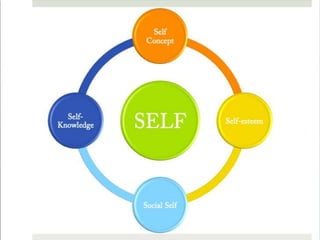
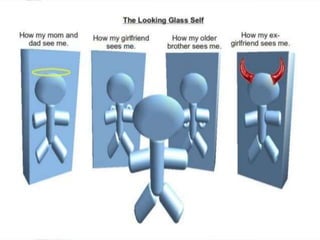
Charles Horton Cooley was an American sociologist associated with the University of Michigan in the early 20th century. He was a founding member of the American Sociological Association and is best known for developing the concept of the "looking-glass self", which describes how individuals perceive themselves based on how they believe others view them. The looking-glass self involves three steps - imagining how one appears to others, imagining others' judgments, and developing feelings like pride or shame based on that imagined judgment. Cooley made important contributions to the concepts of self, socialization, and primary groups in sociological theory.







![Example of Self
The real Alice, known only to her maker.
Her idea of herself
“I [Alice] look well in this hat”
Her idea of Angela’s idea of her
“Angela thinks I look well in this hat”
Her Idea of what Angela thinks she thinks of herself
“Angela thinks I am proud of my looks in this hat”
Angela’s idea of what Alice thinks of herself
“Alice thinks she looks stunning in that hat”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/charlescooley-211211152656/85/Charles-Horton-Cooley-8-320.jpg)