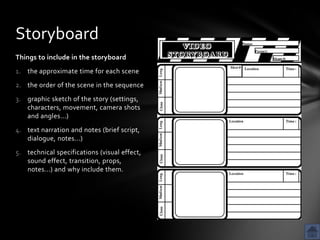
The document outlines the schedule and activities for the second class of an instructional technology integration course, including reviewing assignments from the first class, discussing reading on technology integration in education, and working in groups to plan video projects using storyboards. Students will review videos created in the first class, discuss statistics on technology use in schools and its impact on learning, and learn how to effectively plan video shoots through creating storyboards.