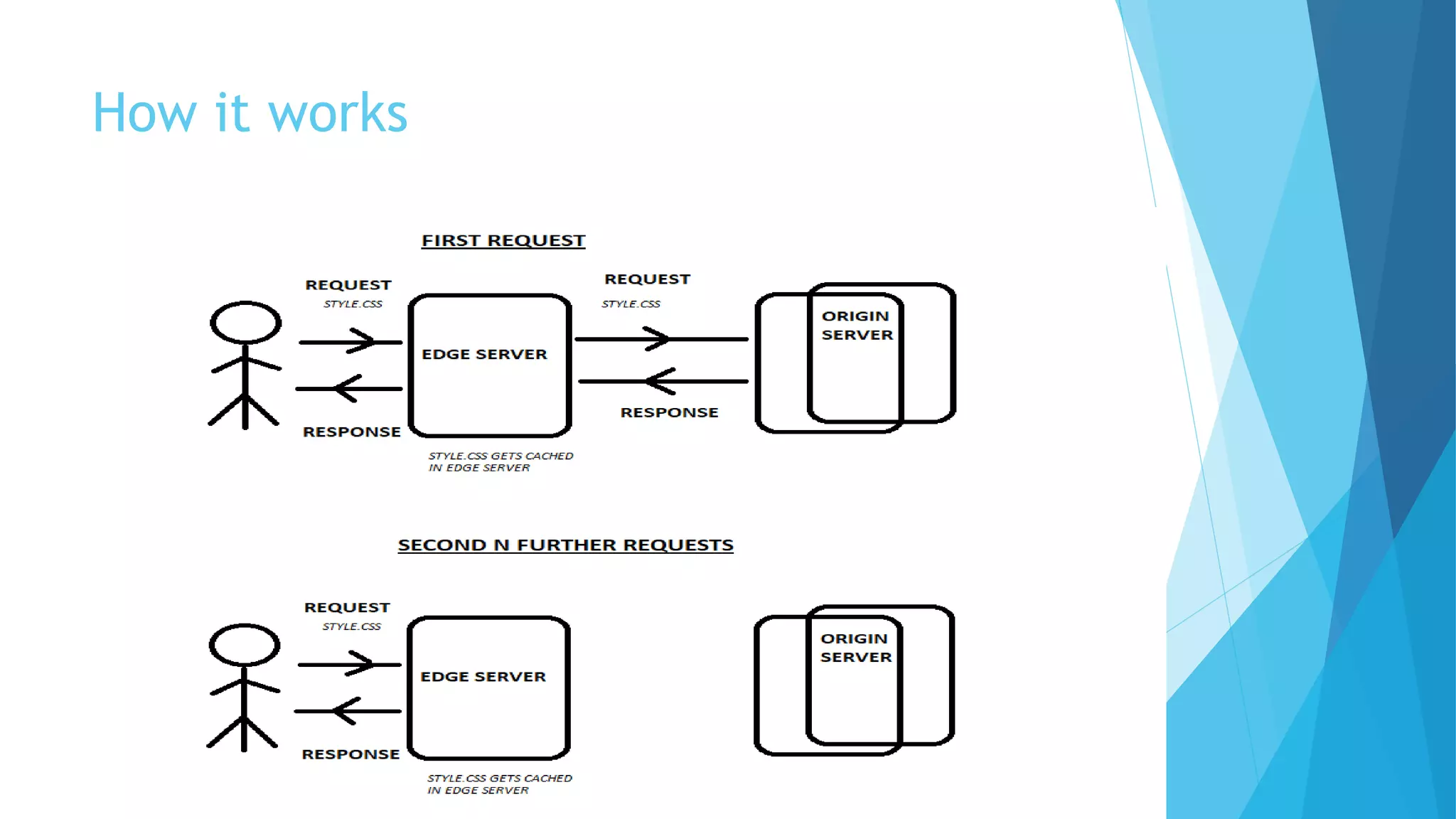
A content delivery network (CDN) is a system of distributed servers that cache and deliver static and dynamic web content to users based on their geographic locations. A CDN improves page load times by serving content from edge servers located close to users. There are two main types of CDNs - push CDNs where content providers upload content to be distributed, and pull CDNs where edge servers pull content from origin servers. Major CDN providers include Akamai, Cloudflare, Amazon CloudFront, and others that help speed up content delivery and reduce load on origin servers.