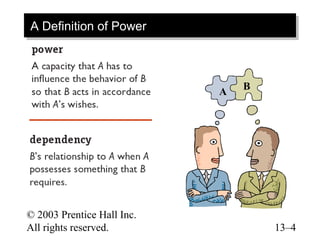
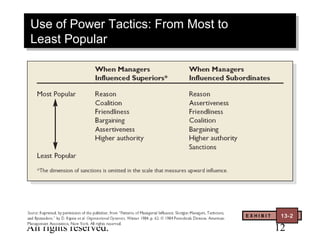
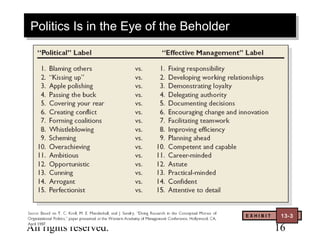
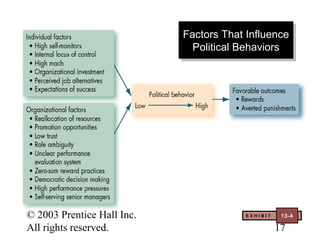
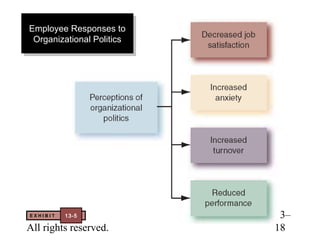
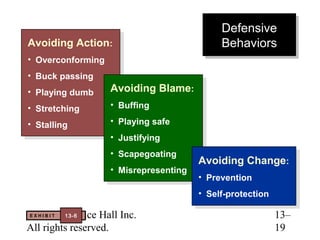
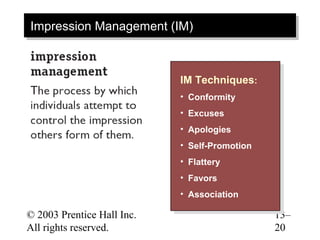
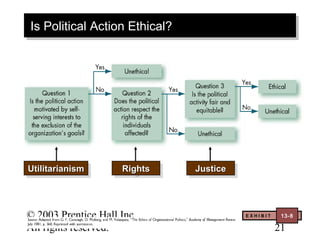
This document contains chapter objectives and content about organizational power and politics from Stephen P. Robbins' 10th edition textbook. It defines power, contrasts it with leadership, and outlines the four bases of power. It also discusses power tactics, dependency in power relationships, sexual harassment in the workplace, and political behaviors in organizations. The document provides information on avoiding and defensive behaviors, impression management techniques, and evaluating the ethics of political actions.