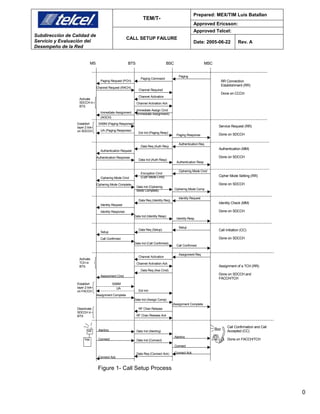
This document details the process of call setup failures in the GSM system, including the various steps involved such as authentication, ciphering, and call initiation. It aims to assess the performance of these processes by examining statistical data and providing troubleshooting recommendations. The document outlines specific procedures, challenges, and the communication flow necessary for successful call setup in the Telcel network.
















![Prepared: MEX/TIM Luis Batallan
TEM/T-
Approved Ericsson:
Approved Telcel:
2424191919191924
Subdirección de Calidad de
Servicio y Evaluación del
Desempeño de la Red
CALL SETUP FAILURE
Date: 2005-06-22 Rev. A
NREJNPRIO: is incremented if the Processor Load Control in BSC/TRC function rejects a location
update.
After Channel Activation there two counters at Cell Level counting the Immediate
Assignment and Immediate Assignment Reject:
CSIMMASS: States the number of CS IMMEDIATE ASSIGNMENT commands sent by the BSC.
REJCSIMMASS: States the number of IMMEDIATE ASSIGNMENT REJECT commands sent by
the BSC.
Using counters from BSC level and Cell level is possible to check the difference
between the “channels required” and “immediate assignment commands sent by
the BSC”. Due to use of different level counters some inconsistent results can be
obtained (for low traffic cases), but for most of cases still useful.
( )
( )
[ ]%*100_
NOFFNPRIONOFFPRIONOFFIEX
SREJCSIMMASCSIMMASSNOFFNPRIONOFFPRIONOFFIEX
ASSIGNLOST
++
−−++
=
Figure 12 – Lost Assignments
The CS IMMEDIATE ASSIGNMENT REJECT message will be sent when no
channel is available for the assignment. Using the immediate assignment
counters is possible to obtain the percentage of immediate assignment rejected
due to lack of radio resources.
( )
[ ]%__
SREJCSIMMASCSIMMASS
SREJCSIMMAS
REJASSIGNIMM
+
=
Figure 13 – Immediate Assignment Reject
Figure 14 – POPTR1 Assignment failure
POPTR1 ASSIGNMENT FAILURE
0.00
0.50
1.00
1.50
2.00
2.50
3.00
3.50
4.00
4.50
5.00
13:00 14:00 15:00 16:00 17:00 18:00 19:00 20:00 21:00 22:00 23:00
IMM_ASSIGN_REJ LOST_ASSIGN
0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/callsetupfailure-190123024117/85/Call-setup-failure-19-320.jpg)
![Prepared: MEX/TIM Luis Batallan
TEM/T-
Approved Ericsson:
Approved Telcel:
2424202020202024
Subdirección de Calidad de
Servicio y Evaluación del
Desempeño de la Red
CALL SETUP FAILURE
Date: 2005-06-22 Rev. A
5.2 SERVICE REQUEST
Figure 15 – Service Request
When the connection is established between the MS and the BTS, it send
Establish Indication message to the BSC that could contain either “page
response” (for mobile terminated calls) or “CM service request” (for mobile
originated calls). Then the BSC will start the establishment of link to the MSC by
sending a “SCCP connection request”. The “SCCP connection confirm” message
is returned to the BSC, which means that the connection oriented signaling is
established on the A interface and then the CMSESTAB counter is stepped.
In order to check the “lost attempts” (i.e. not successful and not congested) in this
process is possible through STS counters count the total of calls attempts which
ones were “lost”.
[ ]%*100__ ⎥
⎦
⎤
⎢
⎣
⎡ −−−
=
CCALLS
CCONGSUBCCONGSCMSESTABCCALLS
ATTEMPTSSDCCHLOST
Figure 16 – Lost SDCCH Attempts
Figure 17 – POPTR1 LOST ATTEMPTS
(CM Service Request)
CMSESTAB
POPTR1 LOST SDCCH ATTEMPTS
0.00
1.00
2.00
3.00
4.00
5.00
6.00
7.00
8.00
9.00
10.00
17/05/05
18/05/05
19/05/05
20/05/05
21/05/05
22/05/05
23/05/05
24/05/05
25/05/05
26/05/05
27/05/05
28/05/05
29/05/05
30/05/05
31/05/05
01/06/05
02/06/05
03/06/05
04/06/05
05/06/05
06/06/05
07/06/05
08/06/05
09/06/05
10/06/05
11/06/05
12/06/05
13/06/05
14/06/05
15/06/05
16/06/05
17/06/05
0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/callsetupfailure-190123024117/85/Call-setup-failure-20-320.jpg)
![Prepared: MEX/TIM Luis Batallan
TEM/T-
Approved Ericsson:
Approved Telcel:
2424212121212124
Subdirección de Calidad de
Servicio y Evaluación del
Desempeño de la Red
CALL SETUP FAILURE
Date: 2005-06-22 Rev. A
Note: Due to the system will try more than one attempt to allocate a channel in
the BTS, it is possible to obtain a little bit higher percentage of “lost attempts”
than we actually have using the above formula.
5.3 SECURITY FUNCTIONS
For security functions (Authentication and Ciphering) there are available counters
at MSC level on the Object Type Security Handling (SECHAND) in order to check
failures in these processes.
NAUTREQTOT: Number of sent authentication requests
NAUTREQSUCC: Number of successful authentications including check of SRES or XRES
NCIPATTTOT: Number of ciphering mode setting attempts
NCIPSETSUCC: Number of successful ciphering mode settings
[ ]%*100_ ⎥
⎦
⎤
⎢
⎣
⎡
=
CNAUTREQSUC
NAUTREQTOT
SUCCAUTHENT
Figure 18 – Authentication Success
[ ]%*100_ ⎥
⎦
⎤
⎢
⎣
⎡
=
NCIPATTTOT
CNCIPSETSUC
SUCCCIPHER
Figure 19 – Ciphering Success
Figure 20 – POPTR1 SECURITY FUNCTIONS
POPTR1 SECURITY FUNCTIONS
98.80
98.90
99.00
99.10
99.20
99.30
99.40
99.50
99.60
18/05/2005
20/05/2005
22/05/2005
24/05/2005
26/05/2005
28/05/2005
30/05/2005
01/06/2005
03/06/2005
05/06/2005
07/06/2005
09/06/2005
11/06/2005
13/06/2005
15/06/2005
17/06/2005
19/06/2005
AUTHENT_SUCC CIPHER_SUCC
0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/callsetupfailure-190123024117/85/Call-setup-failure-21-320.jpg)
![Prepared: MEX/TIM Luis Batallan
TEM/T-
Approved Ericsson:
Approved Telcel:
2424222222222224
Subdirección de Calidad de
Servicio y Evaluación del
Desempeño de la Red
CALL SETUP FAILURE
Date: 2005-06-22 Rev. A
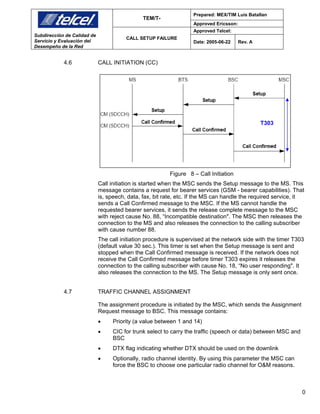
5.4 CALL INITIATION
For the Call Initiation there are two counters belonging to the object type “Layer 3
Call Control Counters for MSC/VLR Server” (L3CCMSG):
NL3CPROC: Number of sent Layer 3 Call Control CALL PROCCEEDING messages
NL3CCONF: Number of received Layer 3 Call Control CALL CONFIRMED messages
[ ]%
3
3
*100_ ⎥
⎦
⎤
⎢
⎣
⎡
=
CPROCNL
CCONFNL
CONFIRMCALL
Figure 21 – Call Initiation Success
Note: L3CCMSG has currently no data on TELCEL network (probably the Object
Type is not activated)
5.5 TRAFFIC CHANNEL ASSIGNMENT
Figure 22 – TRAFFIC CHANNEL ASSIGNMENT
Using the counters for “Assignment Request” and for “Assignment Complete” is
possible to obtain the failure in the Traffic Channel Assignment process.
TASSALL: Assignment attempts for all MS power classes. Successful attempts are
counted in the target cell and failed attempts are counted in the serving cell
TFCASSALL: Assignment complete for all MS power classes
TFCASSALL
TFCASSALLSUB
THCASSALL
THCASSALLSUB
TASSAL
L
(
⎟
⎠
⎞
⎜
⎝
⎛ +++−
×=
TASSALL
UBTHCASSALLSTHCASSALLUBTFCASSALLSTFCASSALLTASSALL
iedServiceDen 100
0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/callsetupfailure-190123024117/85/Call-setup-failure-22-320.jpg)
![Prepared: MEX/TIM Luis Batallan
TEM/T-
Approved Ericsson:
Approved Telcel:
2424232323232324
Subdirección de Calidad de
Servicio y Evaluación del
Desempeño de la Red
CALL SETUP FAILURE
Date: 2005-06-22 Rev. A
POPTR1 Service Denied
0.00
0.05
0.10
0.15
0.20
0.25
0.30
0.35
0.40
0.45
15/06/2005
16/06/2005
17/06/2005
18/06/2005
19/06/2005
20/06/2005
Figure 23 – POPTR1 Service Denied
Figure 24 – Service Denied
Using the Measurements for Traffic Channels is possible to detect failures in the
channel activation on the BTS.
TFCALLS: Call attempt counter
TFMSESTB: Successful MS channel establishment on TCHs
TFCONGSAS: Number of congestion at assignment
TFCONGSHO: Number of congestion at handover
Figure 25 – POPTR1 Channel Activation Failure
[ ]%*100__ ⎥
⎦
⎤
⎢
⎣
⎡ −−−
=
TFCALLS
TFCONGSHOTFCONGSASTFMSESTBTFCALLS
FAILACTCH
Figure 24 – Channel Activation Failure
(
⎟
⎠
⎞
⎜
⎝
⎛ +++−
×=
TASSALL
UBTHCASSALLSTHCASSALLUBTFCASSALLSTFCASSALLTASSALL
iedServiceDen 100
POPTR1 Channel Activation Failure
0.00
0.50
1.00
1.50
2.00
16/06/2005 17/06/2005 18/06/2005 19/06/2005 20/06/2005
0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/callsetupfailure-190123024117/85/Call-setup-failure-23-320.jpg)
