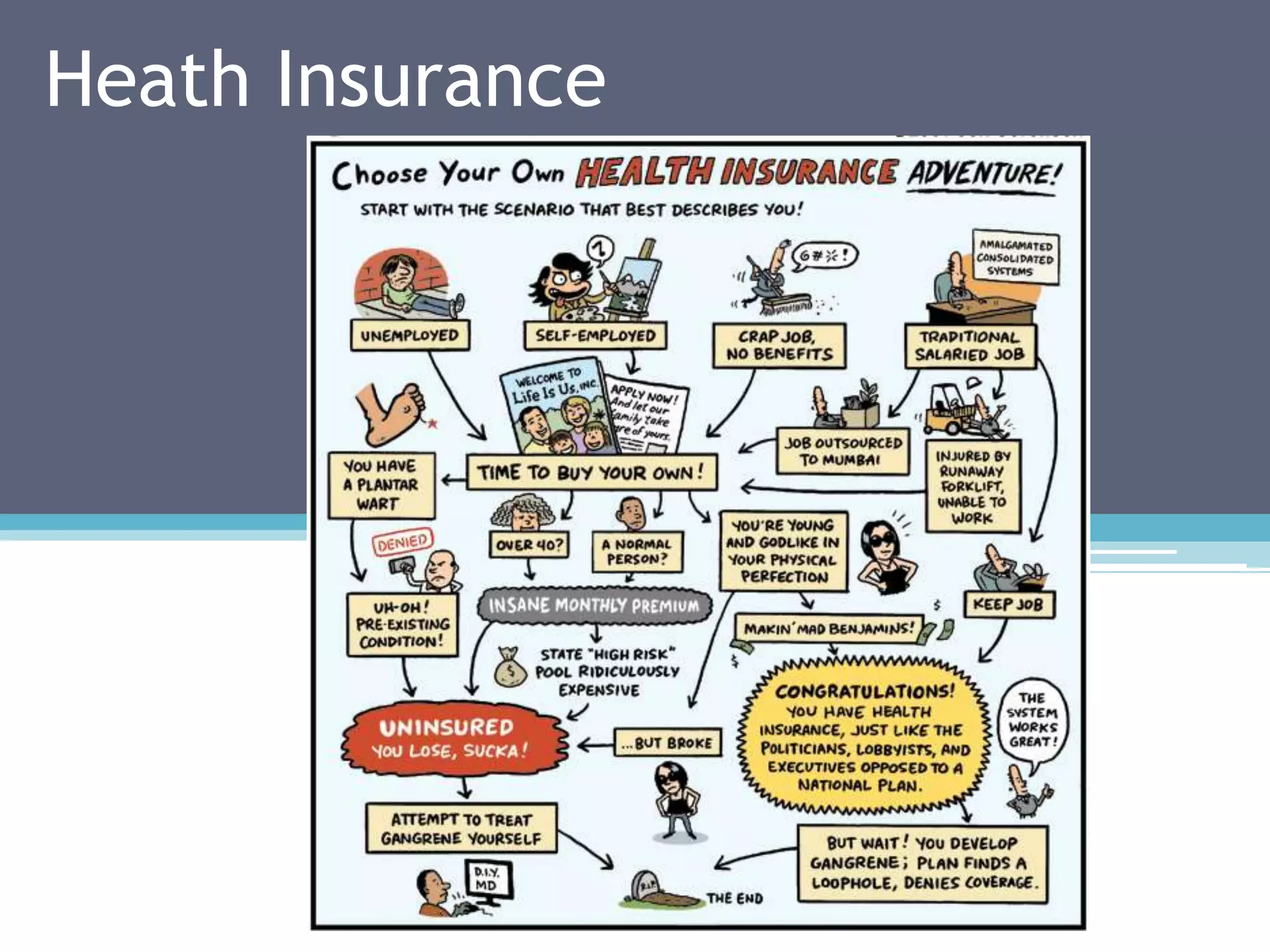
Health insurance in the US has evolved from primarily covering catastrophic illness to also covering preventative care and services. There are various types of health insurance plans including HMOs, PPOs, and consumer-driven plans. Government plans like Medicare and Medicaid provide coverage for specific groups. Providers must verify a patient's insurance coverage and submit claims according to the insurer's requirements to receive reimbursement.