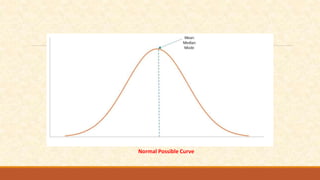
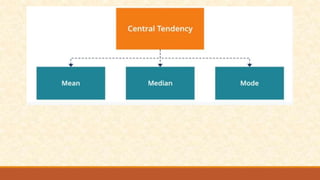
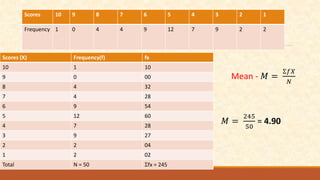
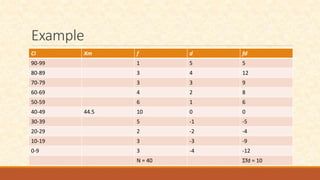
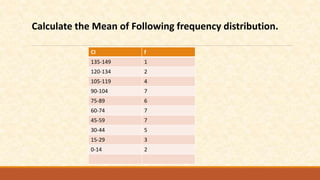
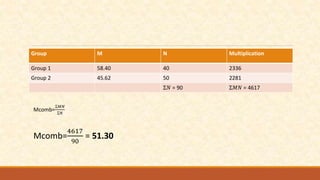
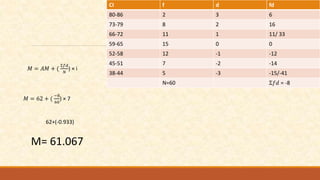
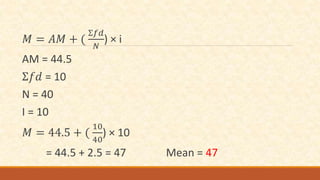The document discusses different measures of central tendency including the mean, median, and mode. It provides formulas and examples for calculating each measure. The mean is the average value and is calculated by summing all values and dividing by the total number. The median is the middle value when values are arranged in order. The mode is the value that appears most frequently in a data set.