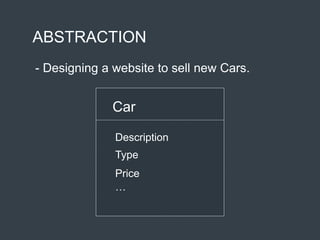
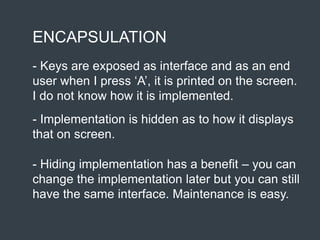
The document discusses the concepts of abstraction and encapsulation in object-oriented programming. Abstraction involves focusing on relevant aspects of an object by excluding unnecessary details, while encapsulation provides a way to access an object's functionality while hiding its implementation. The conclusion emphasizes that abstraction precedes encapsulation in problem-solving approaches.