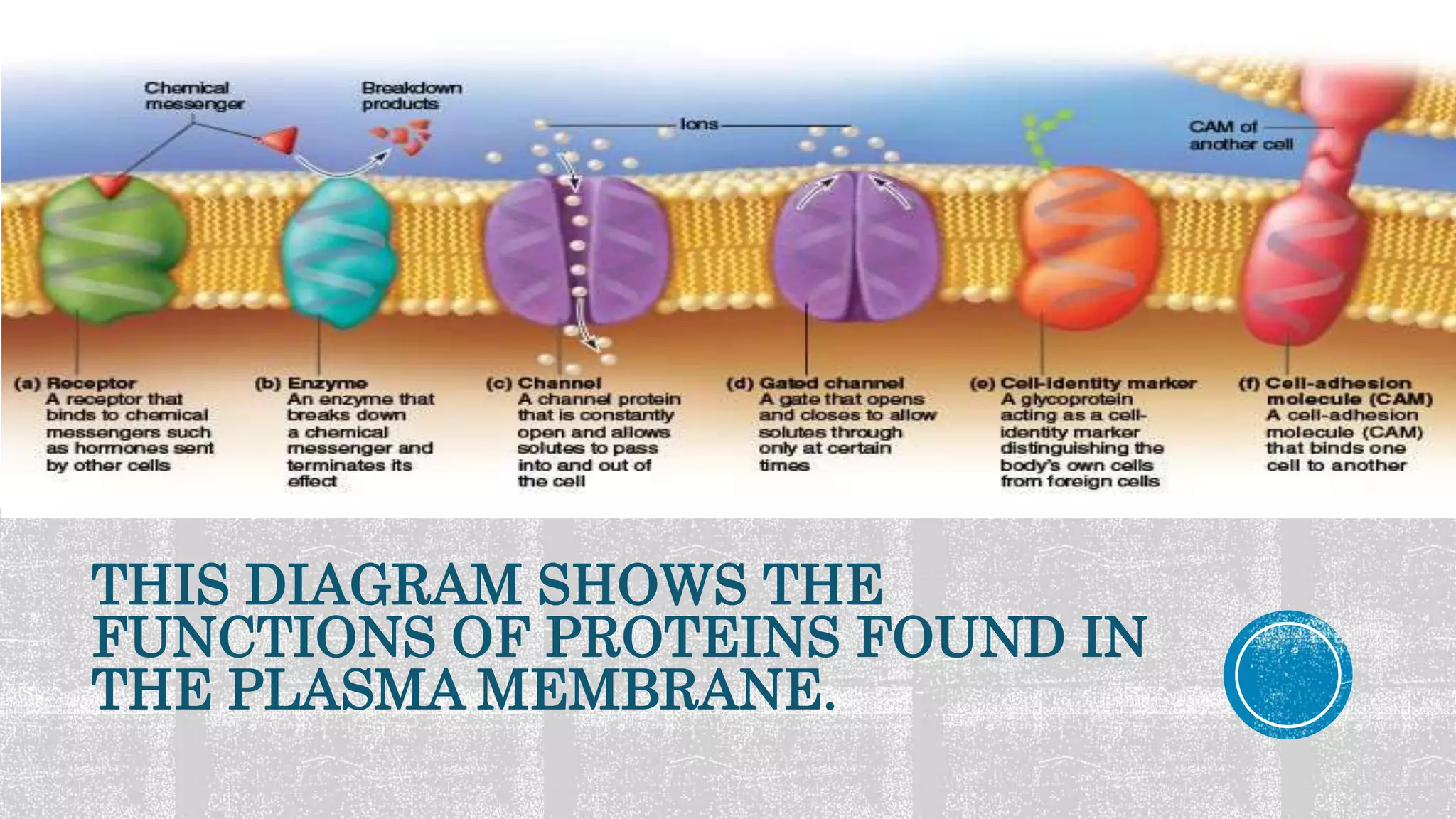
The document discusses hypercholesterolemia, providing details on the structure and function of cell membranes, including the fluid mosaic model. It then focuses on familial hypercholesterolemia, explaining that it is a genetic disorder caused by mutations in genes like LDLR that result in very high LDL cholesterol levels and increased risk of early heart disease. The LDLR gene normally allows cells to remove LDL from the blood, but mutations disrupt this process and lead to excess cholesterol building up in arteries.