The document discusses Renewable Energy Certificates (RECs) and Energy Saving Certificates (ESCs) in India.
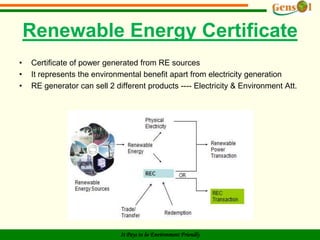
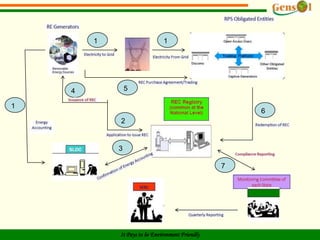
It provides background on India's climate change position and policies like NAPCC. RECs represent the environmental benefits of 1 MWh of renewable energy generated and can be traded separately from electricity. ESCs incentivize energy efficiency in industries. The operational framework for RECs in India involves issuing certificates based on renewable generation amounts, trading on energy exchanges, and using RECs to meet state-level renewable purchase obligations. RECs are intended to overcome geographical barriers and reduce costs for renewable energy transactions in India.