1) The document discusses key concepts in bioenergetics including the first and second laws of thermodynamics, enthalpy, entropy, free energy, coupled reactions, and how these concepts relate to biochemical processes.
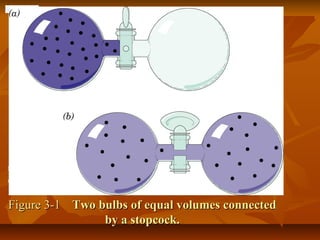
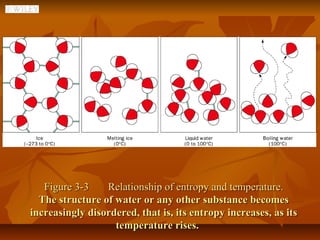
2) Thermodynamics is essential for understanding metabolic pathways, why molecules cross membranes, and how muscles generate force. The first law states that energy is conserved while the second law states that spontaneous processes increase disorder.
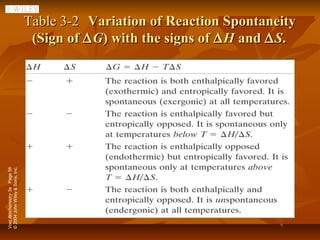
3) Free energy is used to determine reaction spontaneity and how coupled reactions allow endergonic reactions to be driven by exergonic ones, providing a thermodynamic basis for metabolic pathways.