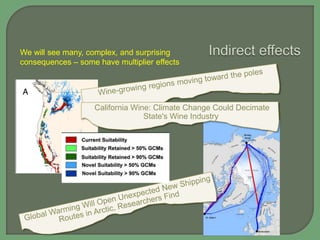
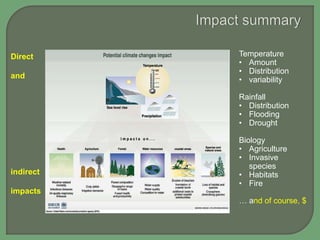
- Impacts of climate change are widespread and complex, affecting weather patterns, sea levels, ecosystems, agriculture, economies and human health and security



![Distance and angle
from sun is directly
linked to climate & ice
ages, warm spells
Regular orbital cycles have major influence on sun’s warming
Atmospheric influence on keeping the warmth [greenhouse effect]
Trend: temp
increase since
10,000 BP
cycle: 5 peaks
over ~400,000
years
Global temps and climate are a combination of cycles and trends](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter10-140118093613-phpapp02/85/Chapter-10-4-320.jpg)
![Atmospheric process
trapping sun’s heat - stuff in
the atmosphere acts as an
insulating blanket
A natural part of the
system, enhanced with
added power
Greenhouse gases:
chemicals [or particles]
contributing to the warming
effect](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter10-140118093613-phpapp02/85/Chapter-10-9-320.jpg)

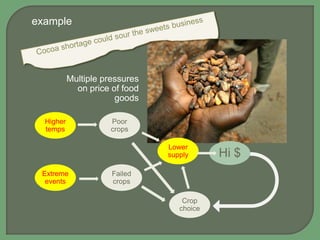
![Environmental campaigners have argued
that to avoid dangerous climate change
[>2ºC] then up to ¾ of the coal, oil and gas
reserves must be left in the ground
SO maybe, if these stashed resources are
mostly worthless, this will have a major
impact on the share values of the fossil fuel
corporations that own them](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter10-140118093613-phpapp02/85/Chapter-10-21-320.jpg)
