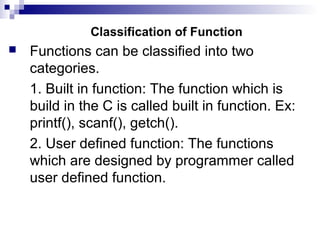
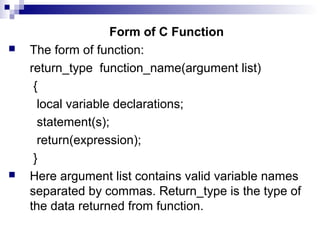
User-defined functions allow programmers to break programs into smaller, reusable parts. There are two types of functions: built-in functions that are predefined in C like printf() and user-defined functions created by the programmer. A function is defined with a return type, name, and parameters. Functions can call other functions and be called from main or other functions. Parameters can be passed by value, where the value is copied, or by reference, where the address is passed so changes to the parameter are reflected in the caller. Functions allow for modularity and code reuse.








![Function with Array
Like the values of simple variables, it is also
possible to pass the values of an array to a
function.
main()
{
static int value[ ]={10,45,25,40};
printf(“Largest value: %d”,maximum(value,4));
}
int maximum(int x[ ], int n)
{ int i, max=0;
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
if(max<x[i])
max=x[i];
return(max);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chap-9functions-150221120827-conversion-gate02/85/Chap-9-functions-12-320.jpg)