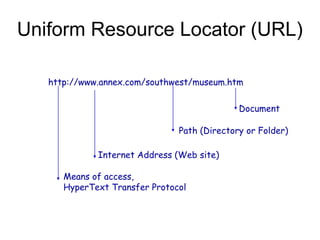
The document provides an overview of the internet and how it functions. It discusses that the internet is a network of networks that began in 1969 as ARPANET and has no central authority. It also describes that the World Wide Web is a subset of the internet consisting of hypertext documents linked together from computers around the world. Finally, it explains the client/server model where servers store documents and clients request and display them through browsers.