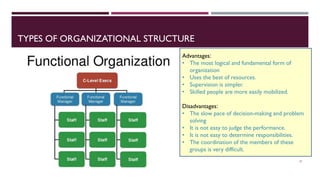
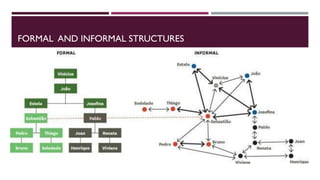
HP was founded in 1963 by David Packard and Bill Hewlett in a garage. It originated as a company designing personal computers and has since expanded into various products. As technology advanced, HP transformed its organizational structure from mechanical to organic to adapt to changing environments. It underwent restructuring like merging divisions to reduce costs and labor. There are different types of organizational structures like functional, divisional, and matrix that have advantages and disadvantages depending on the company's goals and strategy. Formal and informal structures also exist within organizations.