Cell Membrane Structure and Functions
- 1. MEMBRANE BIOLOGY TOPIC: CELL MEMBRANE SUBMITTED BY: EVELIN GEORGE, 19BCU006, 2ND Bsc,. BIOCHEMISTRY
- 2. CELL MEMBRANE Introduction Plasma membrane surrounds the organelles of the cells. It forms a barrier between cell organelles and the outside environment. A plasma membrane plays different roles depending upon its location. For e.g., a plasma membrane encloses the cytoplasm as well the organelles of the cell. It is a tough, rigid and flexible layer made up of proteins, lipids, and carbohydrates. Plasma Membrane Function Following are the important plasma membrane function: The plasma membrane forms a barrier between the cell organelles from the outside environment. It allows only a certain molecules to pass through it. It facilitates communication and signalling between the cells. Key Points on Cell Membrane and Plasma Membrane The cell membrane is a type of plasma membrane that encloses the cell and all its components. Both the membranes are selectively permeable and regulate the entry and exit of components. The cell membrane is the only membrane involved in cytokinesis. Plasma membrane and cell membrane are often confused to be similar terms. The plasma membrane encloses the organelles of the cell, whereas, the cell membrane encloses the entire cell components.
- 3. DEVELOPMENT IN THE THEORIES Charles Overton was the first one to suggest that cell membrane is made up of lipids. In the last years of the 19th century Overton did experimental work, allowing the distinction to be drawn between the cell wall of plants and their cytoplasmic membrane.He studied the permeability of a range of biological materials to around 500 chemical compounds. In 1900, Overton proposed a biomembrane model "Overton Biomembrane Model" which stated that biomembranes are made up of lipids. He gave this statement on the basis of observation of transport of lipid soluble substances across the biomembranes. The next development came in the year 1935 when James Danielli and Hugh Davson stated that some protein molecules are also sprinkled on the surface of the membrane. This theory is famously called the Sandwich Theory or more technically called the Lamellar Theory. Later on, David Robertson came up with the Robertson model. Named after the proposer David Robertson, his model was based on the observation of a red blood cell. He found that it had 3 layers: 2dark staining layers and 1 light staining layer in between. So the outer layers were assumed to be the protein layers and the inner one, the lipid bilayer. Therefore this supported the Lamellar or Sandwich Theory. But David Robertson went one step further in the protein front and suggested that proteins are not necessarily globular. According to the hypothesis, there is a membrane consisting of a phospholipid bilayer sandwiched between two protein monolayers. David Robertson also said that all the various membranes that are in a cell are of just two types: unit membranes or multiples of these unit membranes. Examples of unit membranes are Endoplasmic Reticulum, the Golgi, the Lysosomes, etc. and examples of double unit membranes are Mitochondria, Plastid, etc.
- 4. THE THREE FAMOUS MEMBRANE THEORY BEFORE FLUID MOSAIC MODEL 1.Lamellar Theory: “Sandwitch model” proposed by Danielli and Davson (1935), the plasma membrane exhibit trilaminar structure i.e., a lipid layer is bounded by protein layer on both the sides. In this model, proteins are usually represented in globular form. Subsequently electron microscopic studies favour the idea of trilaminar structure of plasma membrane. 2. Unit Membrane Theory: The universal occurrence of trilaminar pattern of membranes of cells led Robertson to propose in 1959, the concept of a ‘unit membrane’ with a trilaminar appearance. The unit membrane forms not only plasma membrane but also contains other membranes in most of the cell organelles.All the unit membranes consist of a bimolecular layer of phospholipids covered by a layer of proteins. Phospholipid is the main part of lipid. For example, lecithin, cephalin etc.
- 5. Besides it, other lipids like cholesterol, cerebroside and ganglioside as well as some polysaccharides; it is likely that these molecules provide stability to plasma lemma. Phospholipids are oriented with their fatty acid groups towards each other and their water soluble ends (polar groups) facing outwards. 3. Micellar Theory: Hilleir and Hoffman (1963) proposed this theory. According to them the plasma membrane includes a mosaic of globular subunits (micelles) which are closely packed together having a central core of lipid molecules with hydrophilic (water loving) polar end. Each lipid micelle measures about 40-70 A in diameter.
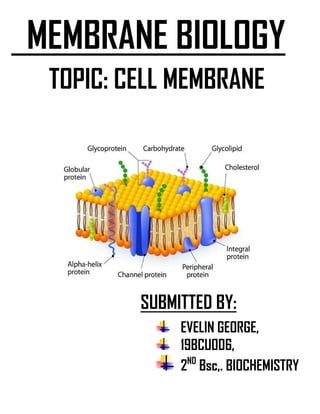
- 6. FLUID MOSAIC MODEL: THE BEST ACCEPTED MODEL TILL DATE The fluid mosaic model was proposed by S.J. Singer and Garth L. Nicolson. This model explains the structure of the plasma membrane of animal cells as a mosaic of components such as phospholipids, proteins, cholesterol, and carbohydrates. These components give a fluid character to the membranes. Components of plasma membranes are Cholesterol – It is located between the phospholipids and phospholipid bilayers. It helps the plasma membrane to retain the fluidity and prevents the compaction of hydrophilic tails at low temperatures and their expansion at high temperatures.
- 7. Phospholipids – Phospholipids are the main fabric of the plasma membrane. amphipathic molecules with a hydrophilic head and a hydrophobic tail and attached to a glycerol molecule by a covalent bond. Proteins – The plasma membrane has three types of proteins they are (1) Integral Proteins: These proteins form channels to allow the movement of large molecules and ions across the hydrophobic layer of the membrane. (2) Peripheral Proteins: These are found embedded in a single leaflet of the membrane. They carry signals from one segment of the membrane and relay it to the another. (3) Glycoproteins: They stabilize the membrane and are responsible for intercellular communication. Carbohydrates – These are attached to proteins on the outside membrane layer. REFERENCE: BOOKS OF LEHNINGER AND SATHYANARAYANA WEBSITE OF NCBI, BYJU’S, SCIENCE DIRECT