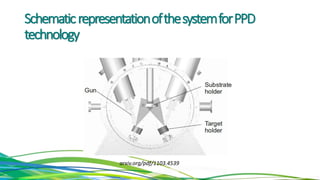
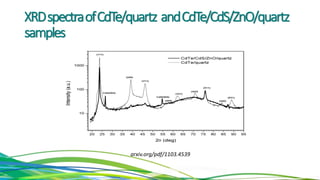
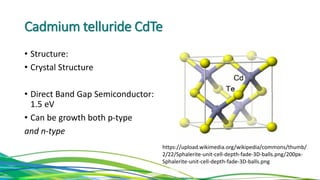
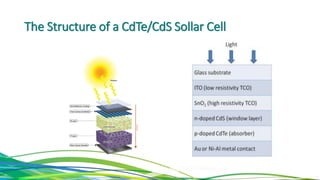
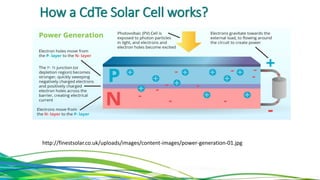
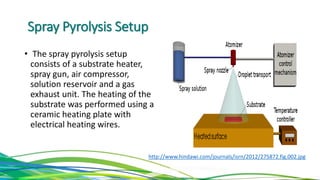
The document discusses cadmium telluride thin film solar cells. It describes how CdTe solar cells work and the fabrication process using spray pyrolysis to deposit CdS thin films and pulsed plasma deposition to deposit CdTe layers at low temperature. Characterization of the films using XRD showed the CdS films were polycrystalline hexagonal structures and the CdTe films had an optical bandgap of 1.50eV, matching the expected value.





![Solution Preparation
• The precursor solution used for Cadmium sulphide thin films was
obtained by dissolving the salts of cadmium chloride and
Thioacetamide in the molar ratio of 1:2 in double distilled water,
ammonia as complexing agent and N, N-DMF as a solvent were
added drop by drop. The amount of solution was made to 50 ml.
Cadmium Chloride [CdCl2.2H2O] and Thioacetamide[CH3CSNH2 ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/64a930fe-f088-4b48-ad98-c824045f5fa4-151223064923/85/CdTe-CdS-thin-film-in-Solar-Cell-10-320.jpg)