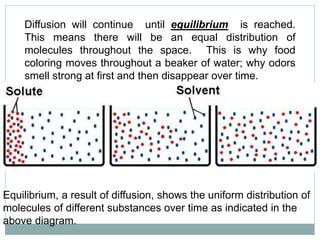
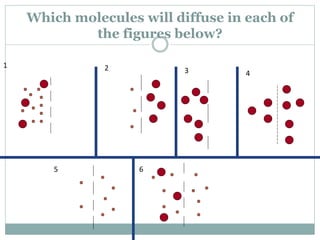
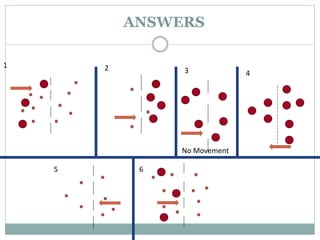
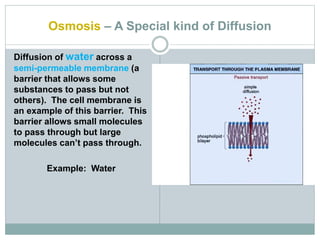
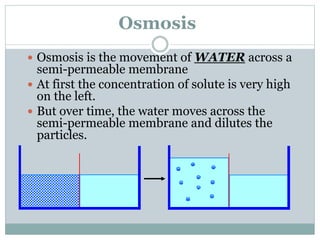
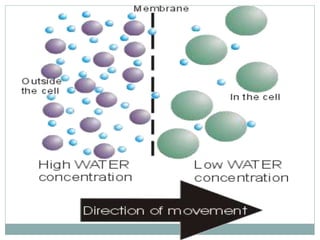
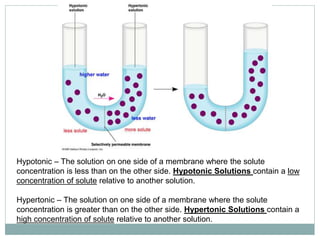
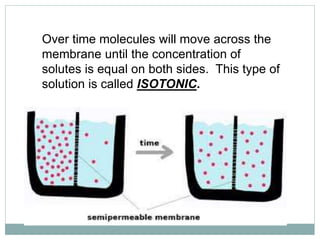
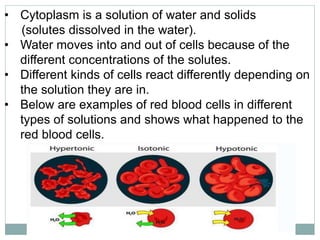
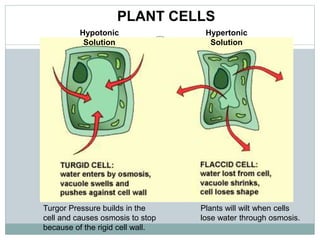
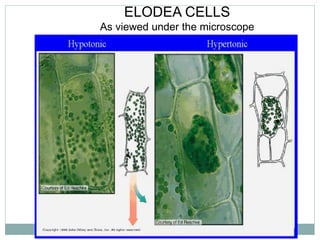
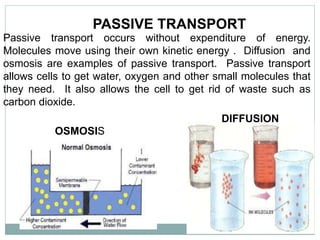
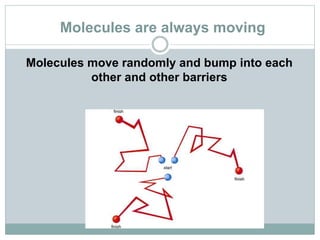
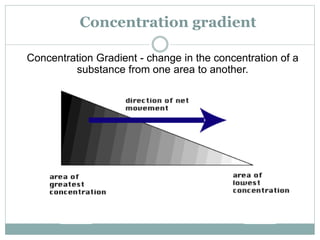
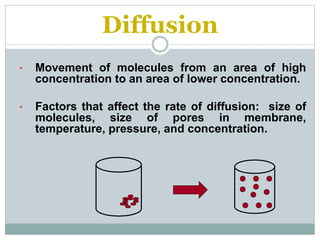
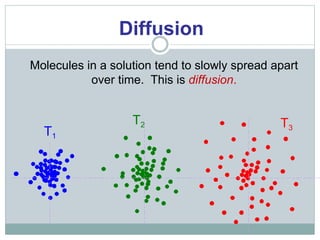
Osmosis and diffusion are types of passive transport where molecules move from areas of higher to lower concentration without expending energy. Osmosis is a special type of diffusion where water molecules move through a semi-permeable membrane from an area of higher water concentration to lower. The rate of diffusion and osmosis is affected by factors like molecule size, membrane pore size, temperature, and concentration gradient. Through diffusion and osmosis, concentrations will even out until equilibrium is reached with an equal distribution of molecules.

![Diffusion
[High] [Low]
concentrated, high energy molecules
diffuse, low energy molecules](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/130711251-240223022807-22287d2b/85/Differentiate-between-Osmosis-and-diffusion-ppt-6-320.jpg)