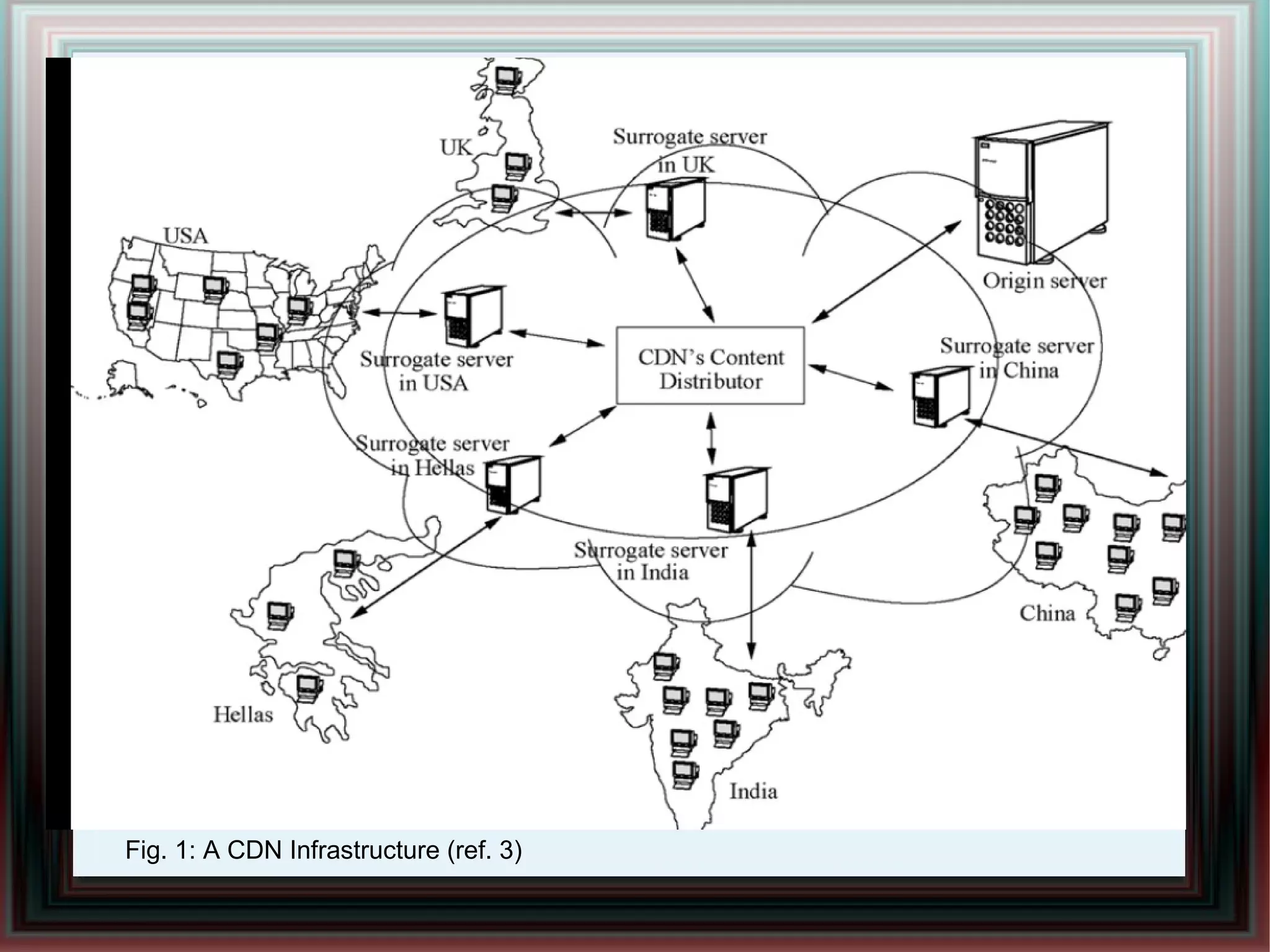
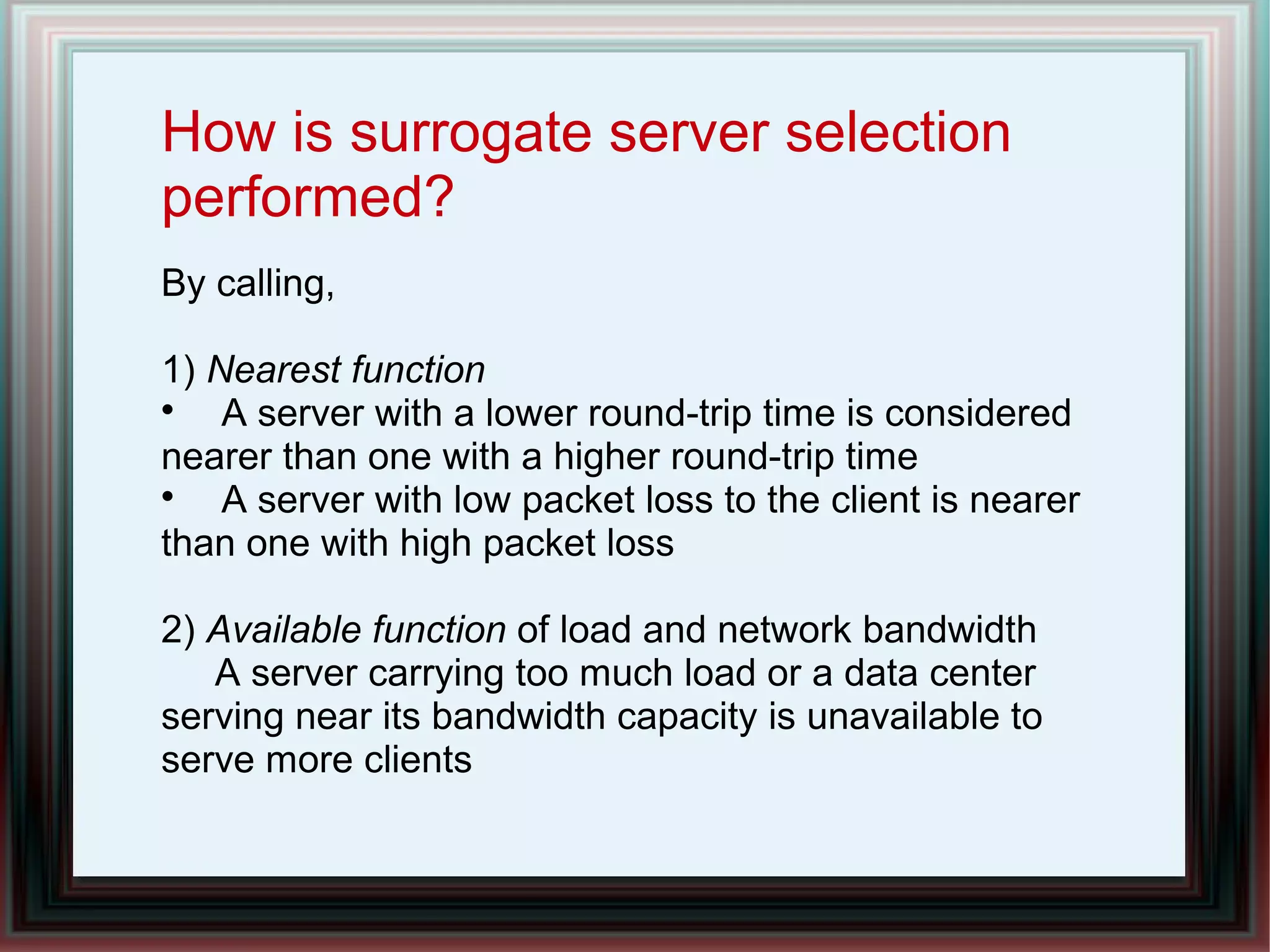
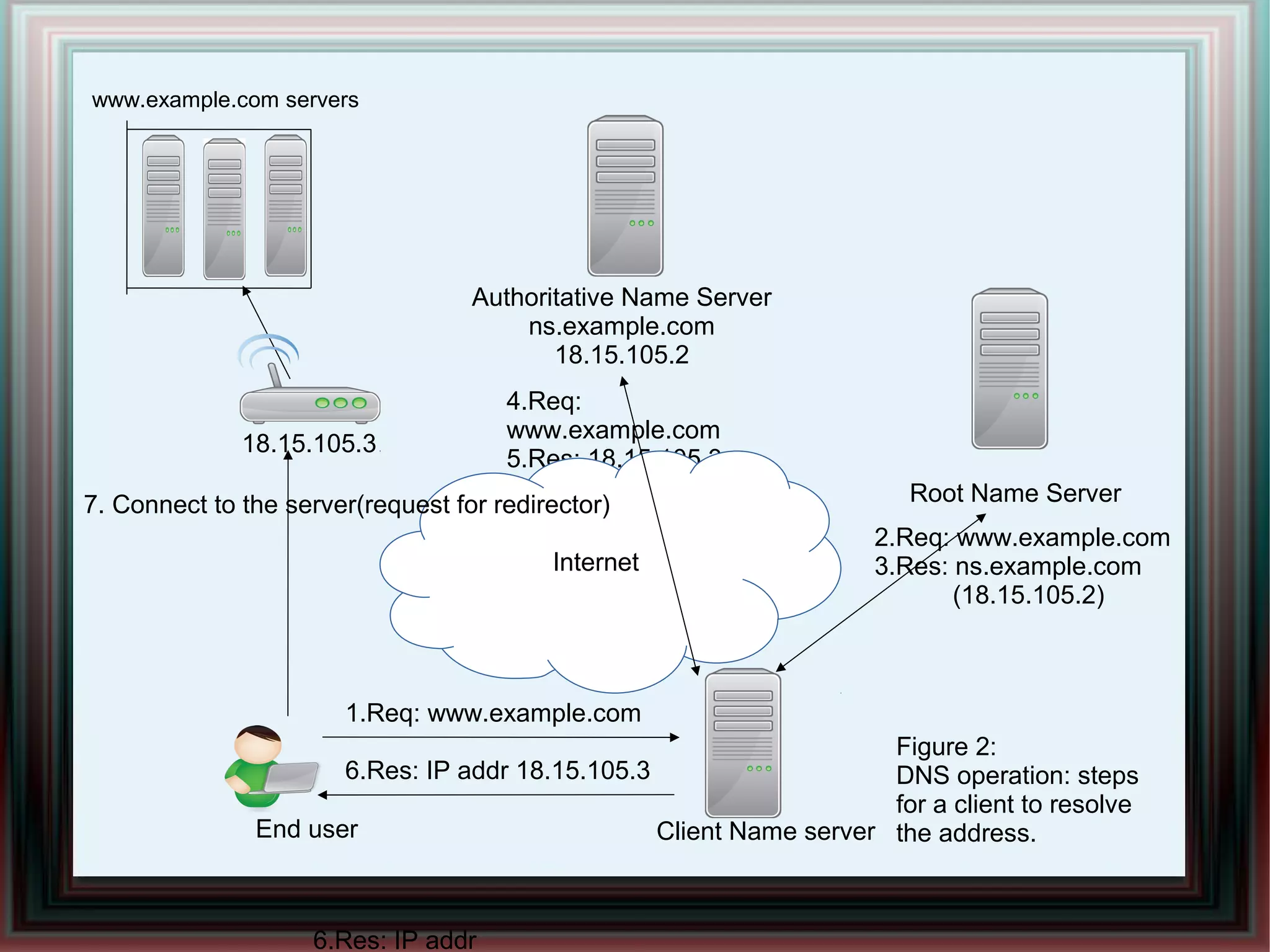
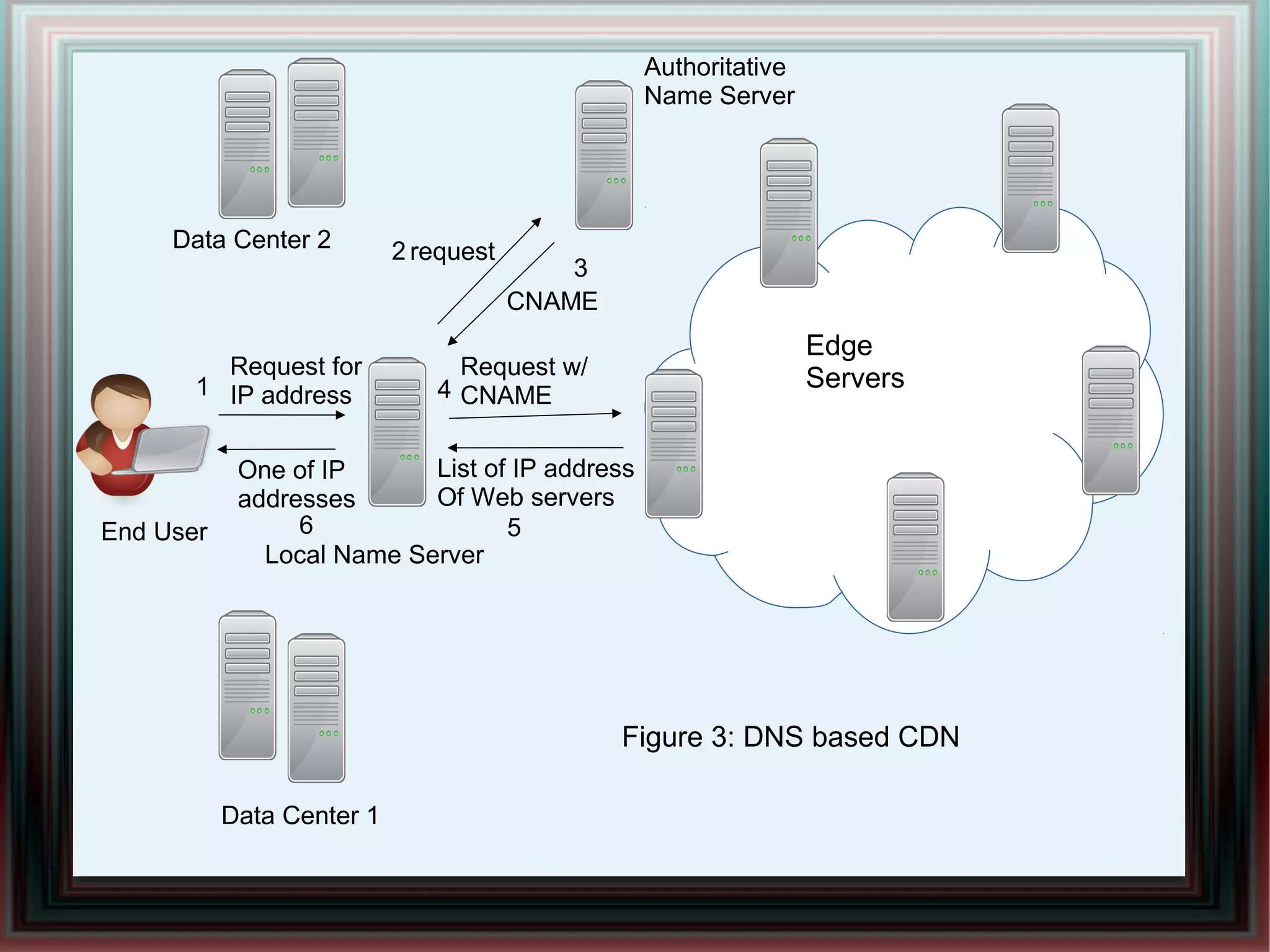
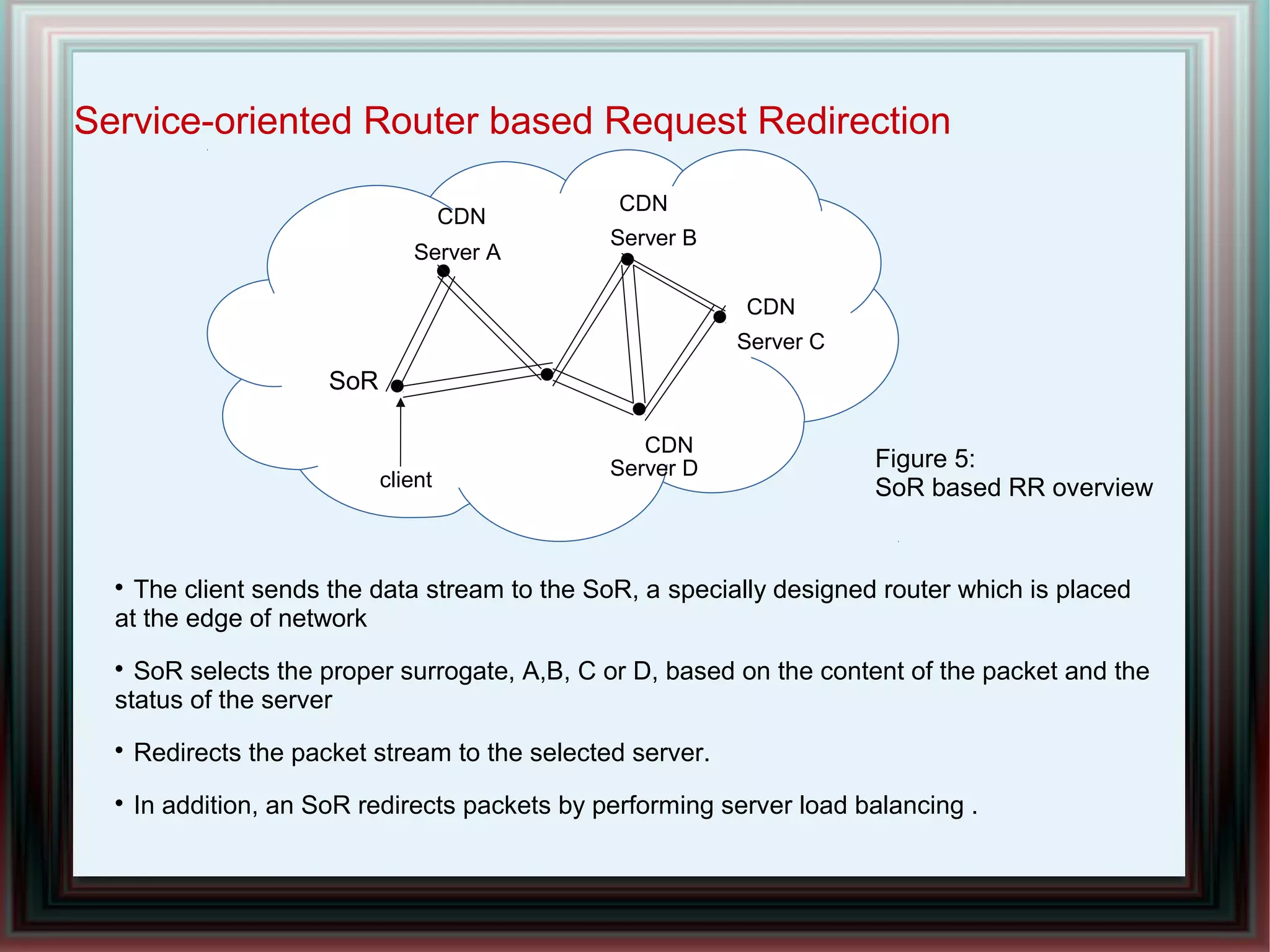
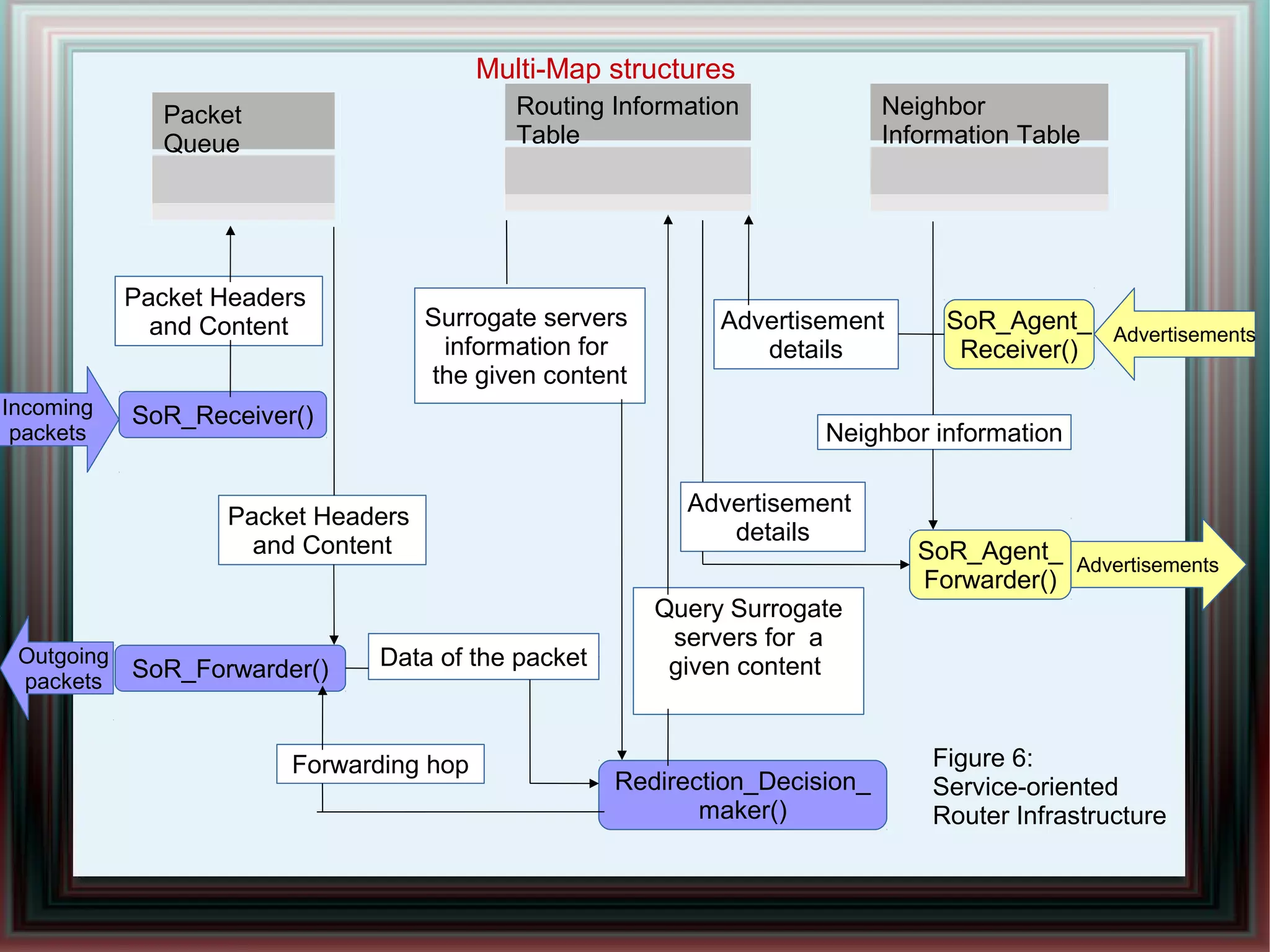
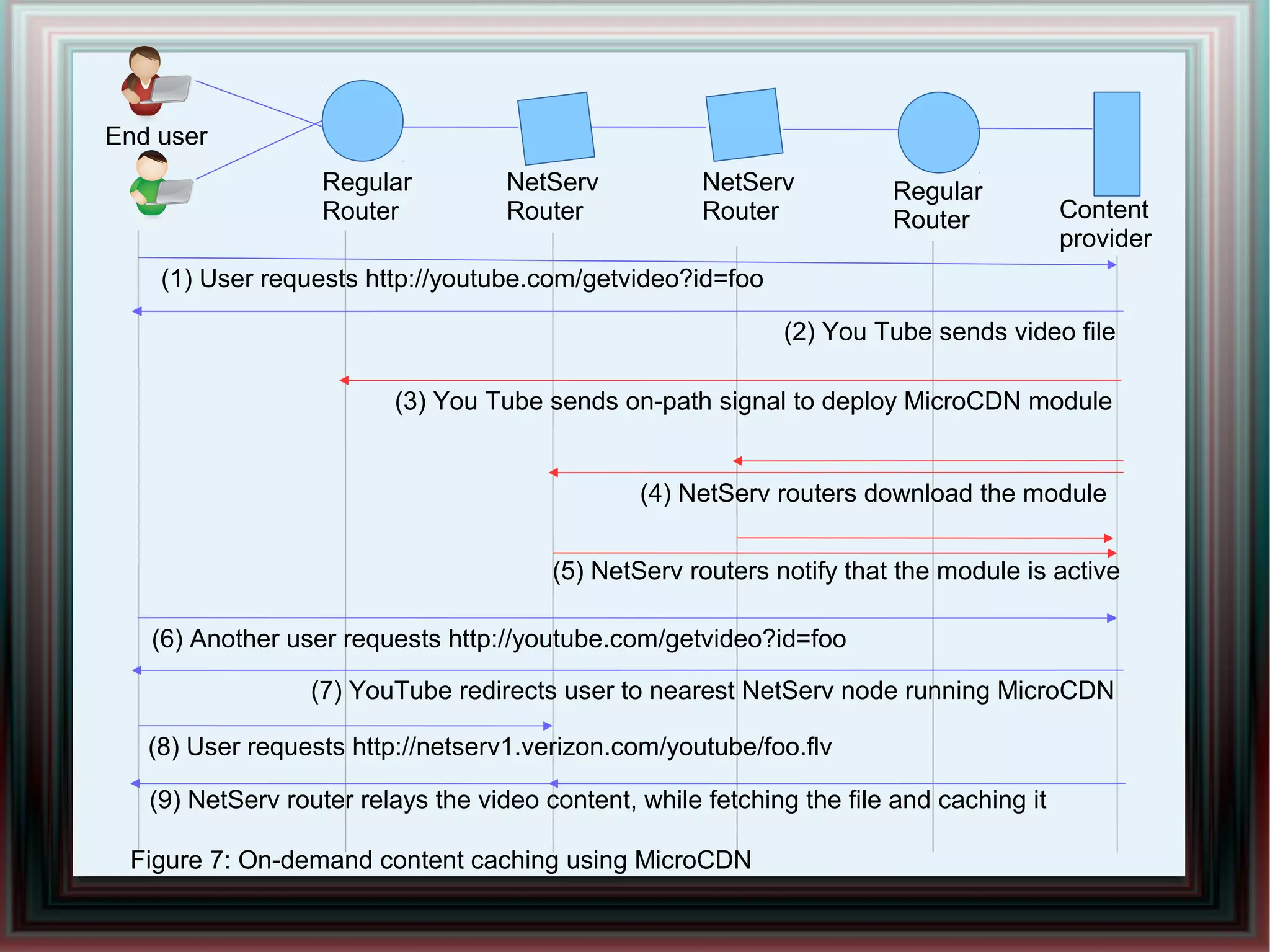
CDNs improve response times and enable streaming of audio/video by distributing content across multiple servers located close to users. DNS-based CDNs select the nearest surrogate server using DNS lookups, but this has delays. Service-oriented routers select servers based on packet contents and server loads, improving performance. NetServ routers can dynamically deploy "MicroCDN" modules to cache content on nearby routers for future user requests.