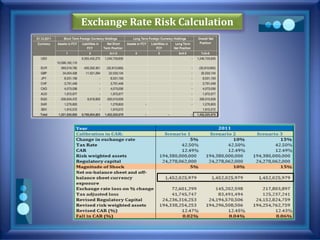
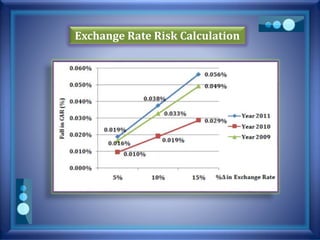
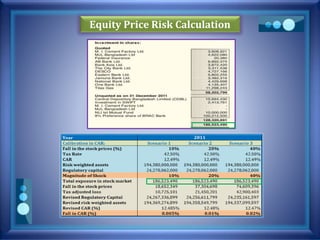
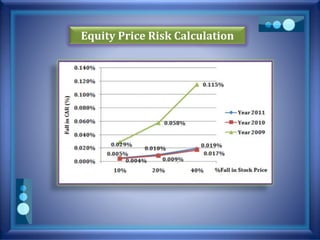
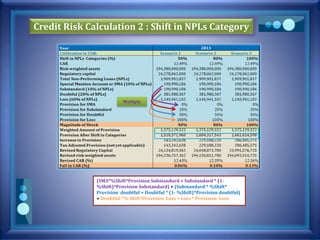
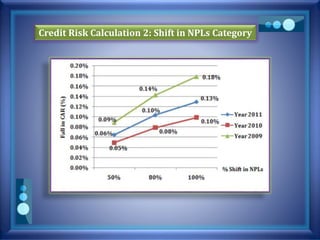
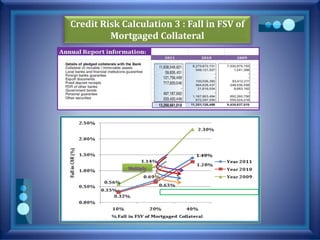
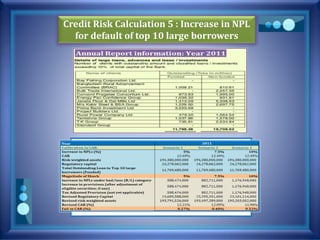
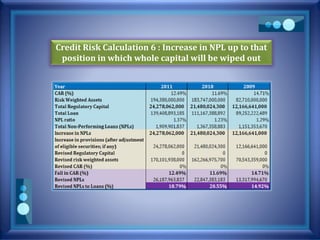
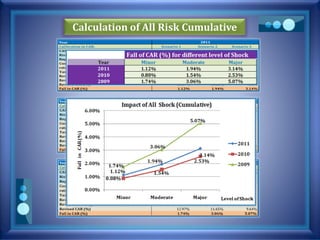
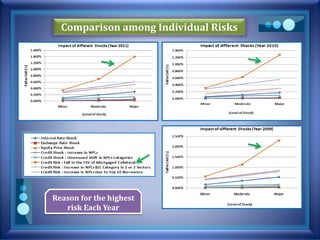
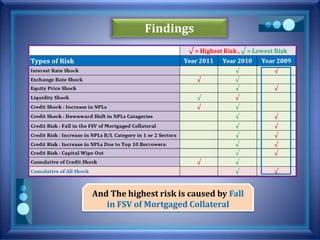
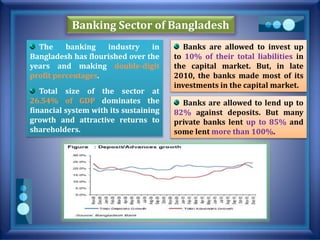
This document discusses stress testing conducted on Prime Bank Limited (PBL) in Bangladesh from 2009-2011. It analyzes various risks, including interest rate risk, exchange rate risk, equity price risk, liquidity risk, and credit risk. Credit risk, specifically the risk of a fall in the forced sale value of mortgaged collateral, posed the highest risk to PBL's capital adequacy ratio during this period. The stress testing assessed the potential impact of shocks to different risk factors and determined that PBL had sufficient capital to absorb minor and moderate shocks, but may have required additional capital to withstand cumulative shocks across multiple risk areas.








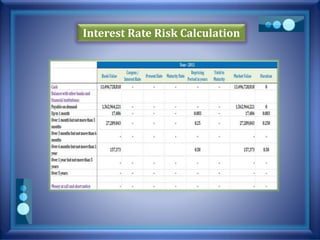
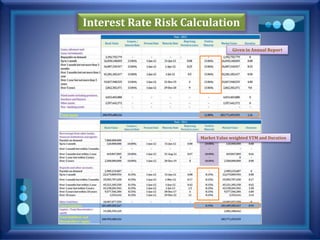
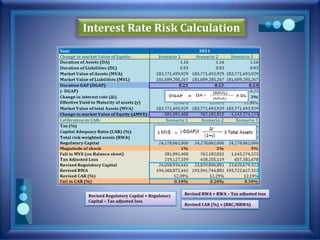
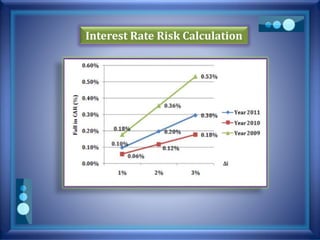
![Interest Rate Risk Calculation
Current market rate PV (rate, nper, pmt, [fv] )
DURATION (settlement, maturity, coupon,
yield, frequency)
Settlement date = Present date
Maturity date = Settlement Date + Repricing Period
Assumption
Excel File](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pblst13-008-150323154618-conversion-gate01/85/Pubali-Bank-Limited-stress-testing-11-320.jpg)