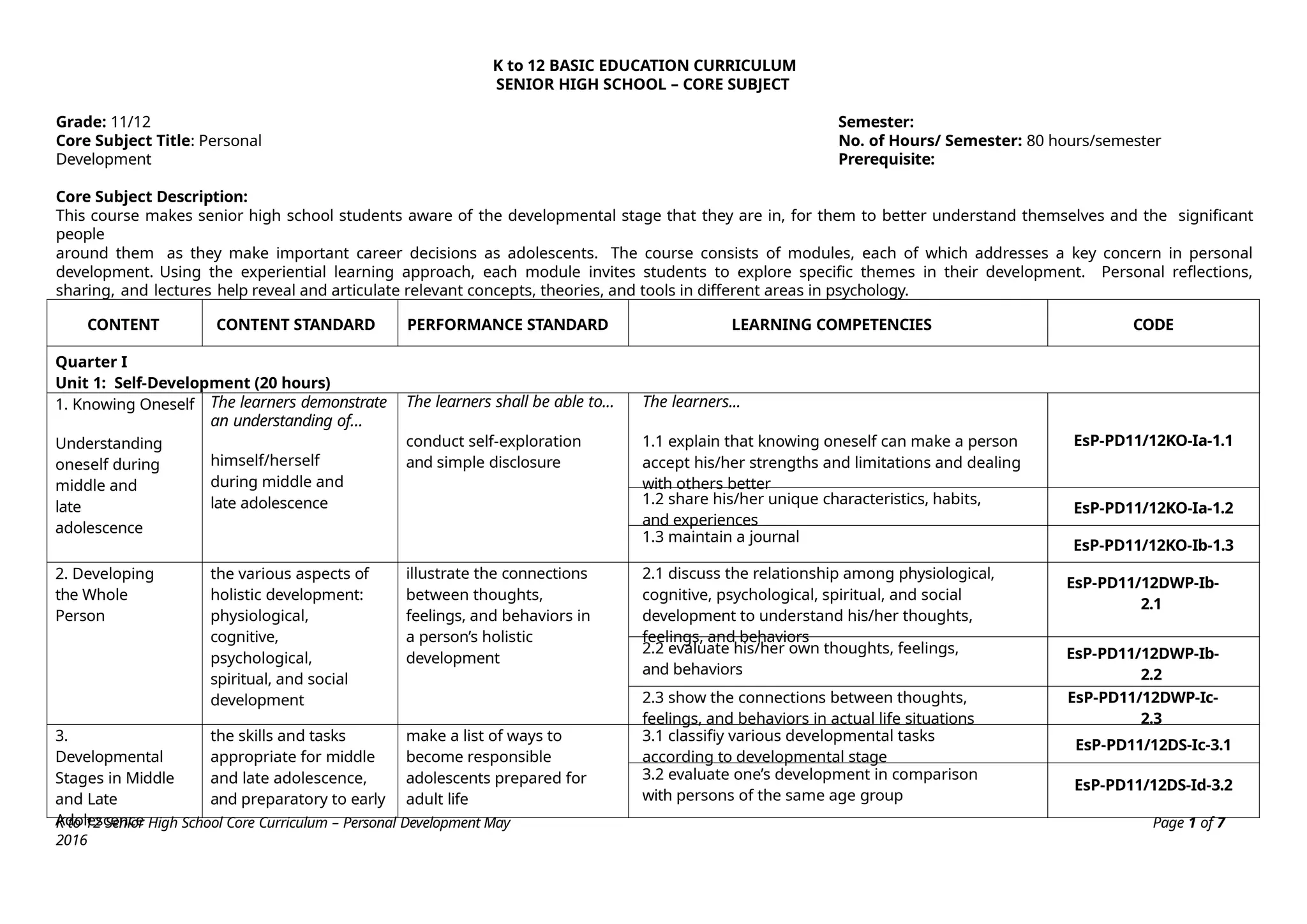
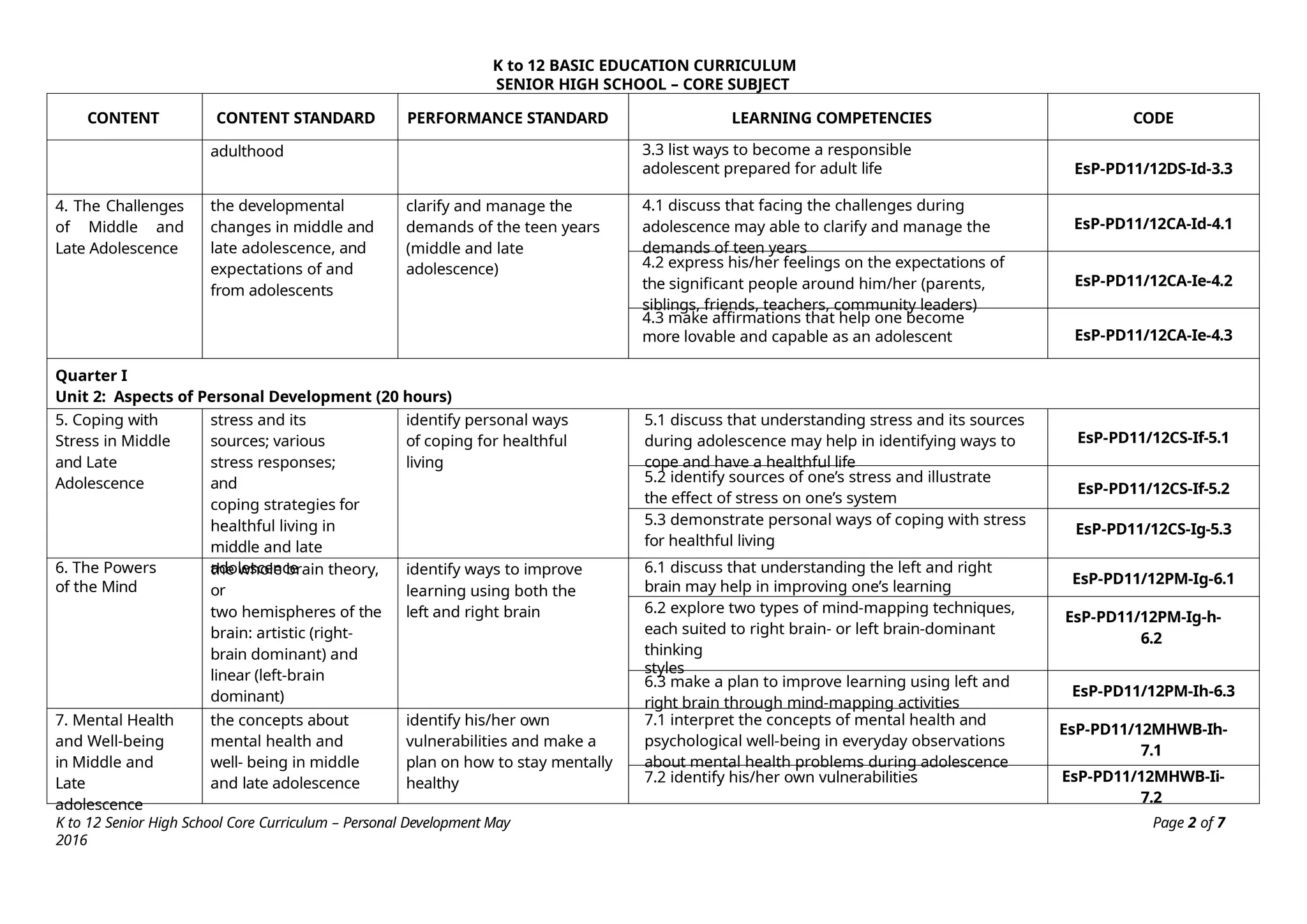
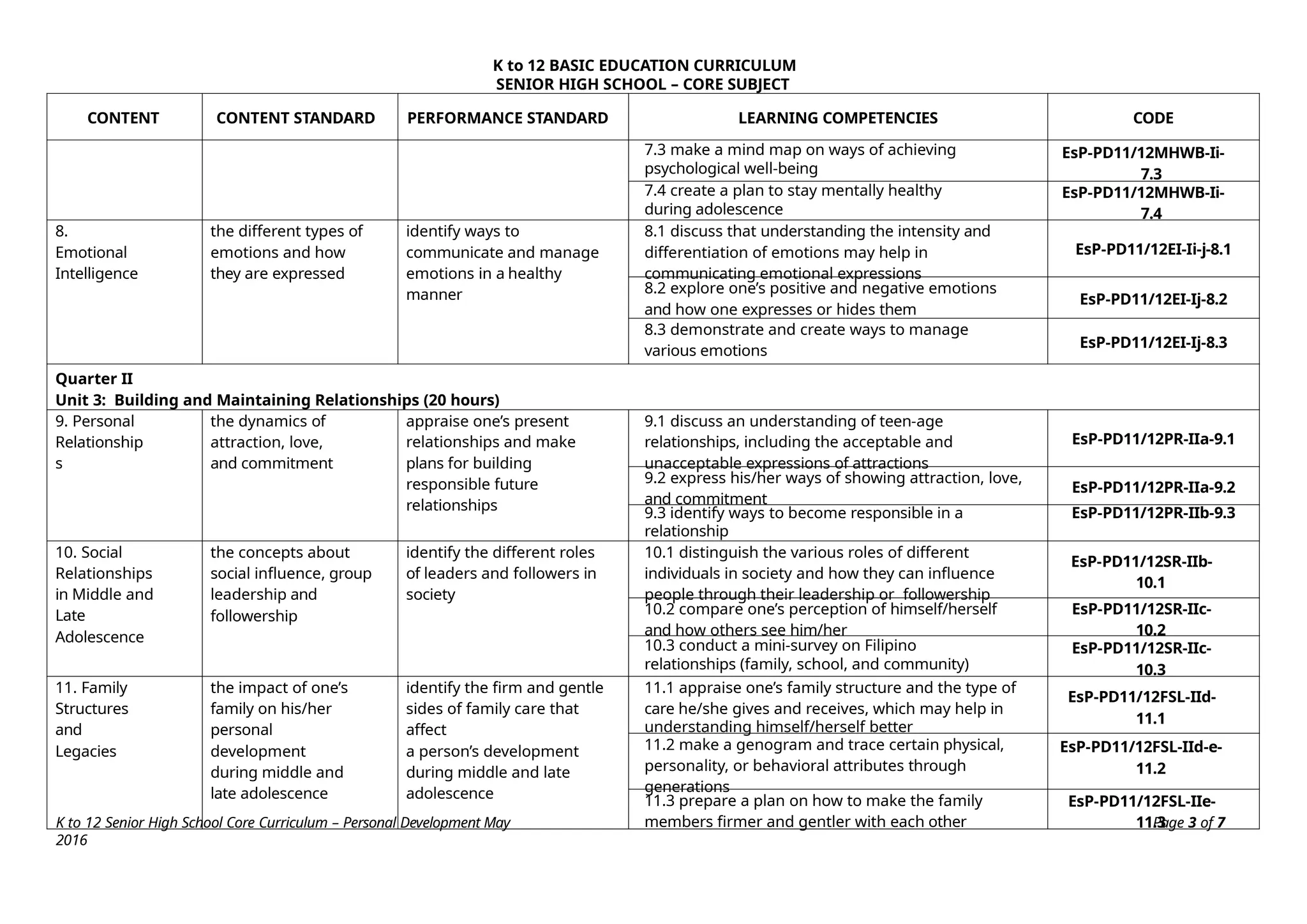
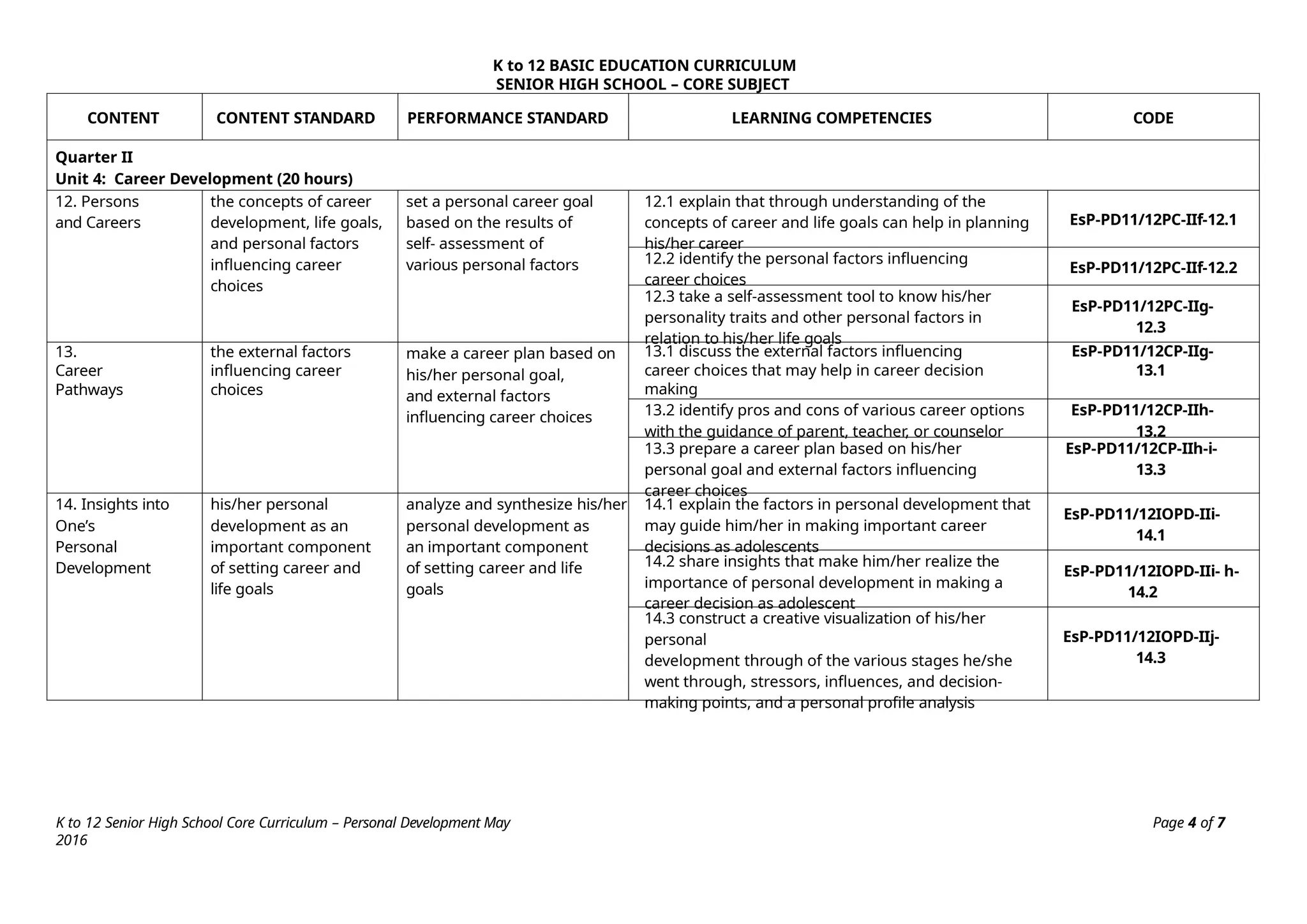
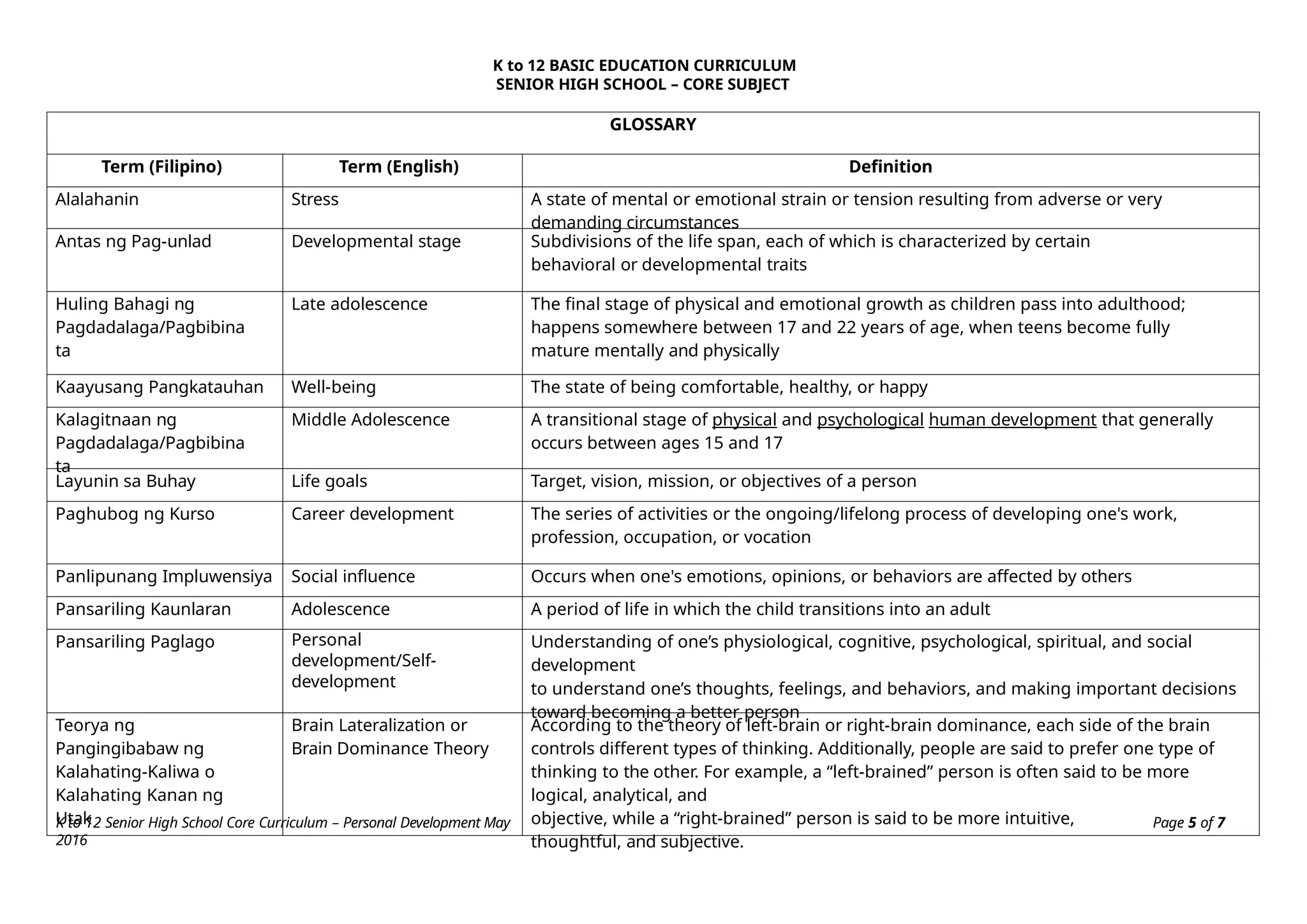
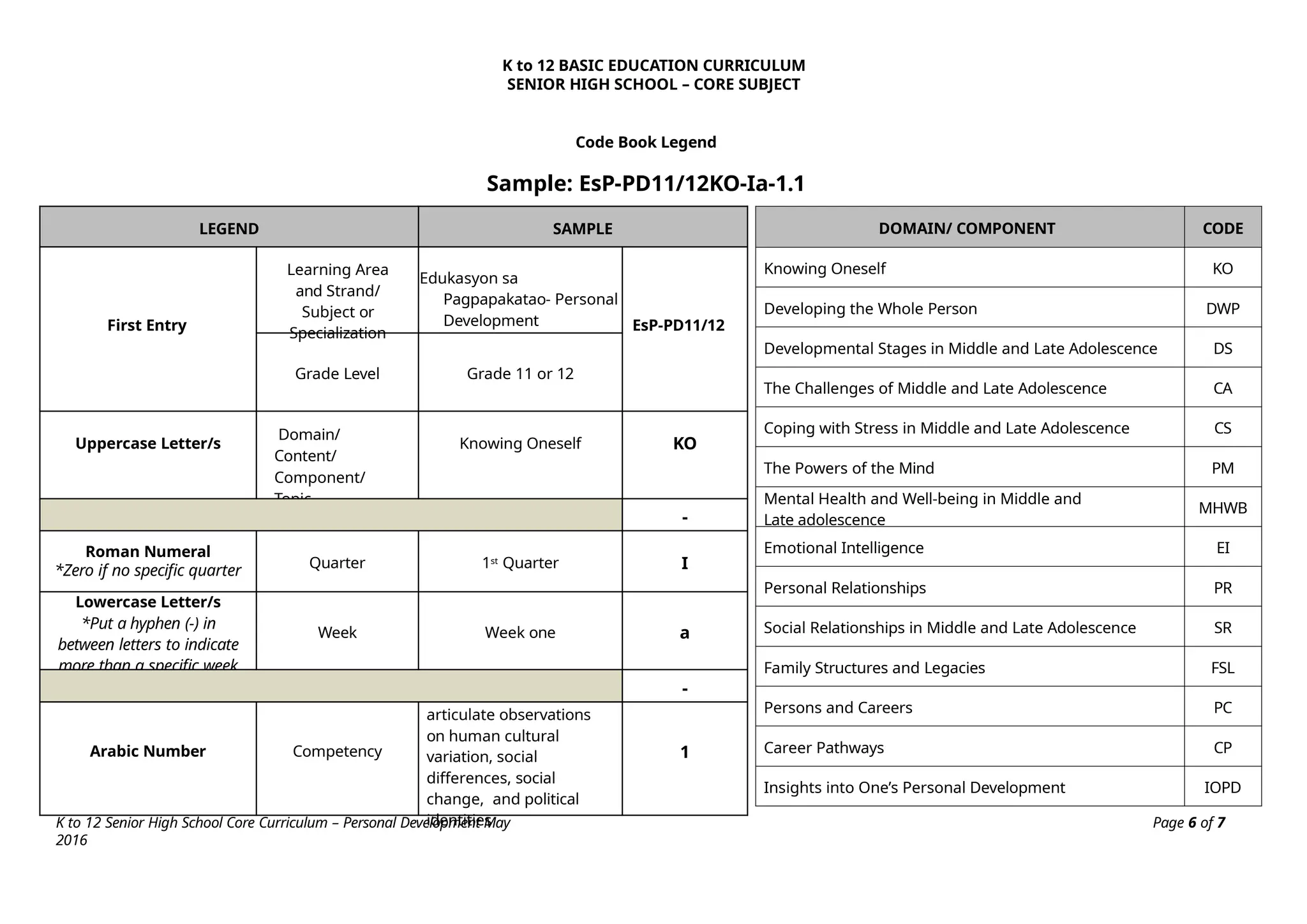
The K to 12 Basic Education Curriculum for senior high school includes a core subject titled Personal Development that aims to help students understand themselves during their developmental stage while preparing for career decisions. It consists of modules covering self-development, coping with stress, mental health, building relationships, and career development, all employing an experiential learning approach. The course emphasizes personal reflections and practical applications to foster holistic growth and readiness for adulthood.