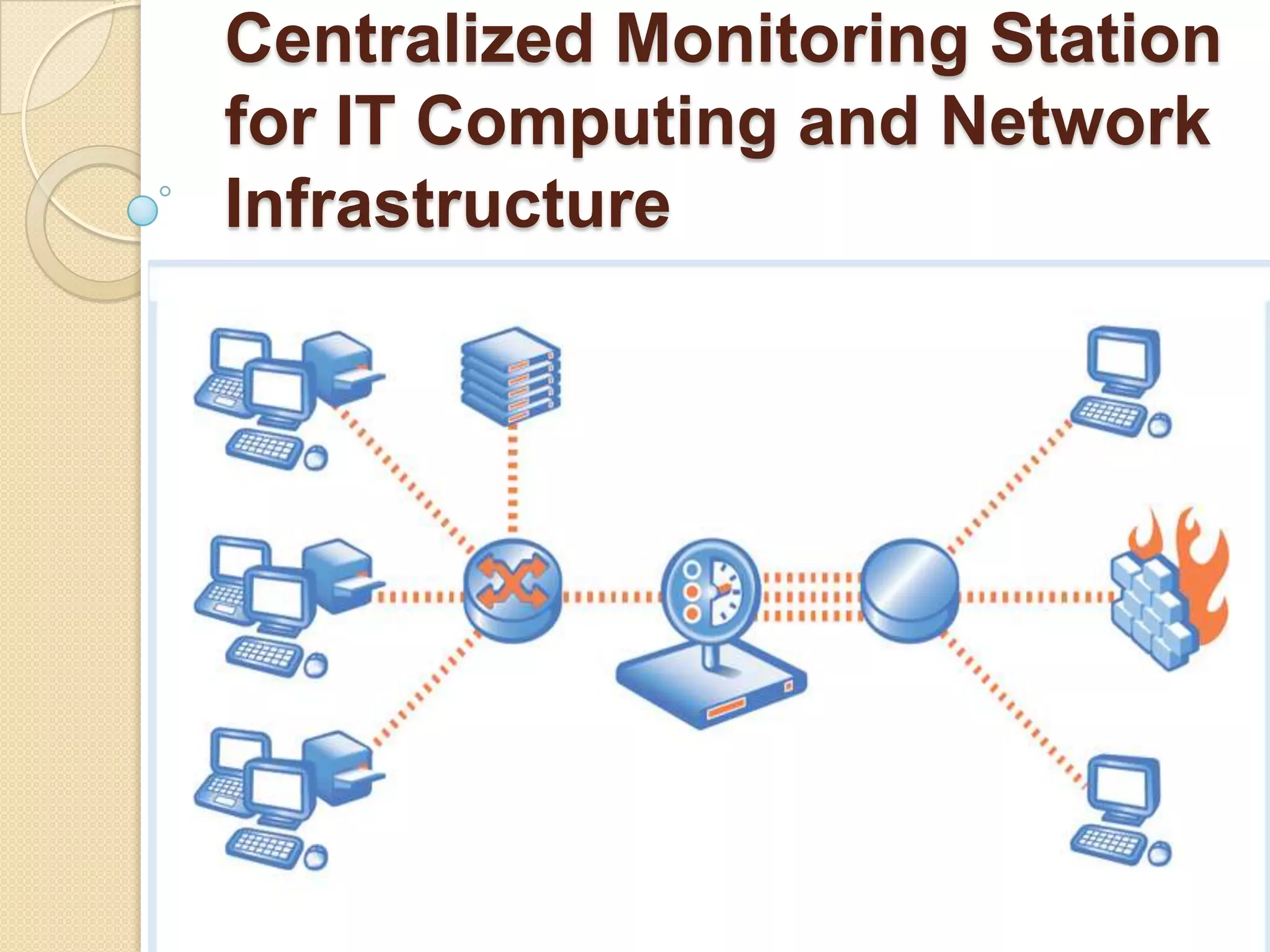
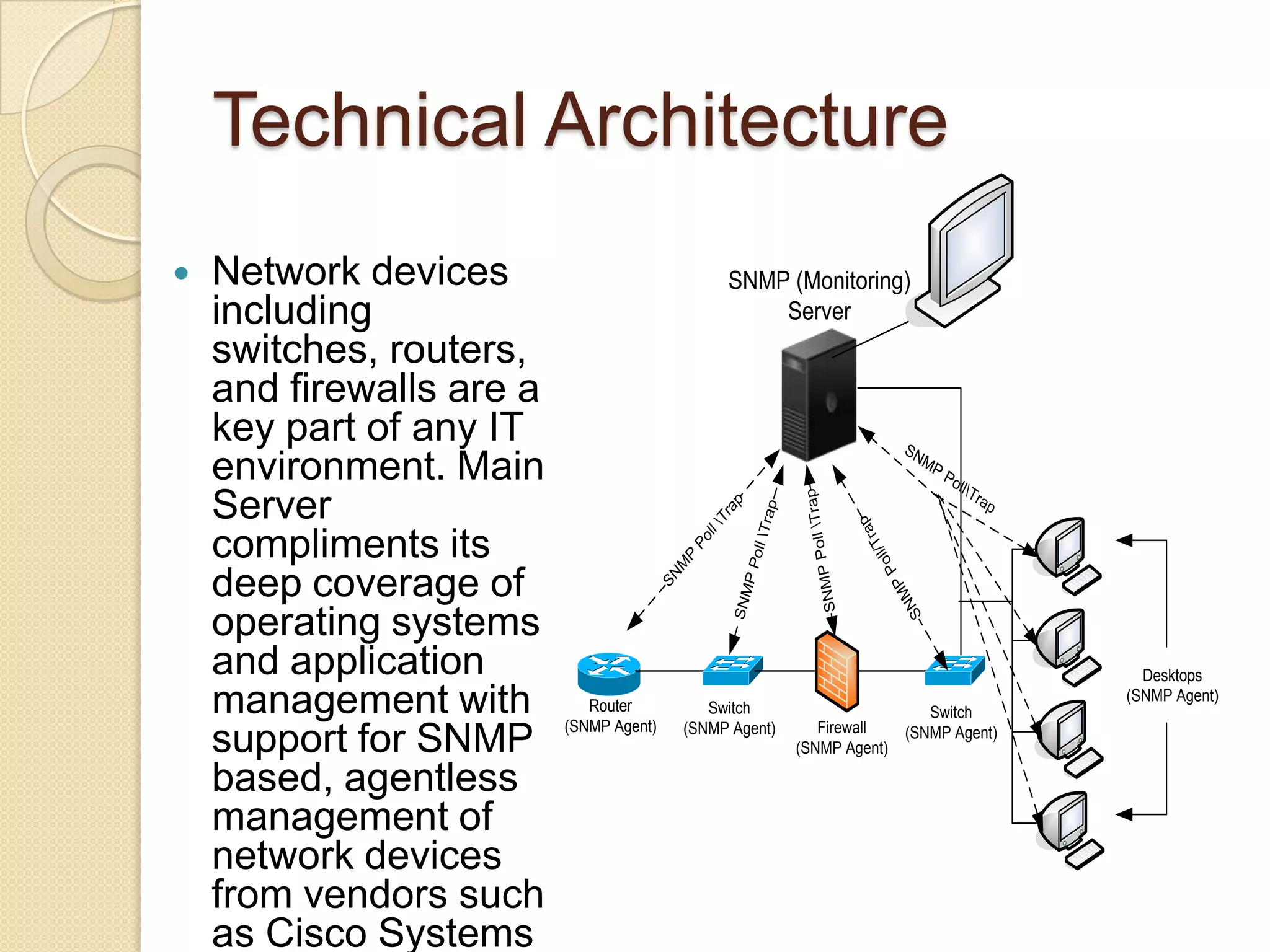
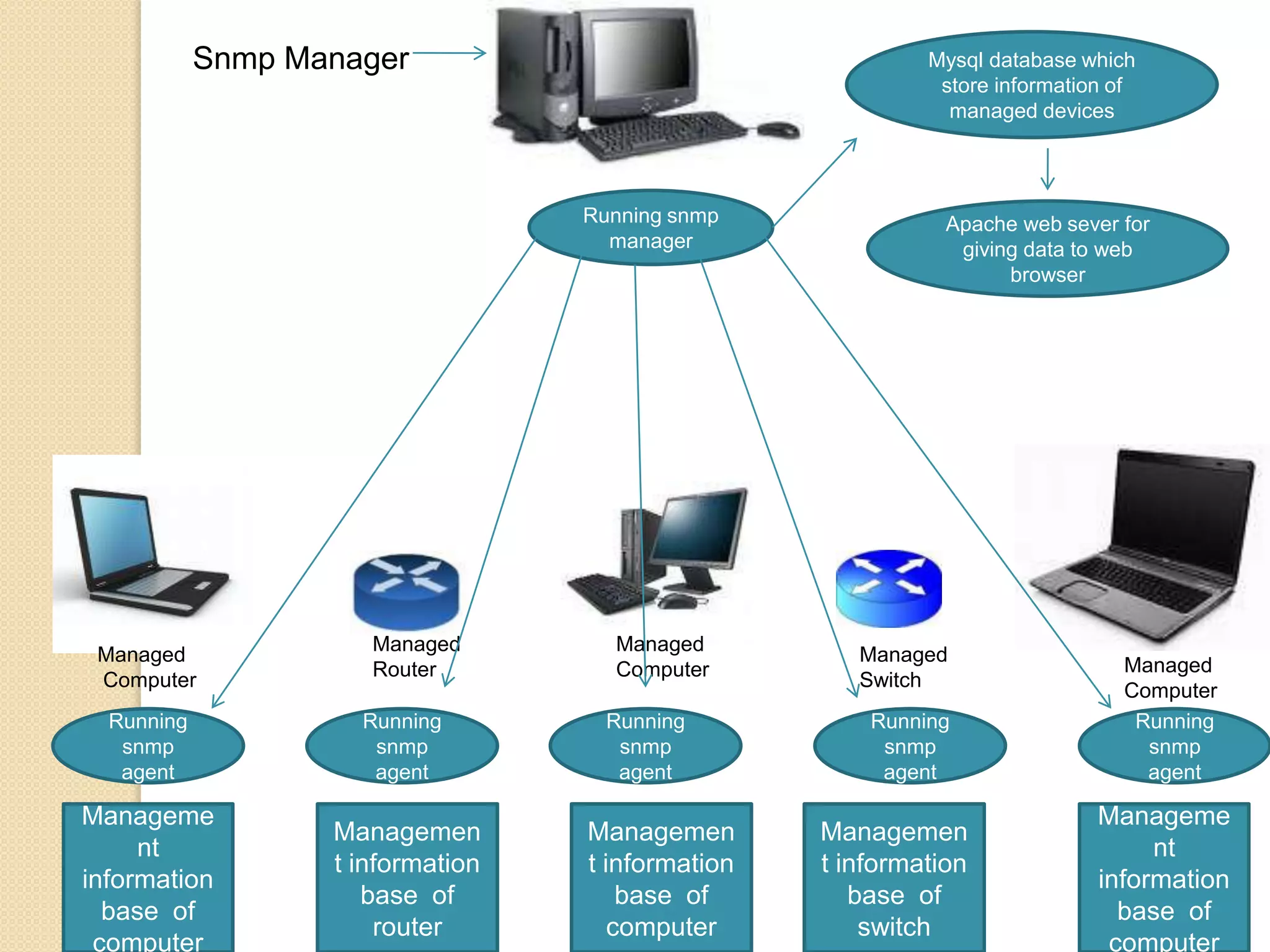
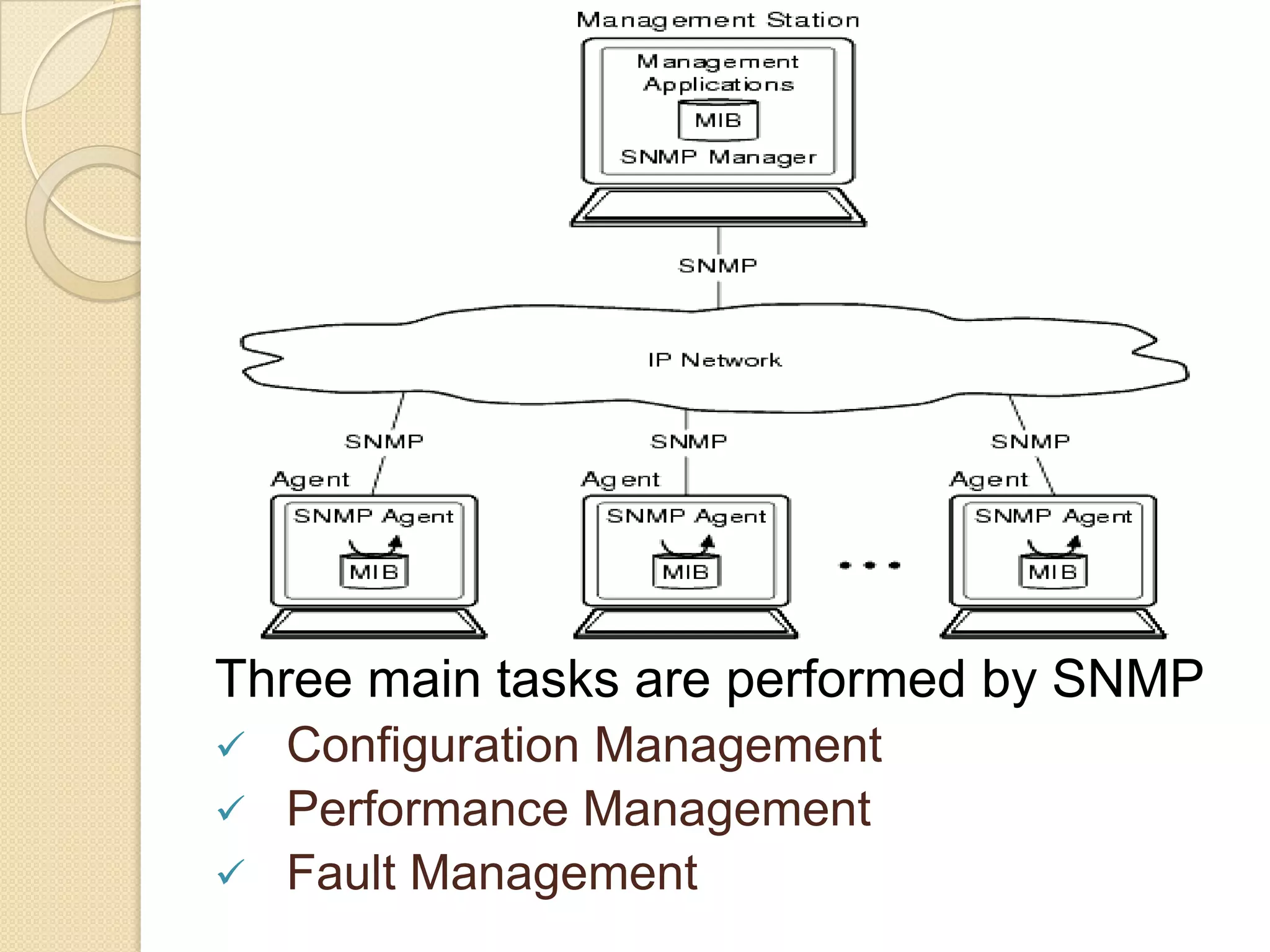
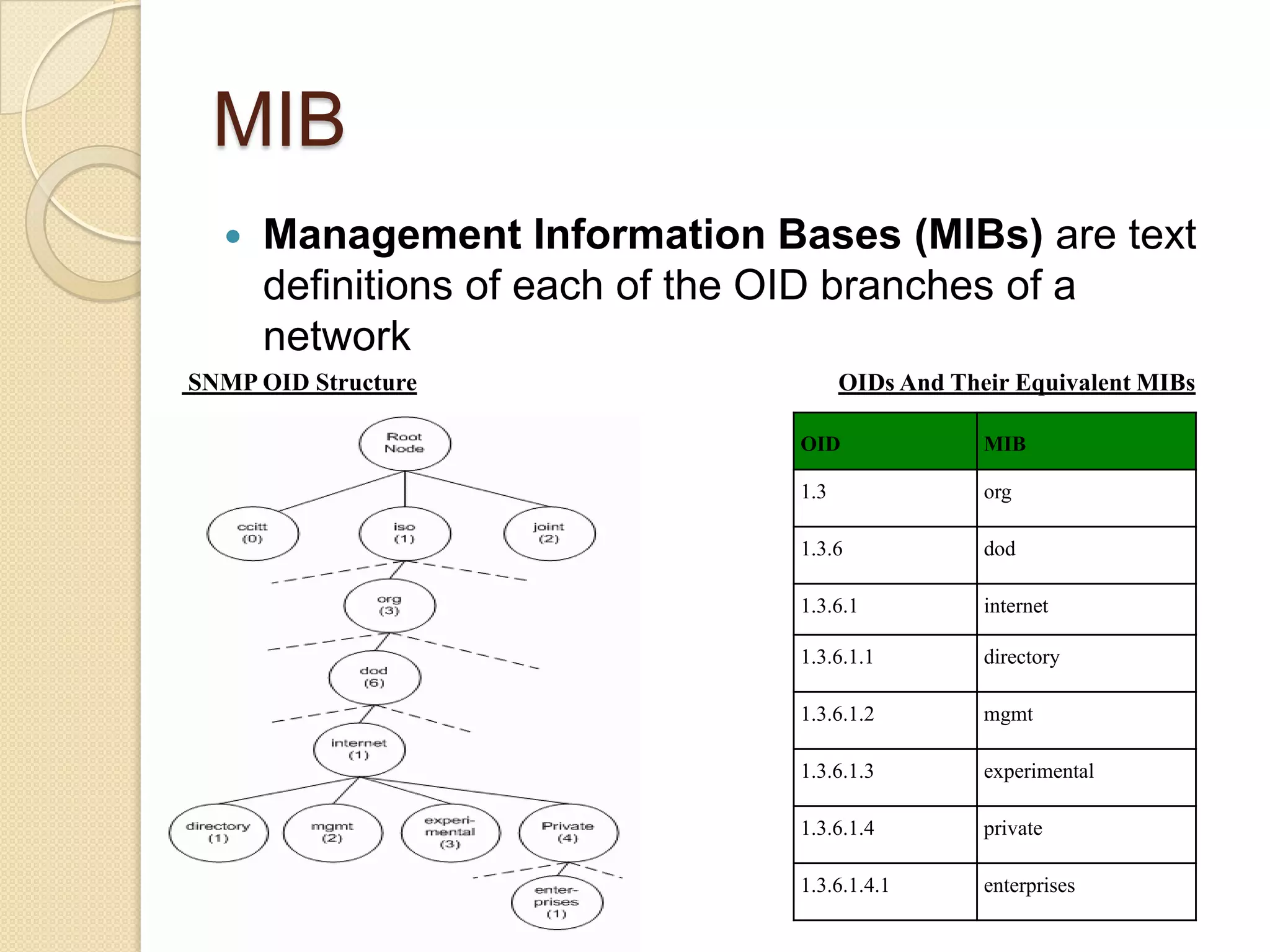
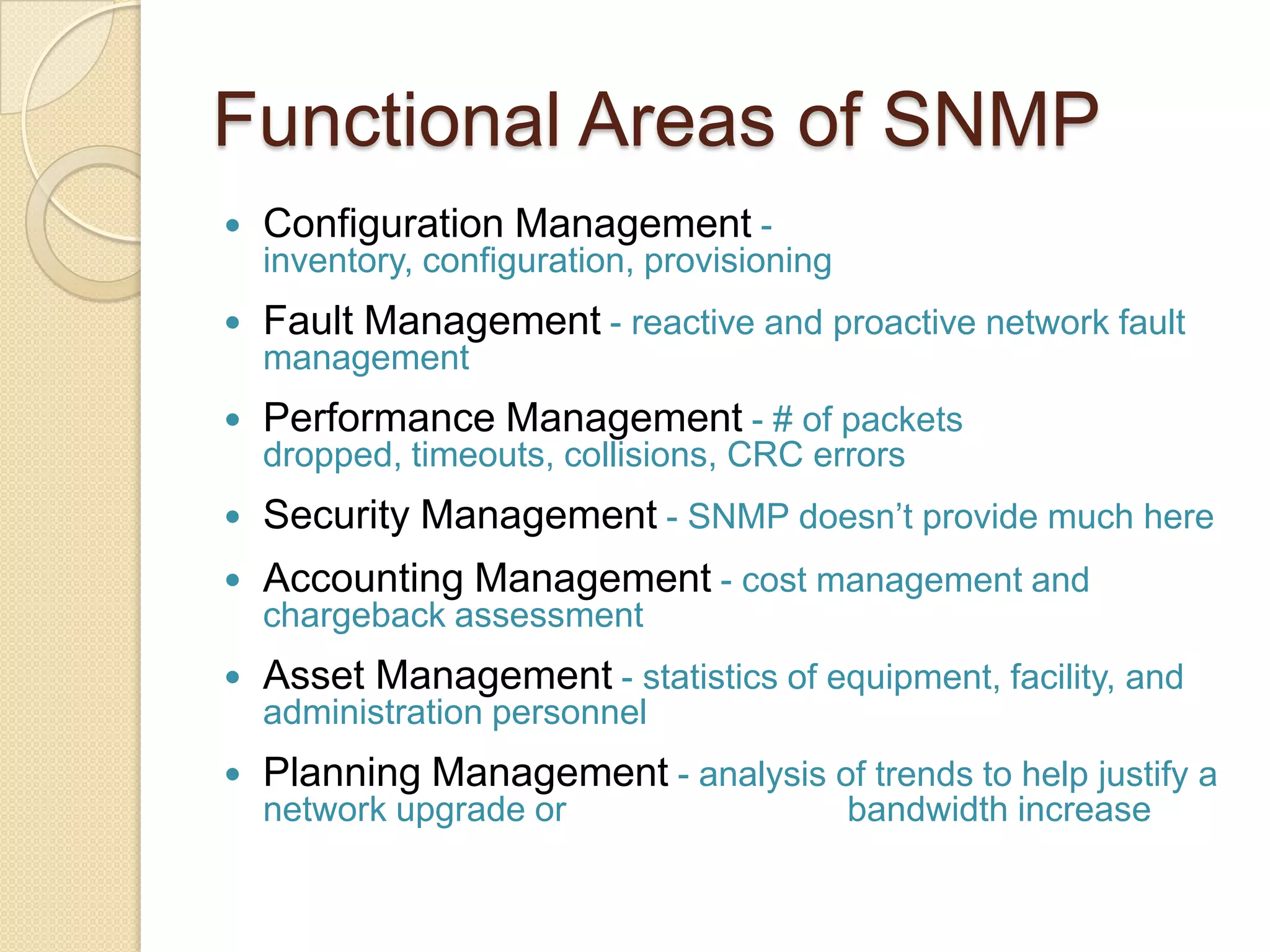
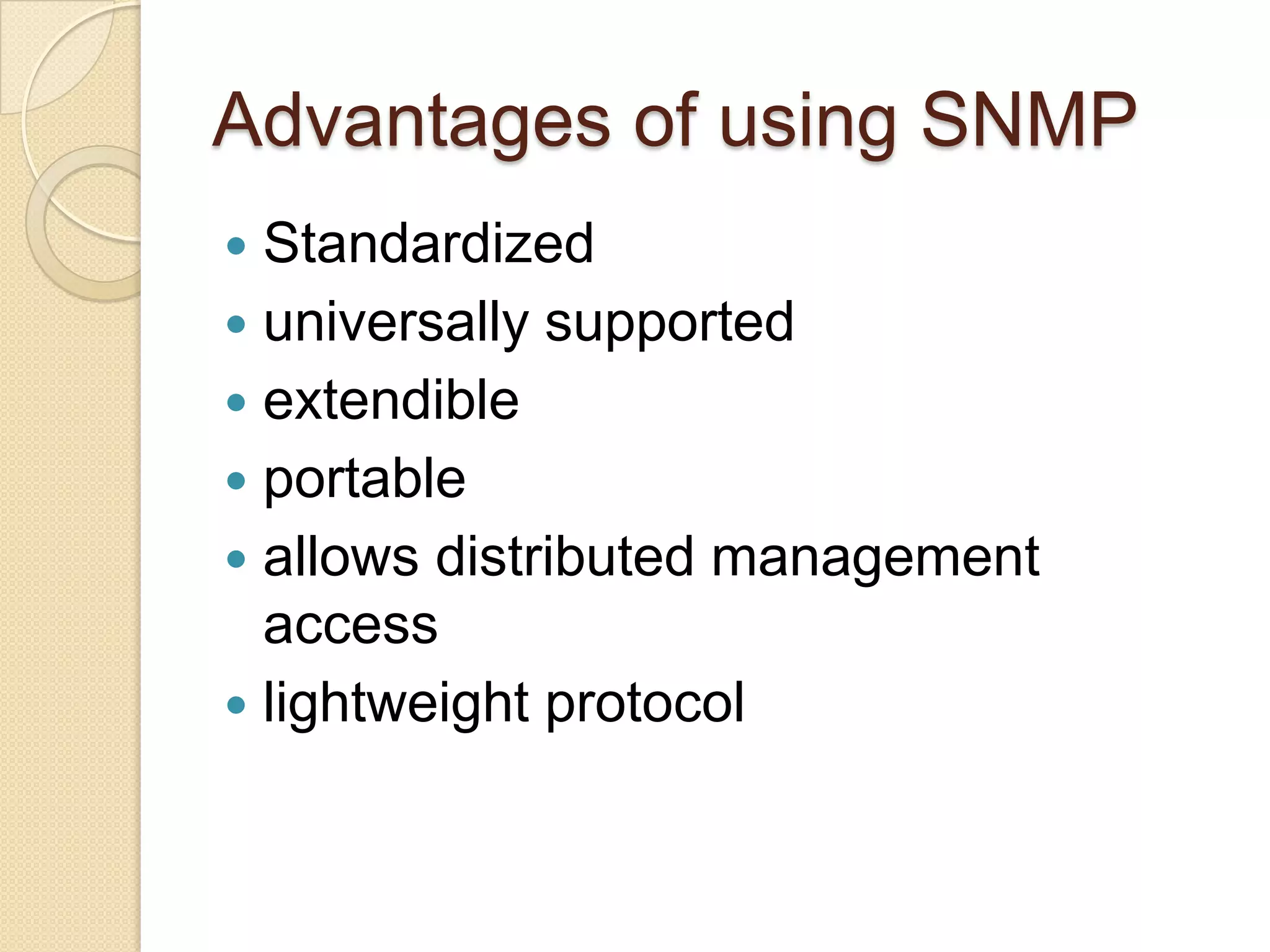
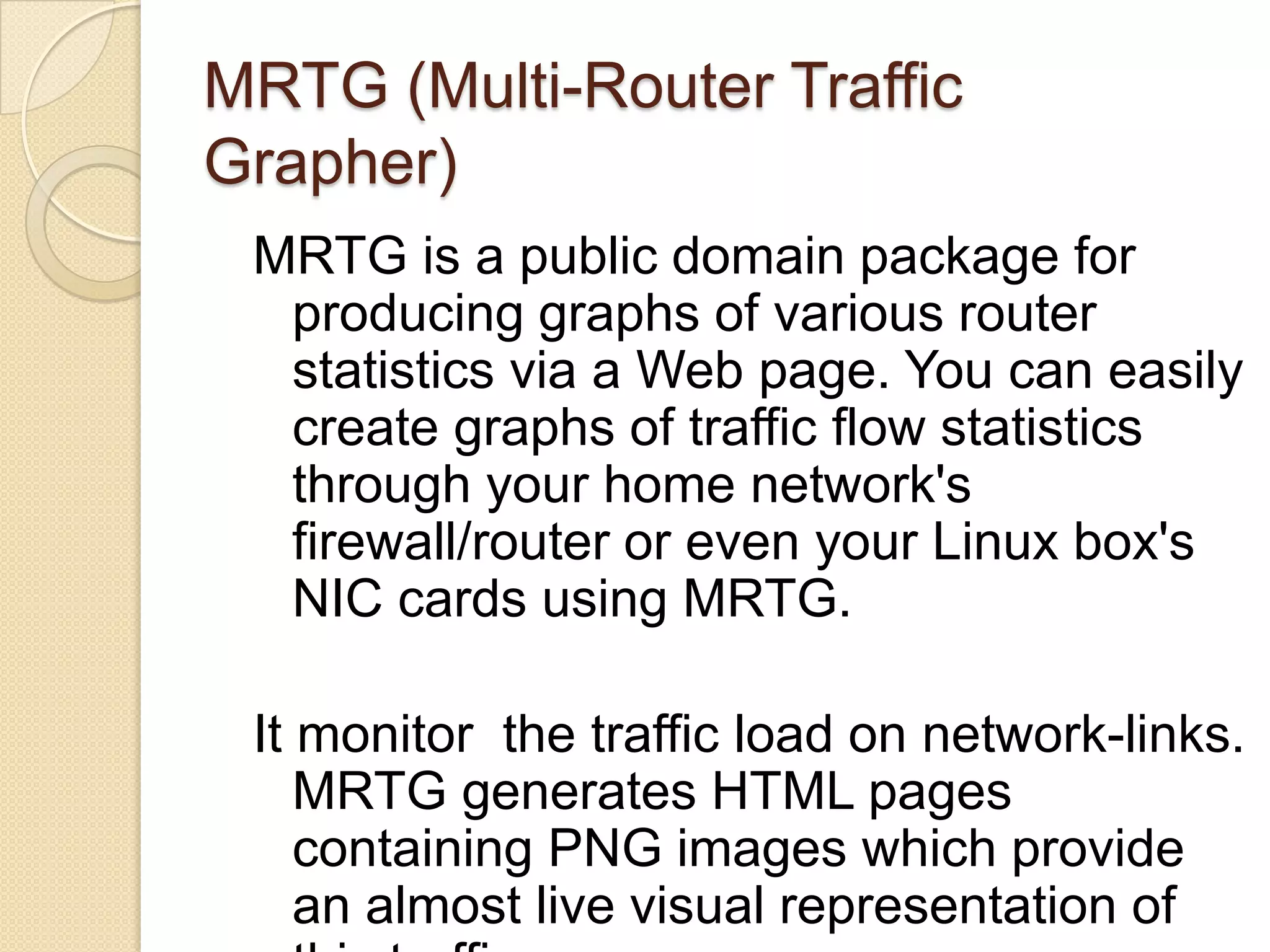
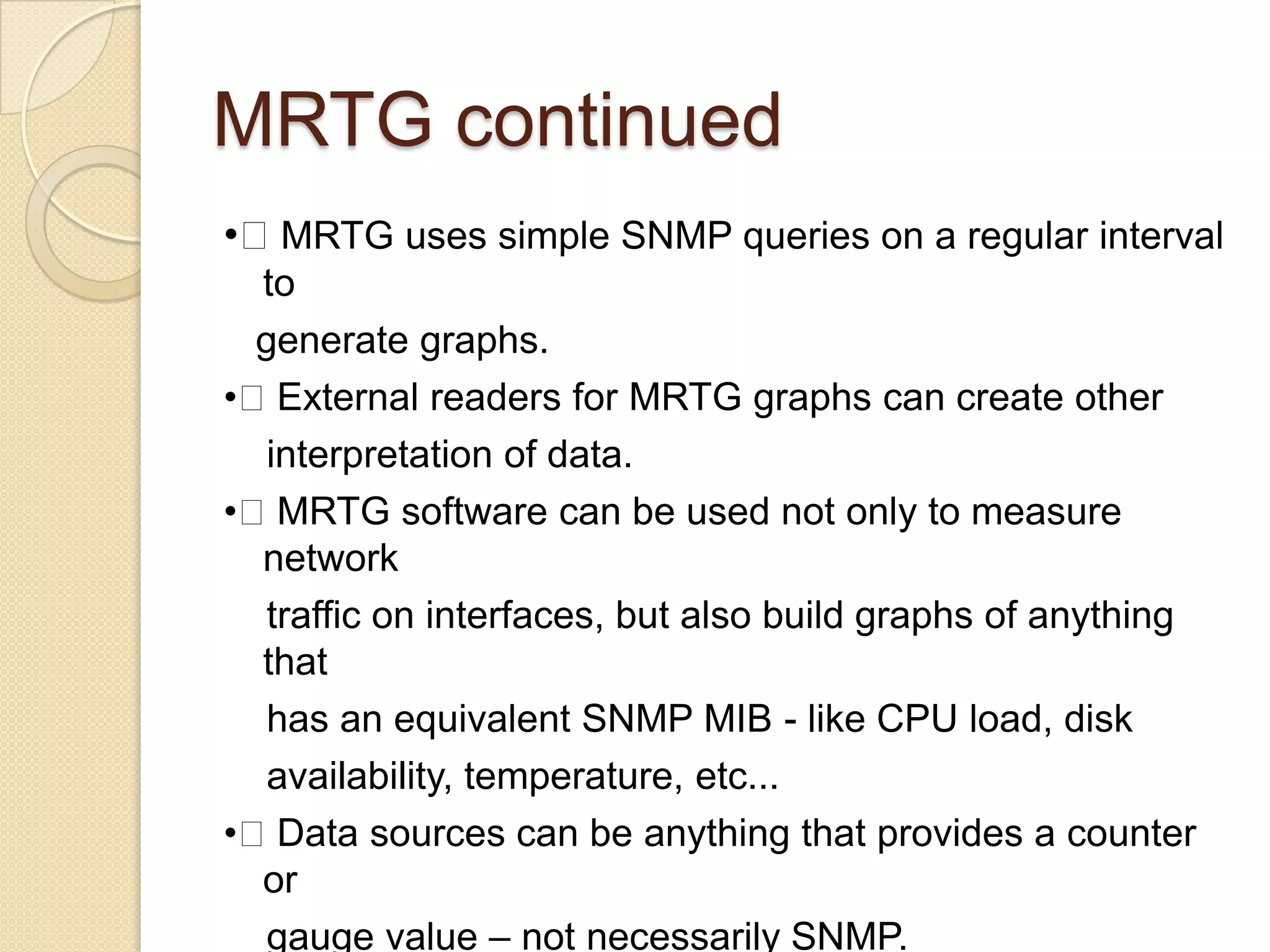
This document describes a centralized monitoring system for an IT network using Linux, SNMP, and MRTG. SNMP is used to collect data from network devices and store it in a MySQL database. MRTG generates graphs of this SNMP data over time through an Apache web server. This allows network administrators to monitor performance, faults, and security across various devices from a central location to maintain network availability.