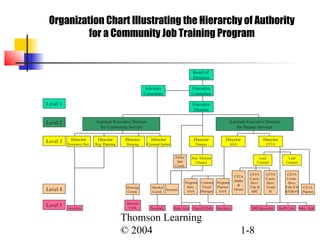
This document discusses key topics in organization theory, including definitions of organizations, their importance, and characteristics. It describes organizations as open systems that take in resources to produce goods and services. Organizations must adapt to changing environments, create value for stakeholders, and address challenges such as diversity. The document also examines organization structure, comparing mechanistic and organic designs, and analyzing dimensions such as formalization, specialization, and hierarchy across different organizations.