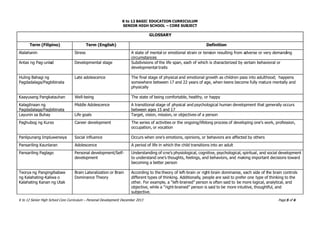
This document outlines the curriculum for a Personal Development core subject for senior high school students in the Philippines. The course aims to help students understand themselves and their development during adolescence. It covers topics like self-development, managing stress, mental health, and building relationships. The course uses experiential learning approaches across various modules to help students explore concepts in psychology and their own development.