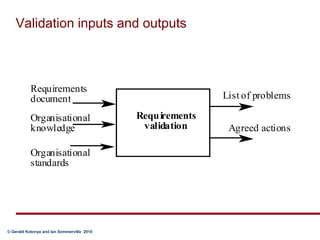
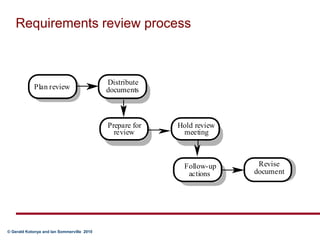
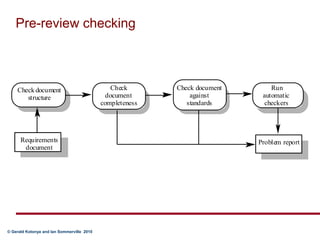
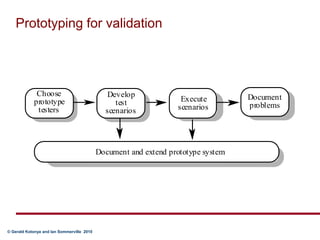
Requirements validation certifies that the requirements document accurately describes the system to be built. It checks for completeness, consistency, standards compliance, and technical errors. Validation analyzes the final requirements document, while analysis works with initial requirements. Validation inputs include the requirements document and organizational standards. Outputs are a problem list and agreed actions. Requirements reviews involve analyzing the document for problems, discussing issues, and agreeing on solutions. Validation techniques include reviews, prototyping, modeling, and testing.