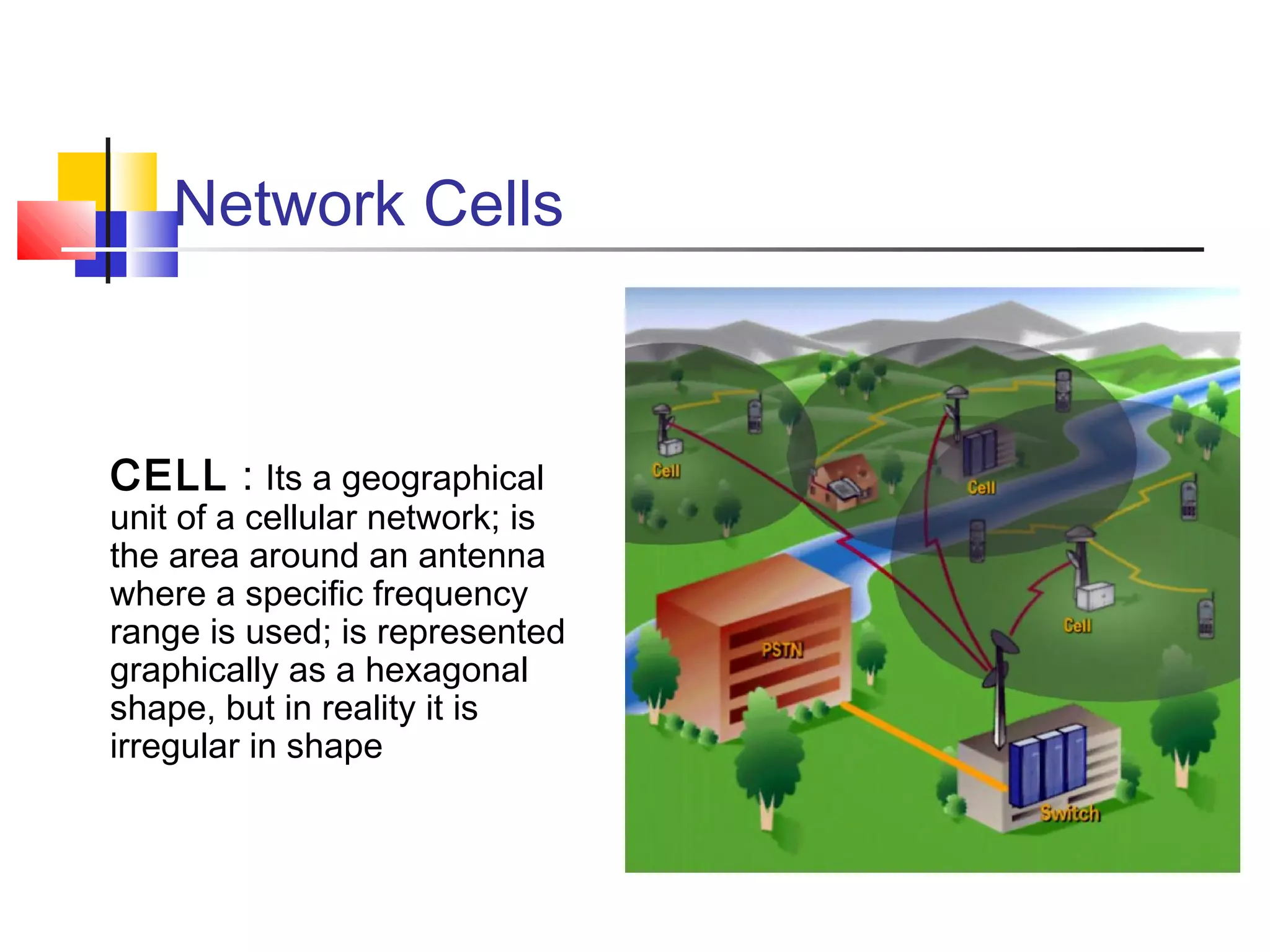
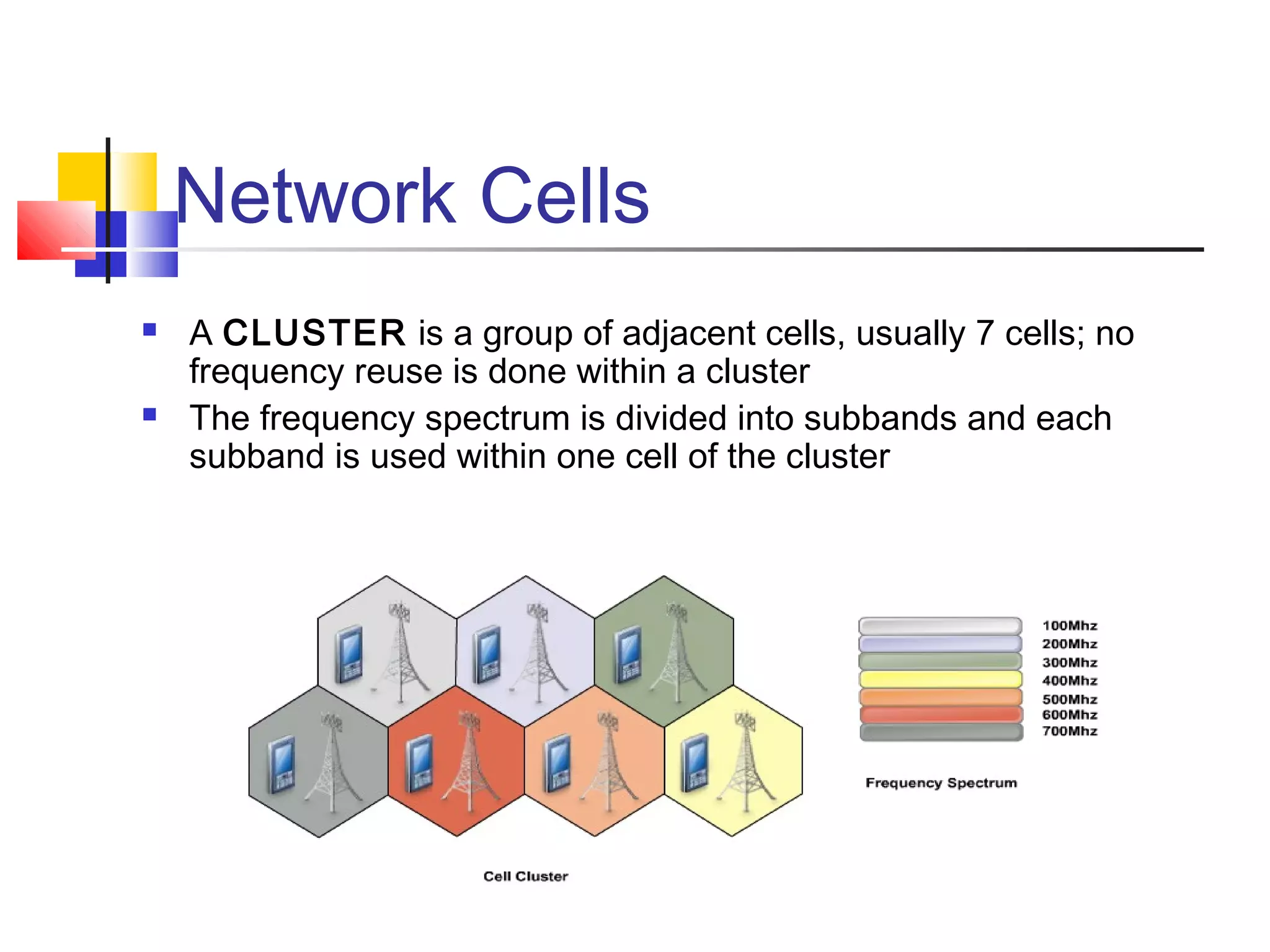
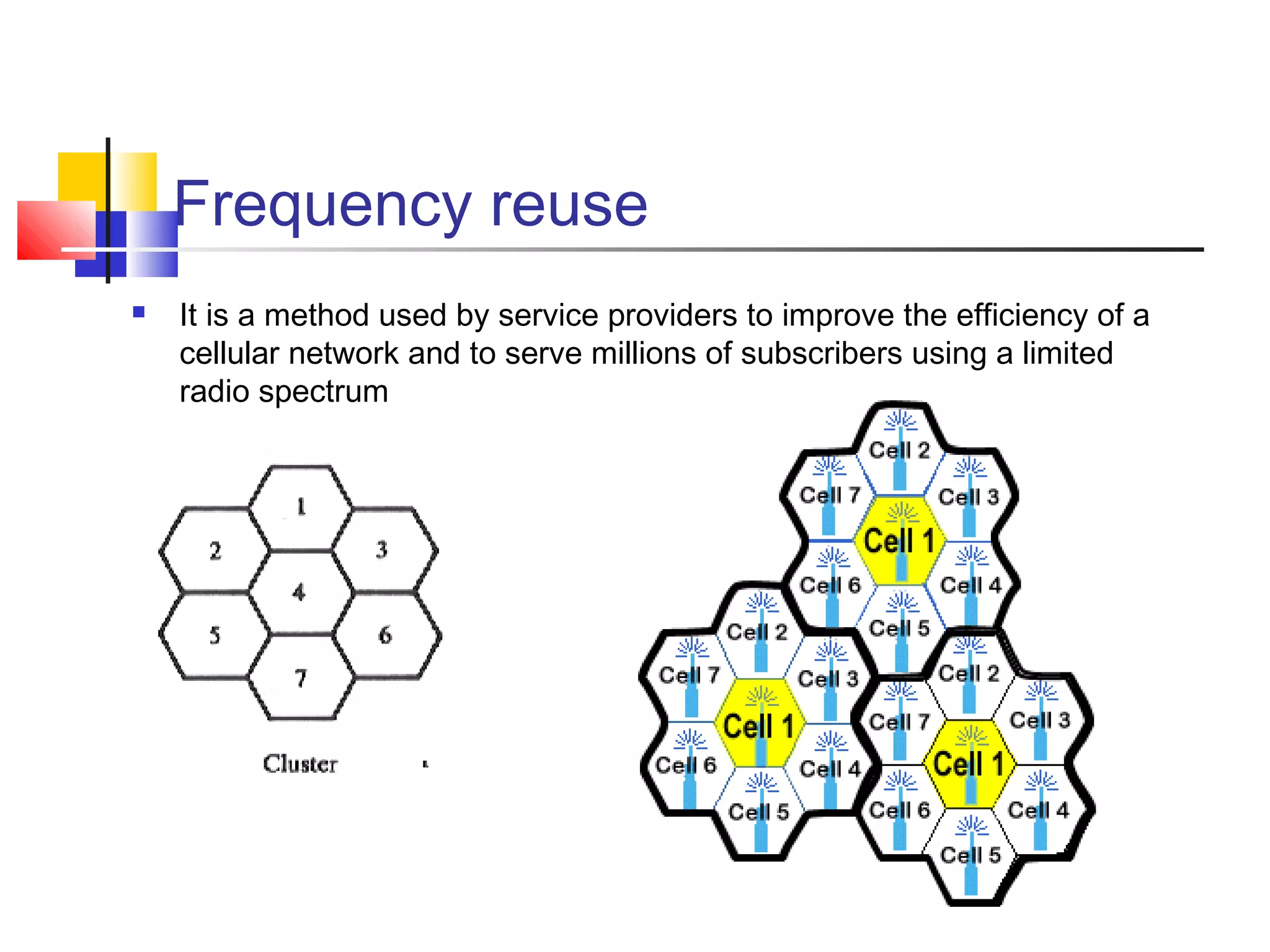
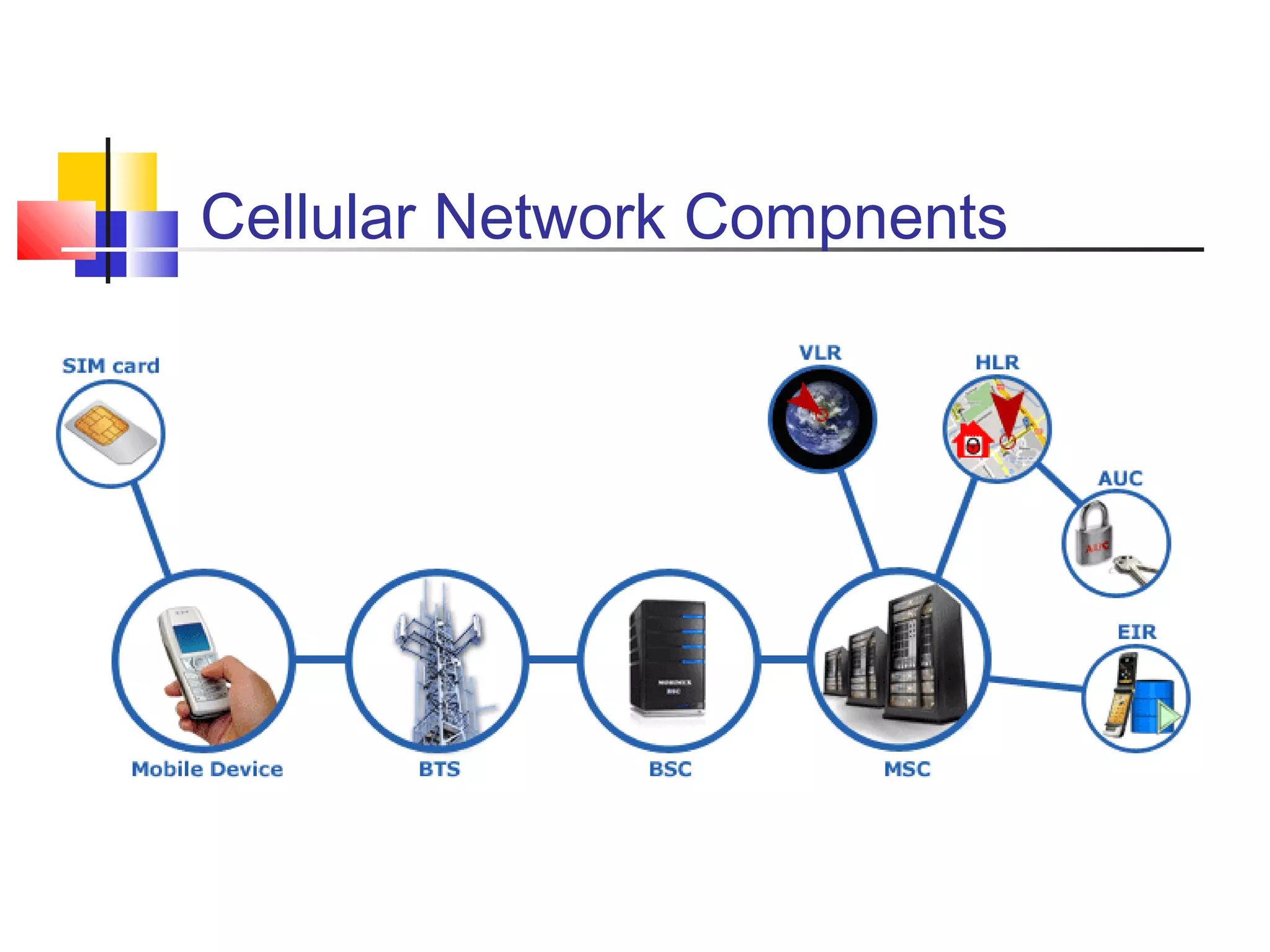
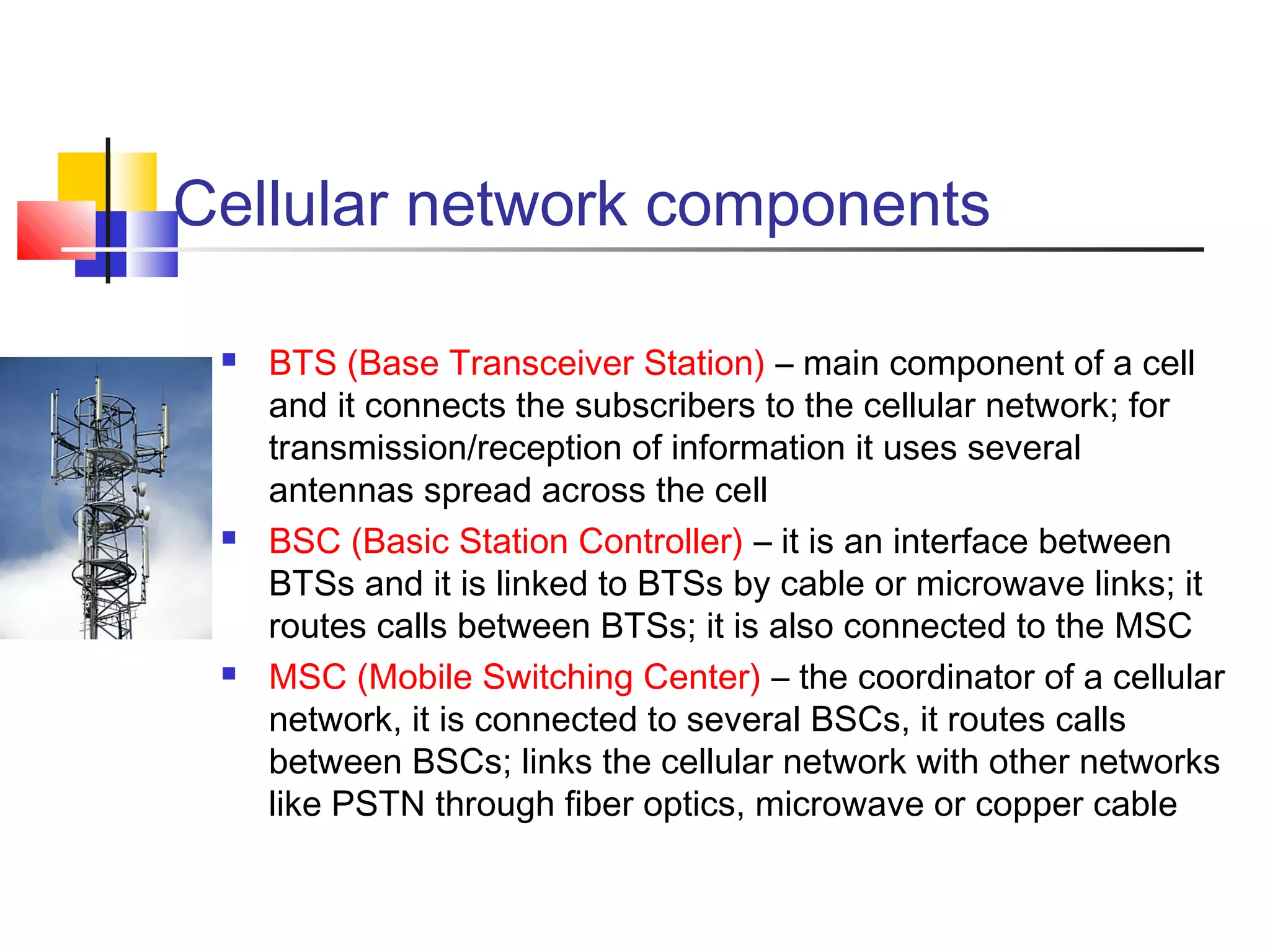
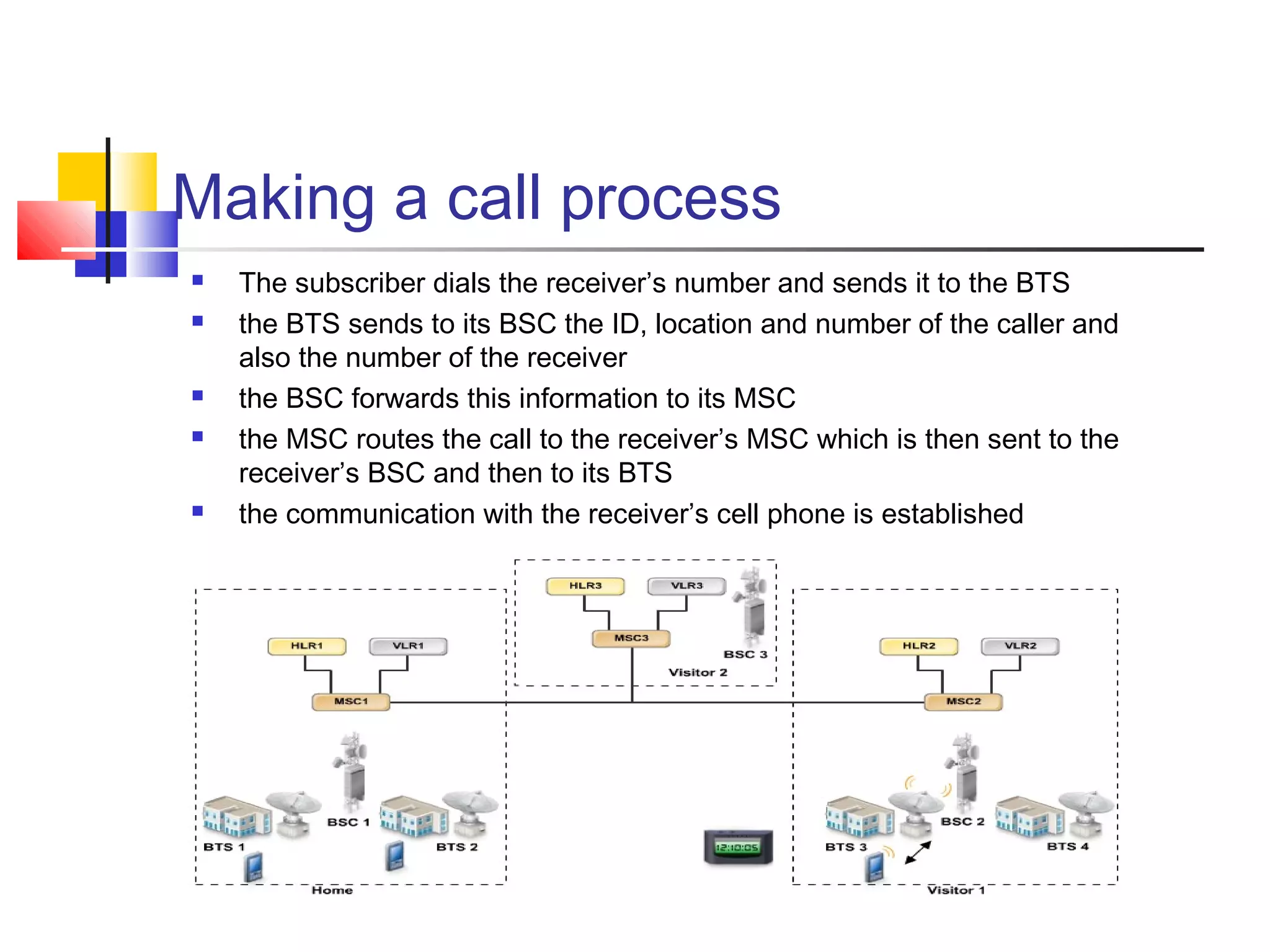
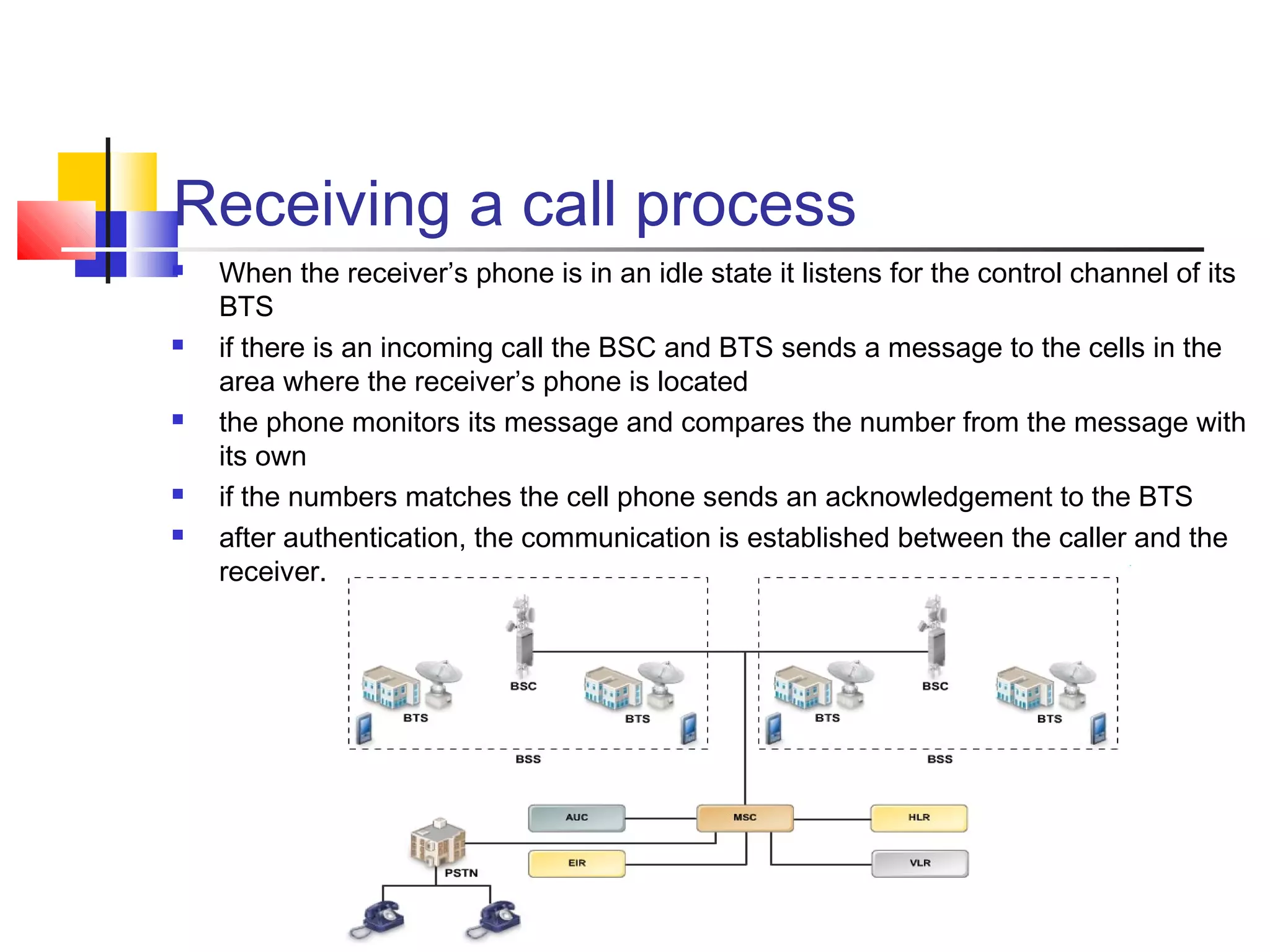
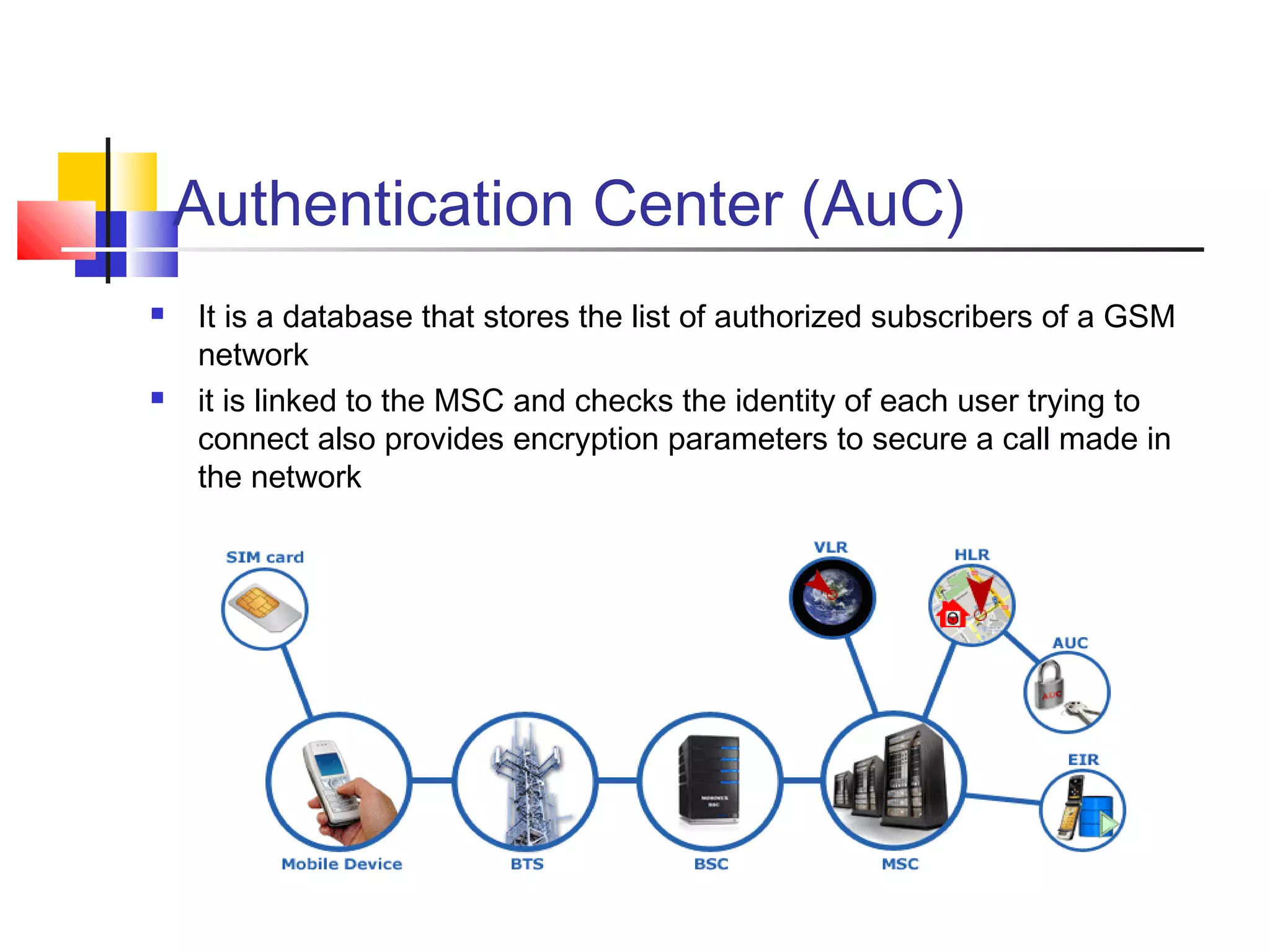
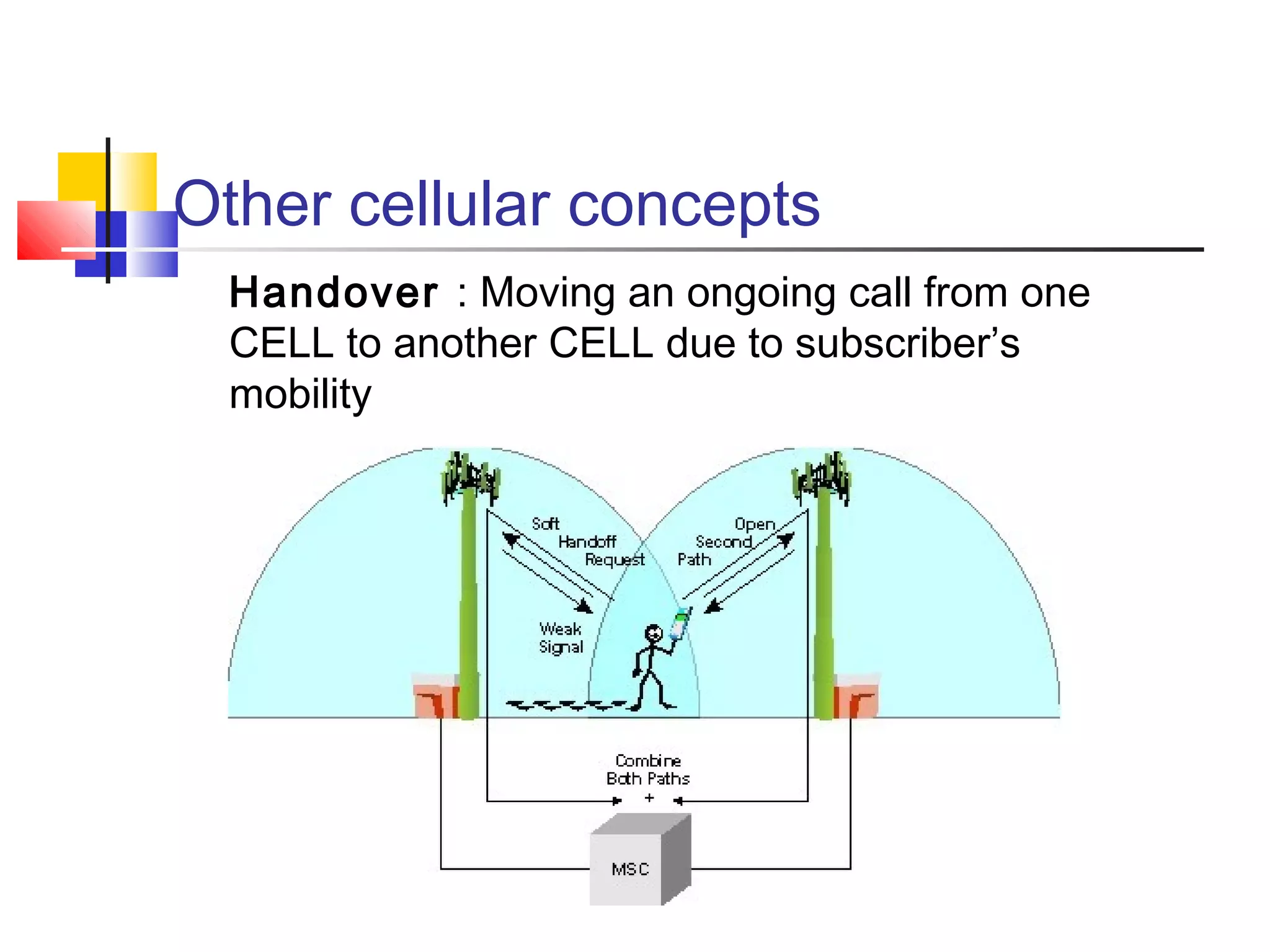
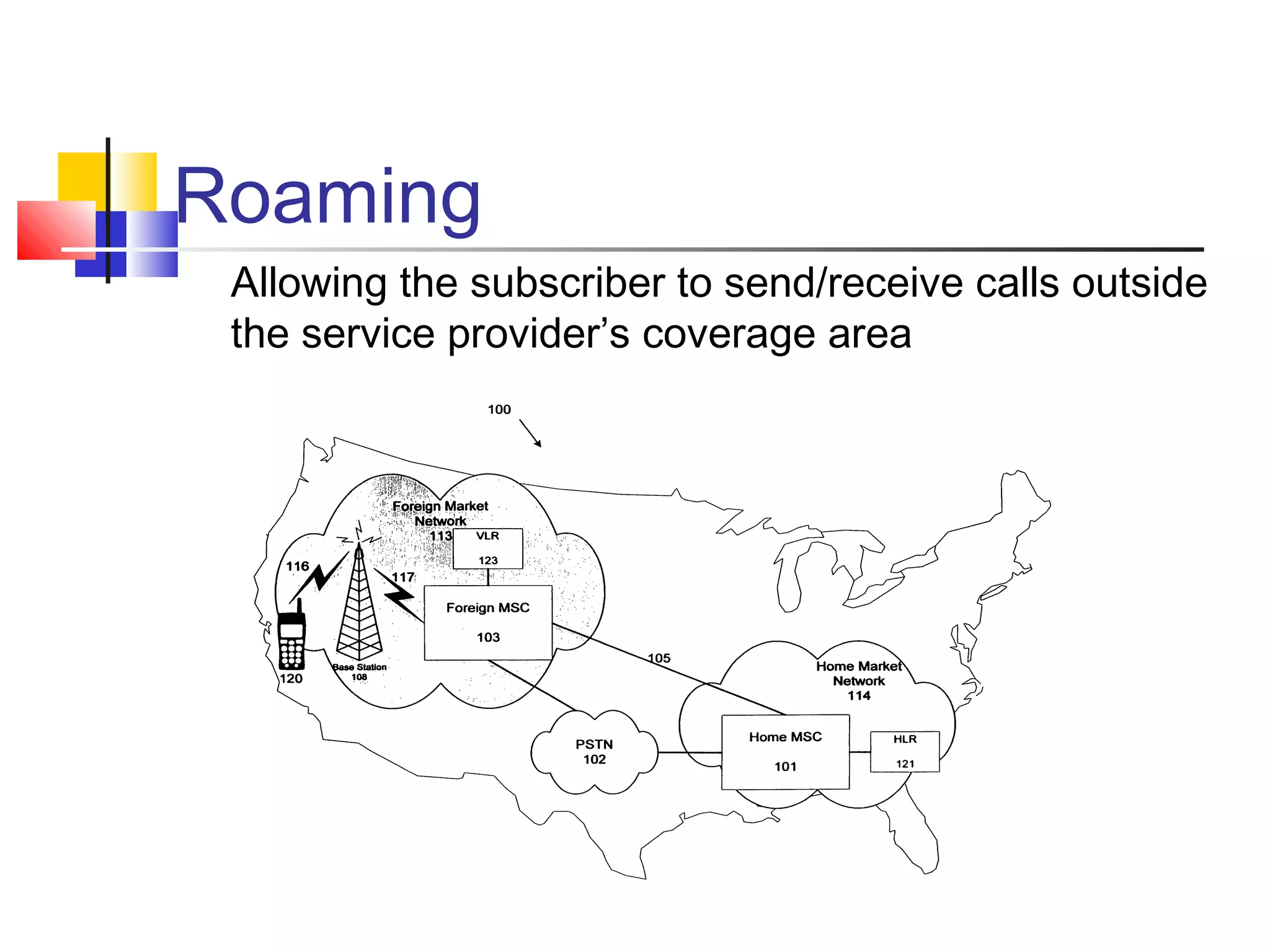
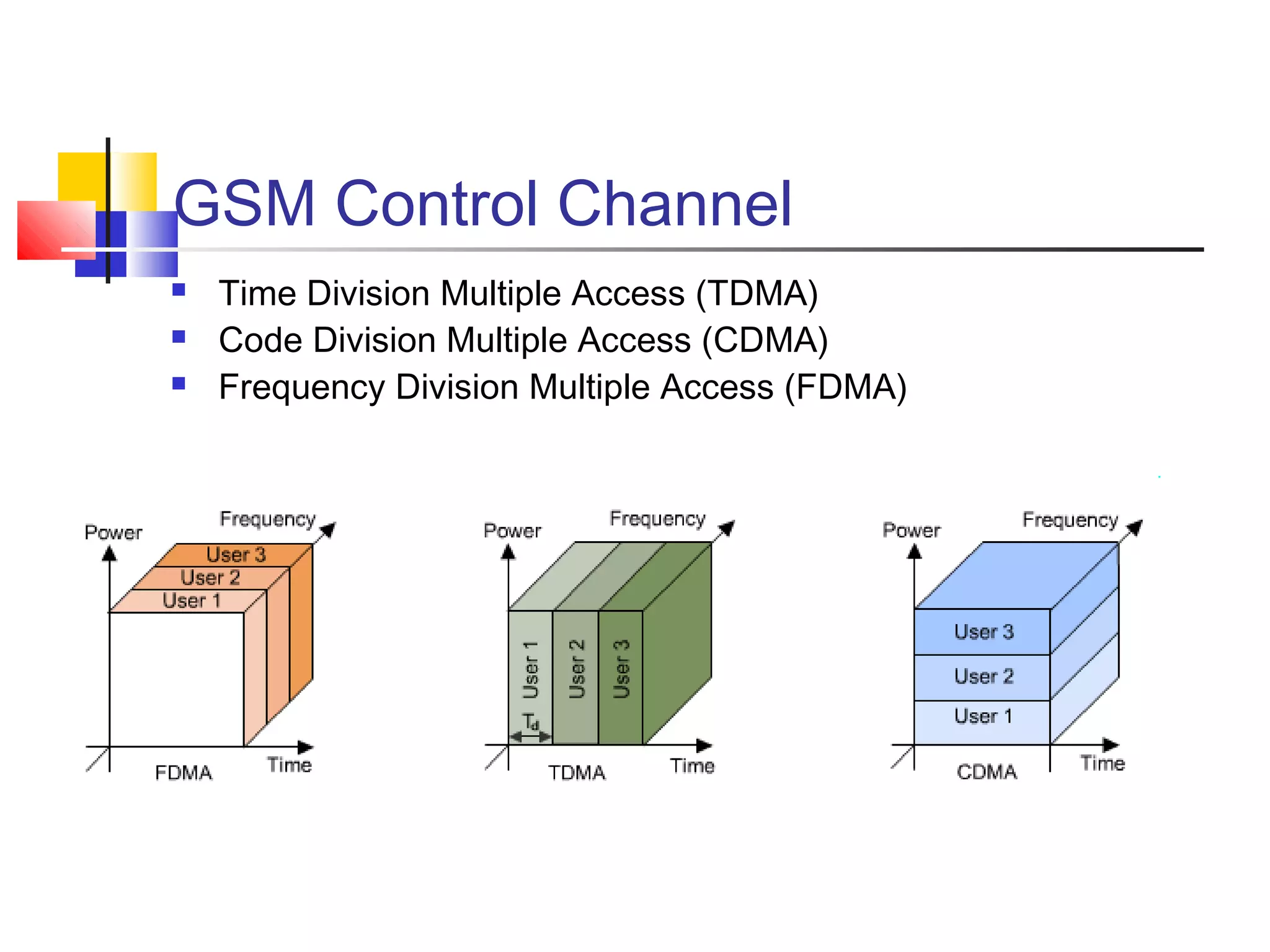
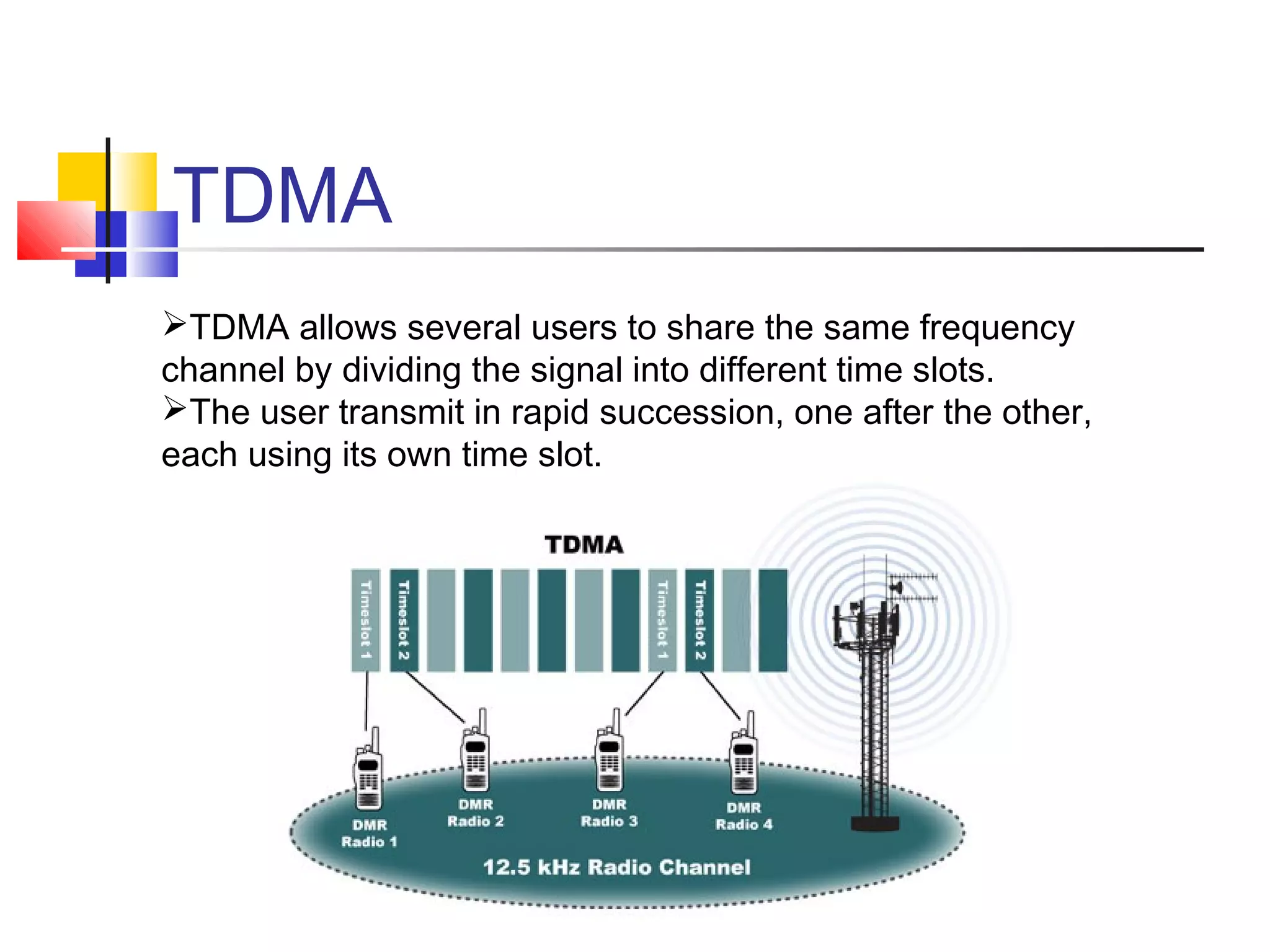
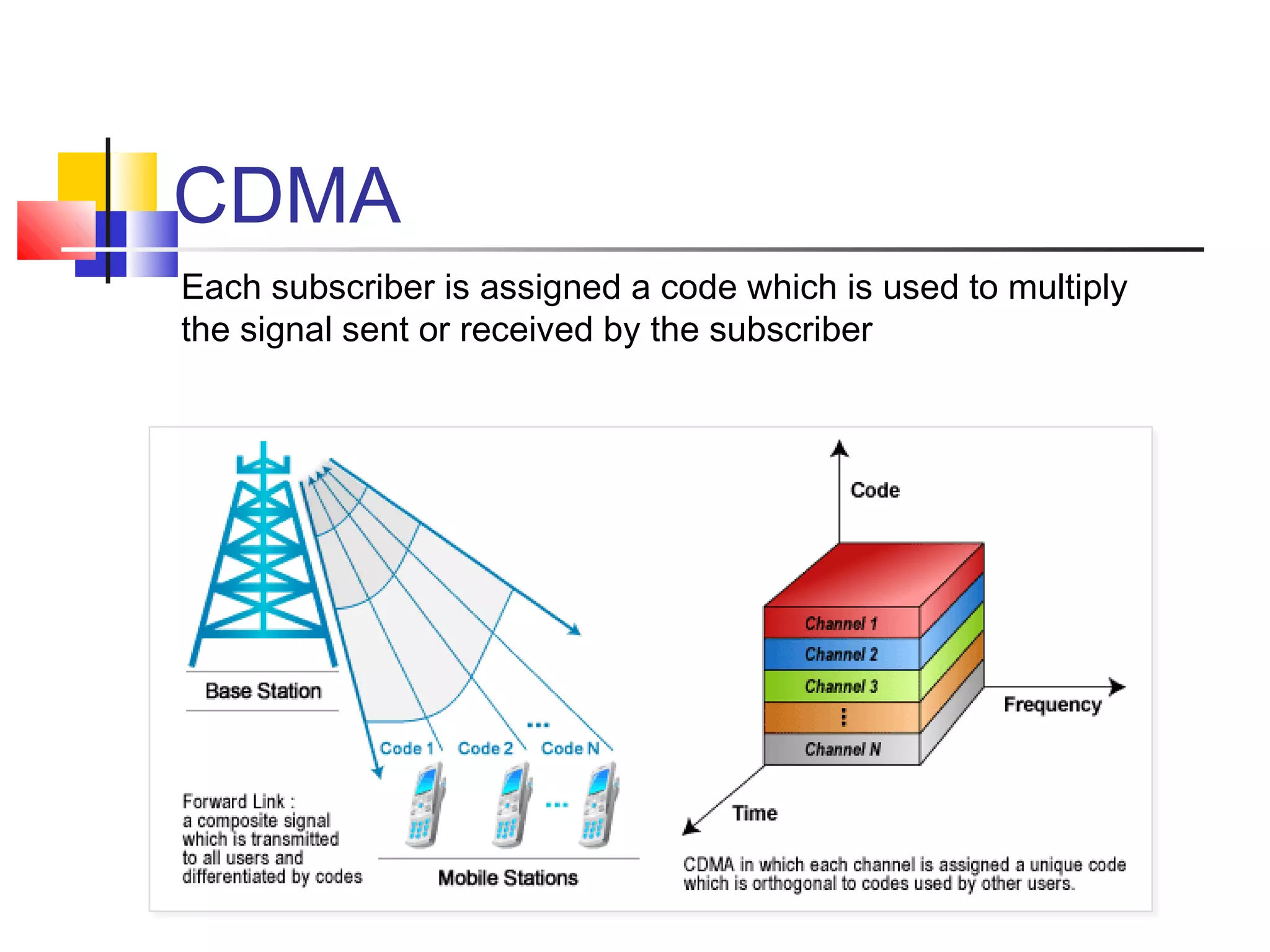
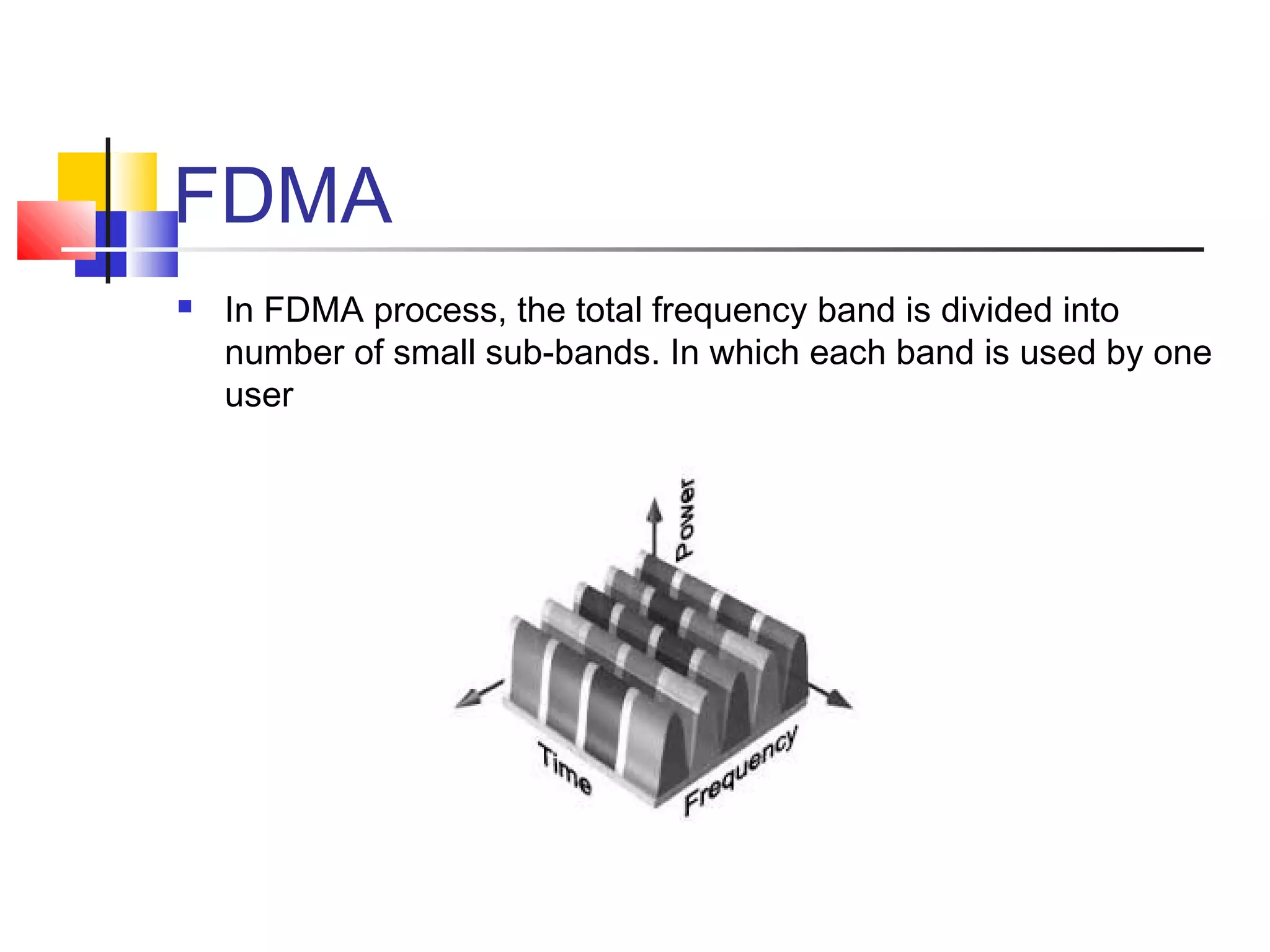
Cellular communication systems have evolved through multiple generations from analog 1G to digital 4G systems. A cellular network is divided into geographical areas called cells served by base transceiver stations. Cells are grouped into clusters where frequencies are reused to allow for more subscribers. When making a call, the cellular phone communicates with the local base station which routes the call through switching centers to establish communication with the intended recipient. Global systems like GSM use SIM cards and encryption to authenticate users and secure calls within the cellular network.