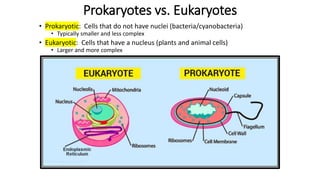
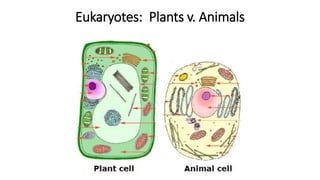
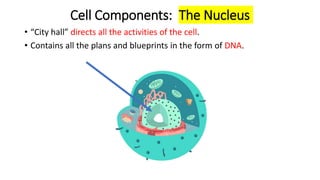
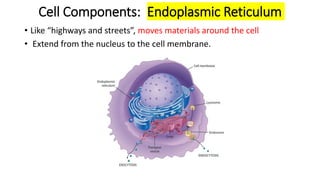
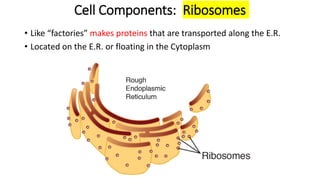
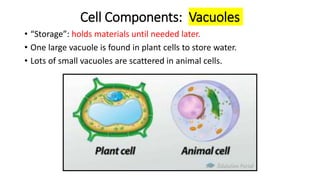
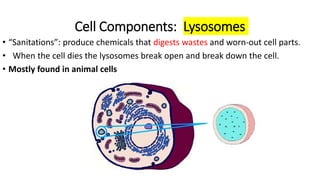
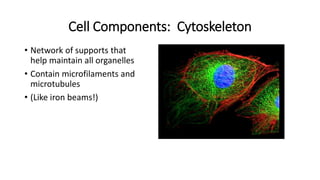
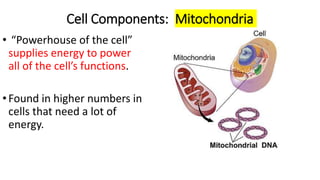
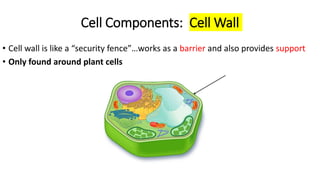
The document compares eukaryotic cell components to parts of a city. It describes prokaryotes as typically smaller cells without nuclei, while eukaryotes are larger and more complex with nuclei. The main cell components of eukaryotes are then summarized as the cytoplasm being like the inner city containing organelles as businesses, the nucleus directing activities as the city hall, the endoplasmic reticulum transporting materials like highways and streets, and ribosomes, Golgi apparatus, vacuoles, lysosomes, cytoskeleton, chloroplasts, mitochondria, cell wall, and cell membrane each playing roles analogous to various city infrastructure and services.