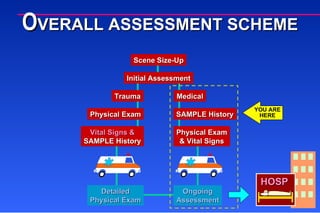
The document discusses how to assess medical patients, including:
1) Performing a focused history and physical exam for responsive patients, including SAMPLE history and focused exam.
2) Differences in assessing responsive vs. unresponsive patients, rapid exam for unresponsive.
3) Ongoing assessment includes repeating initial assessment, vital signs, focused exam, and checking treatments.