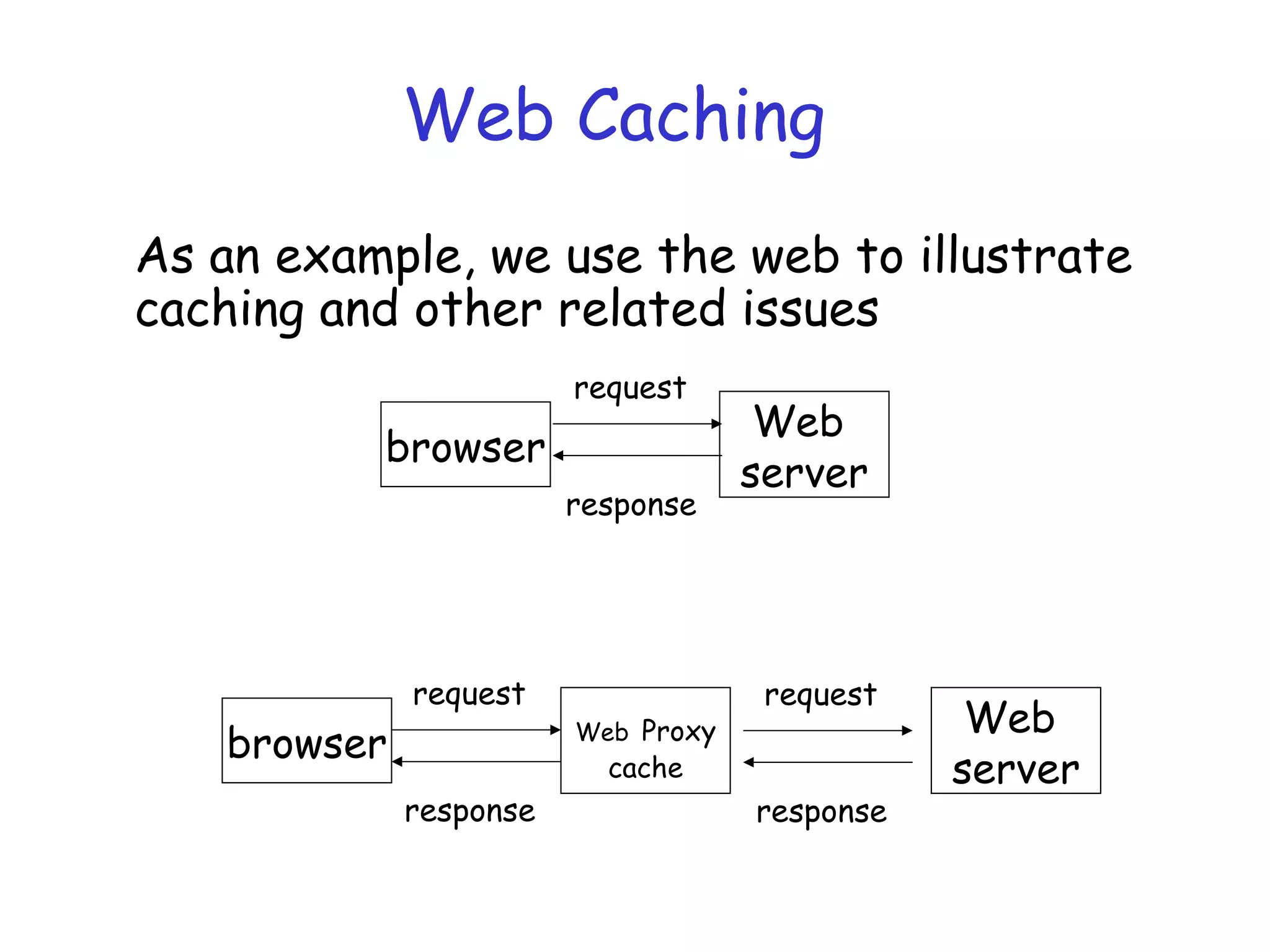
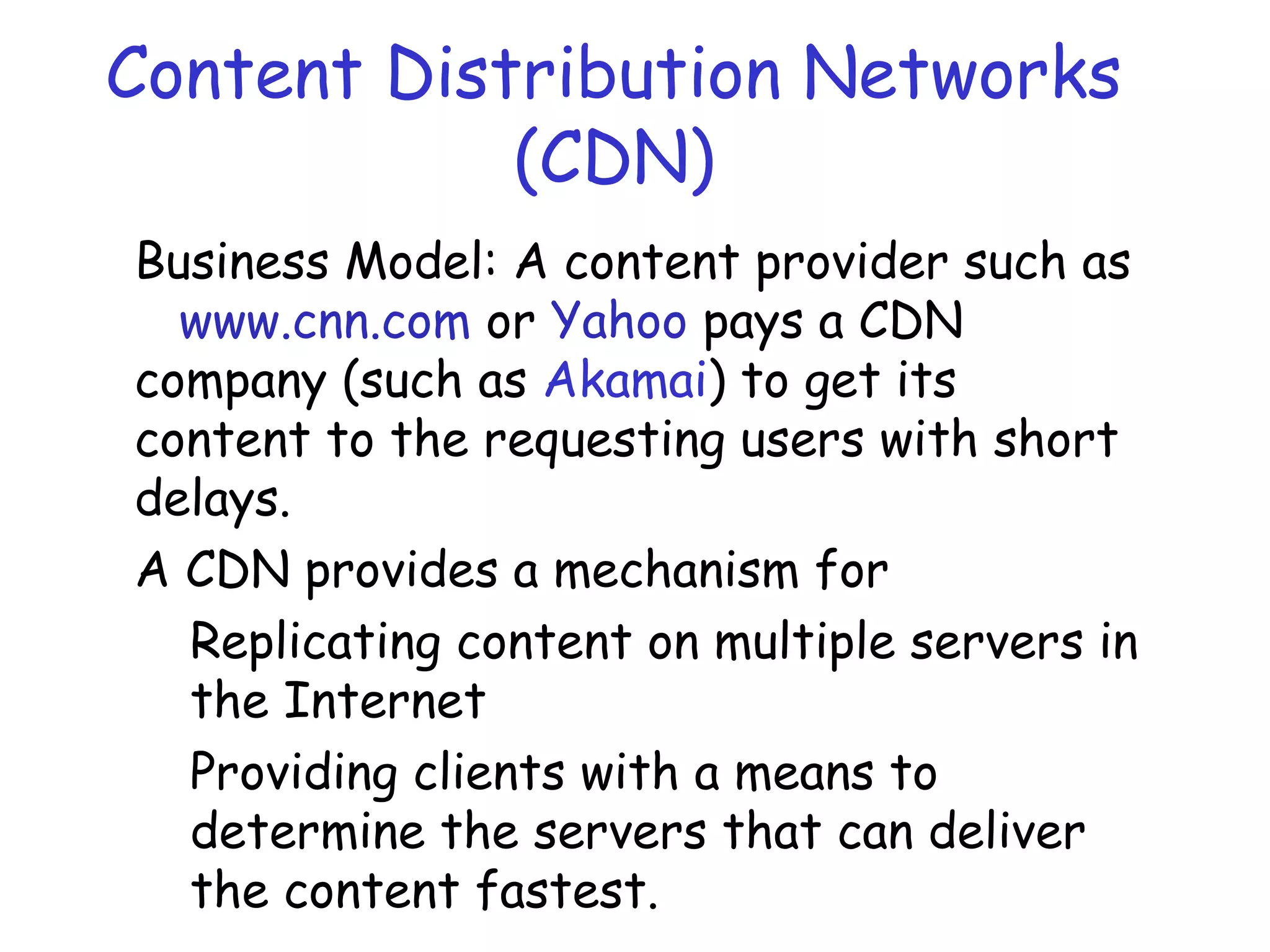
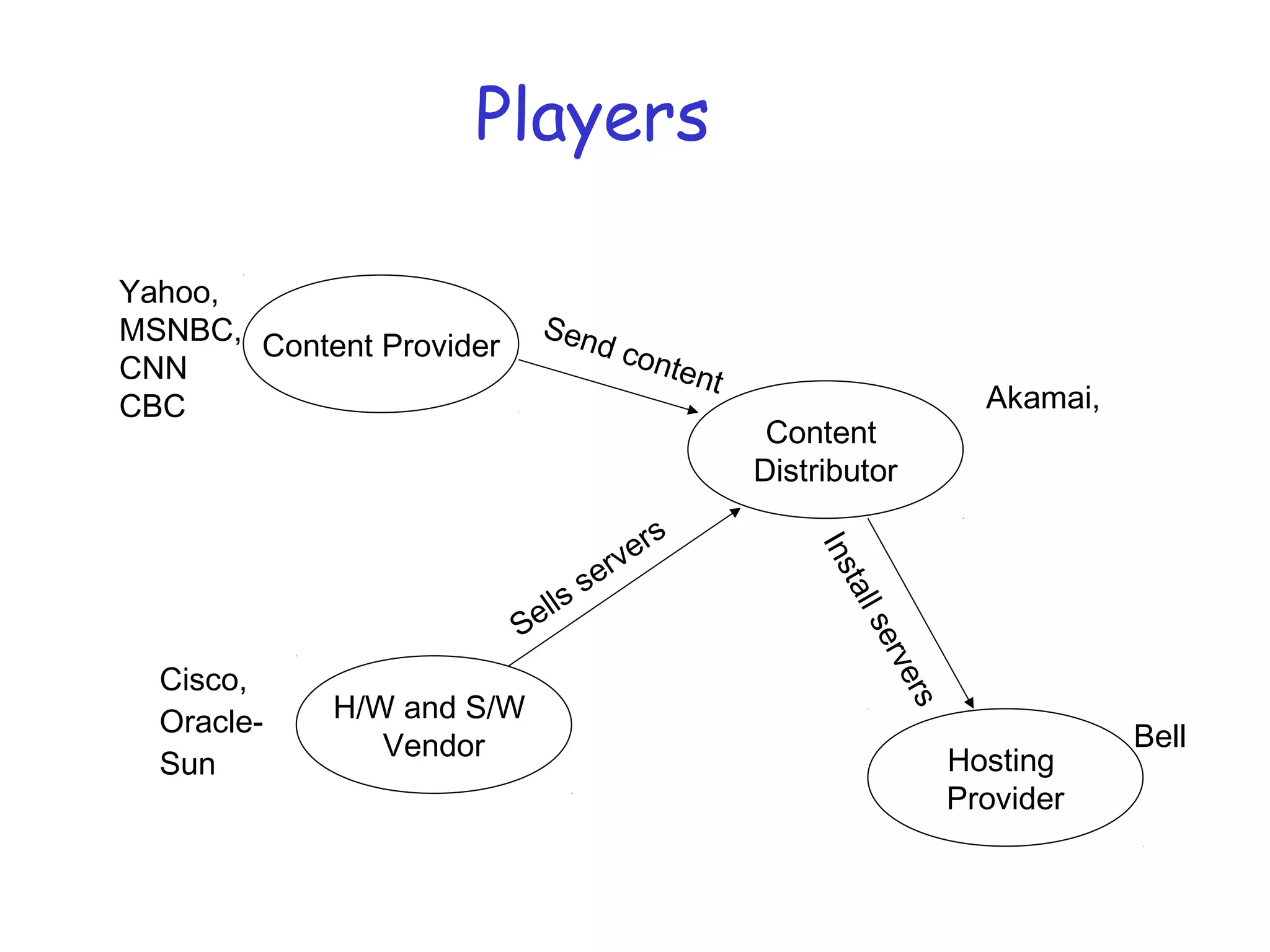
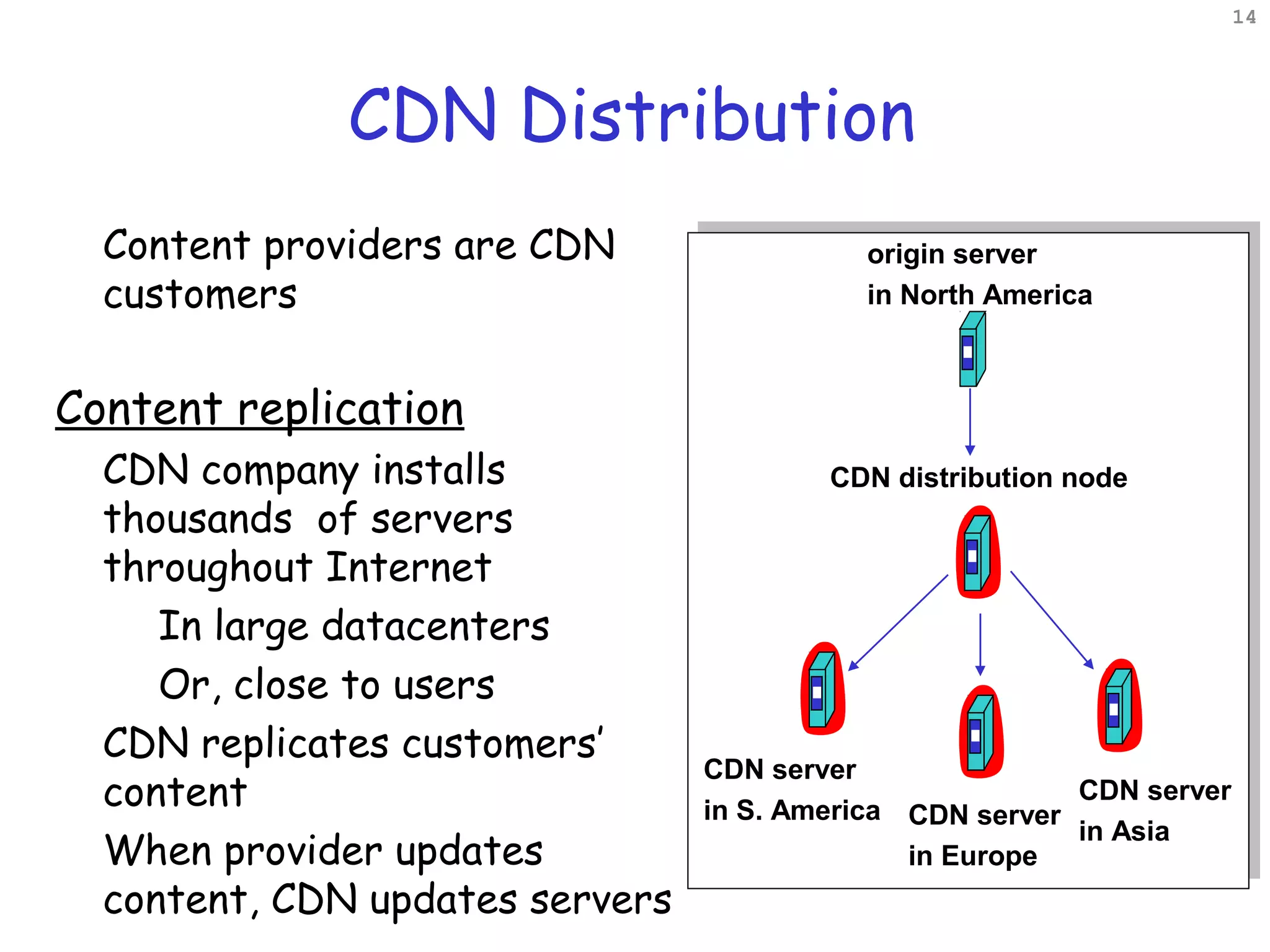
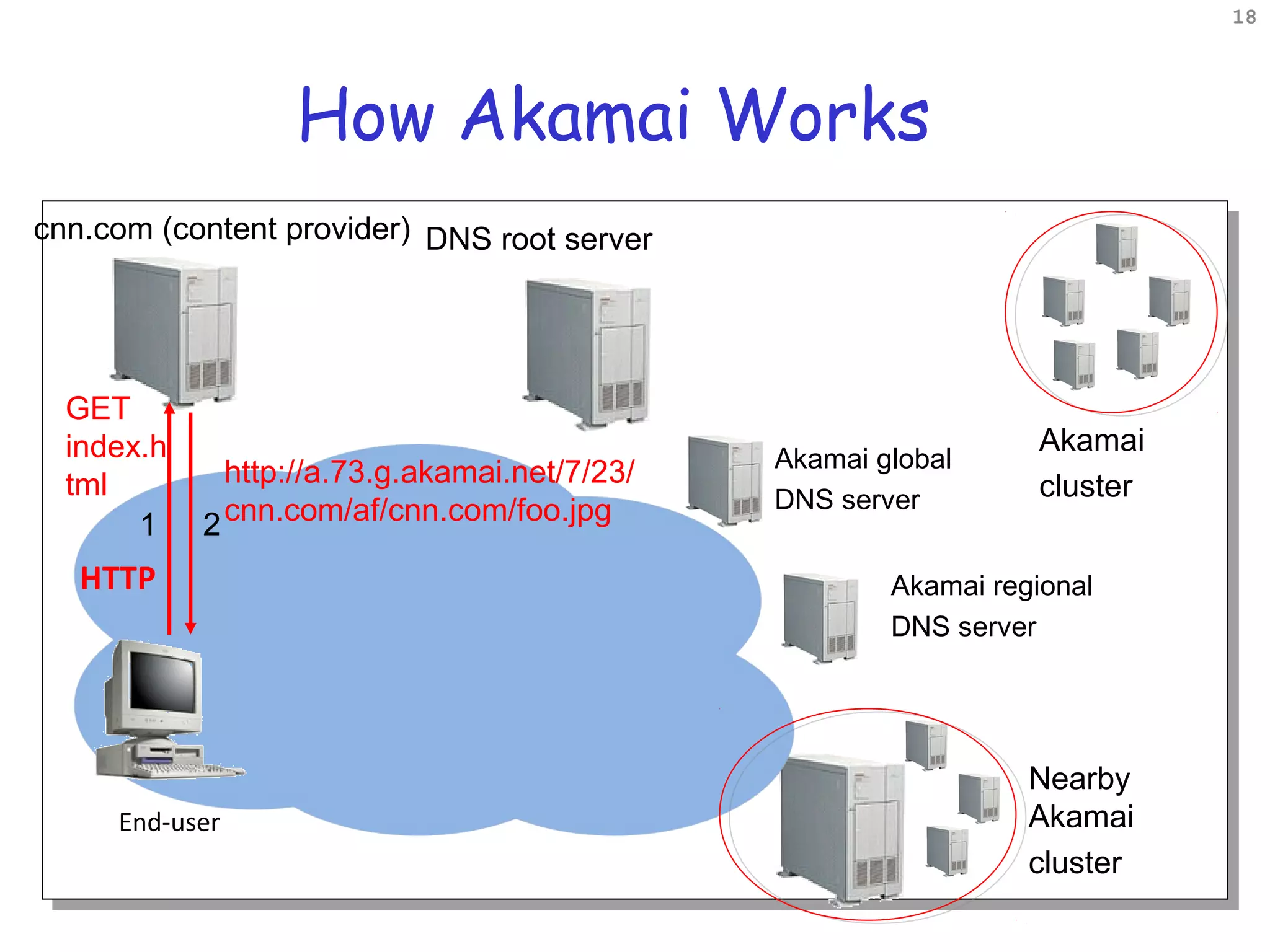
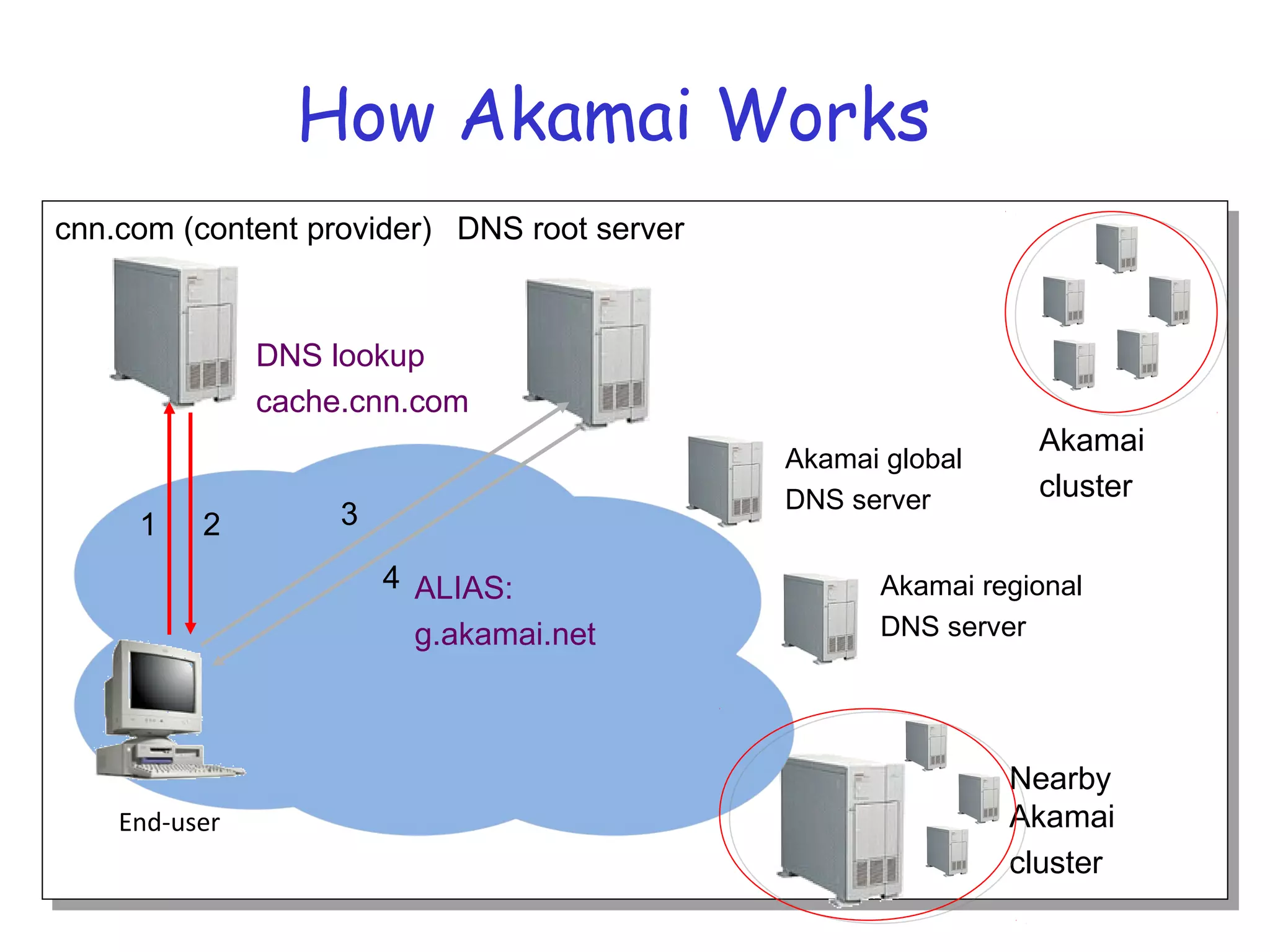
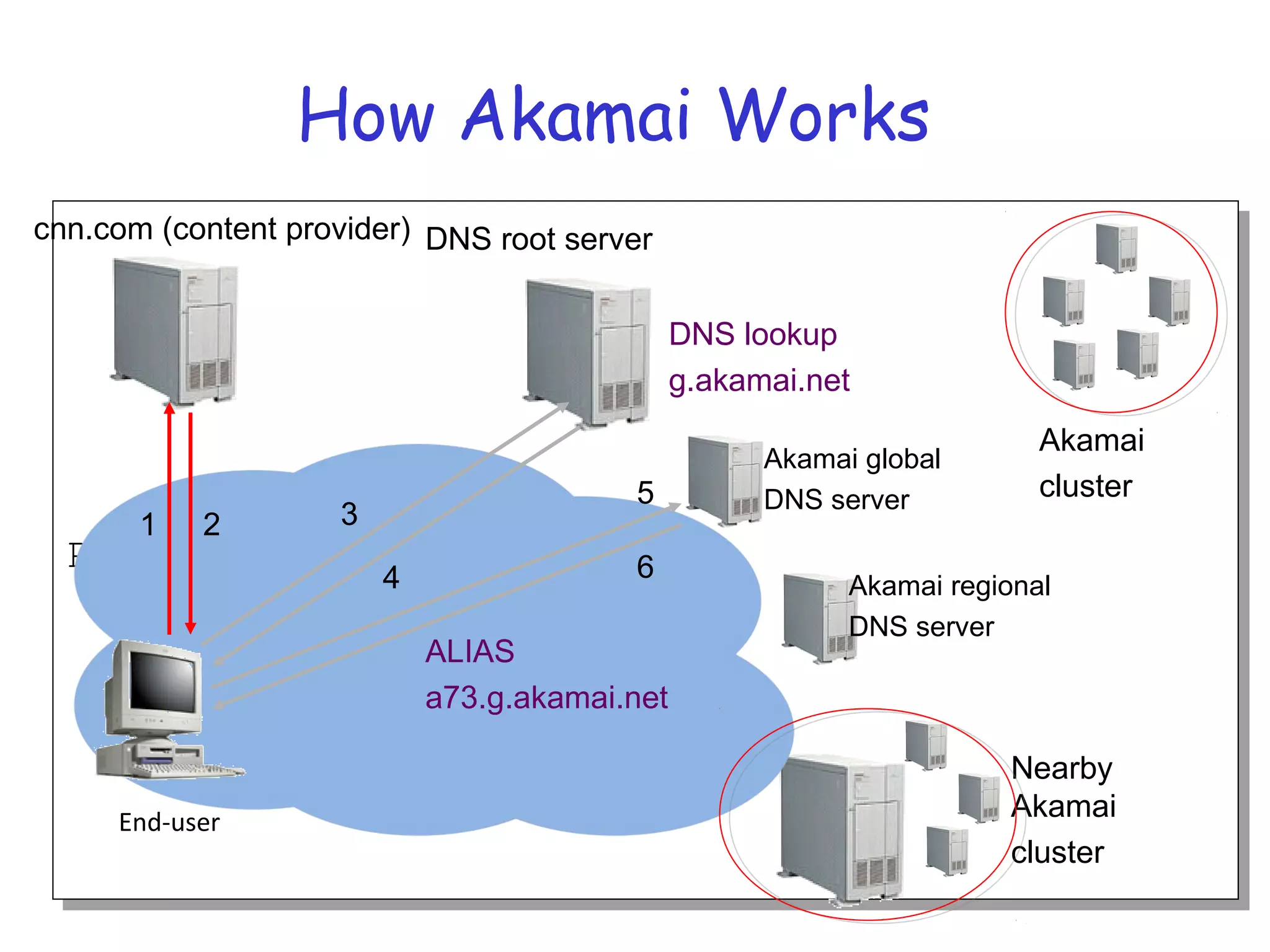
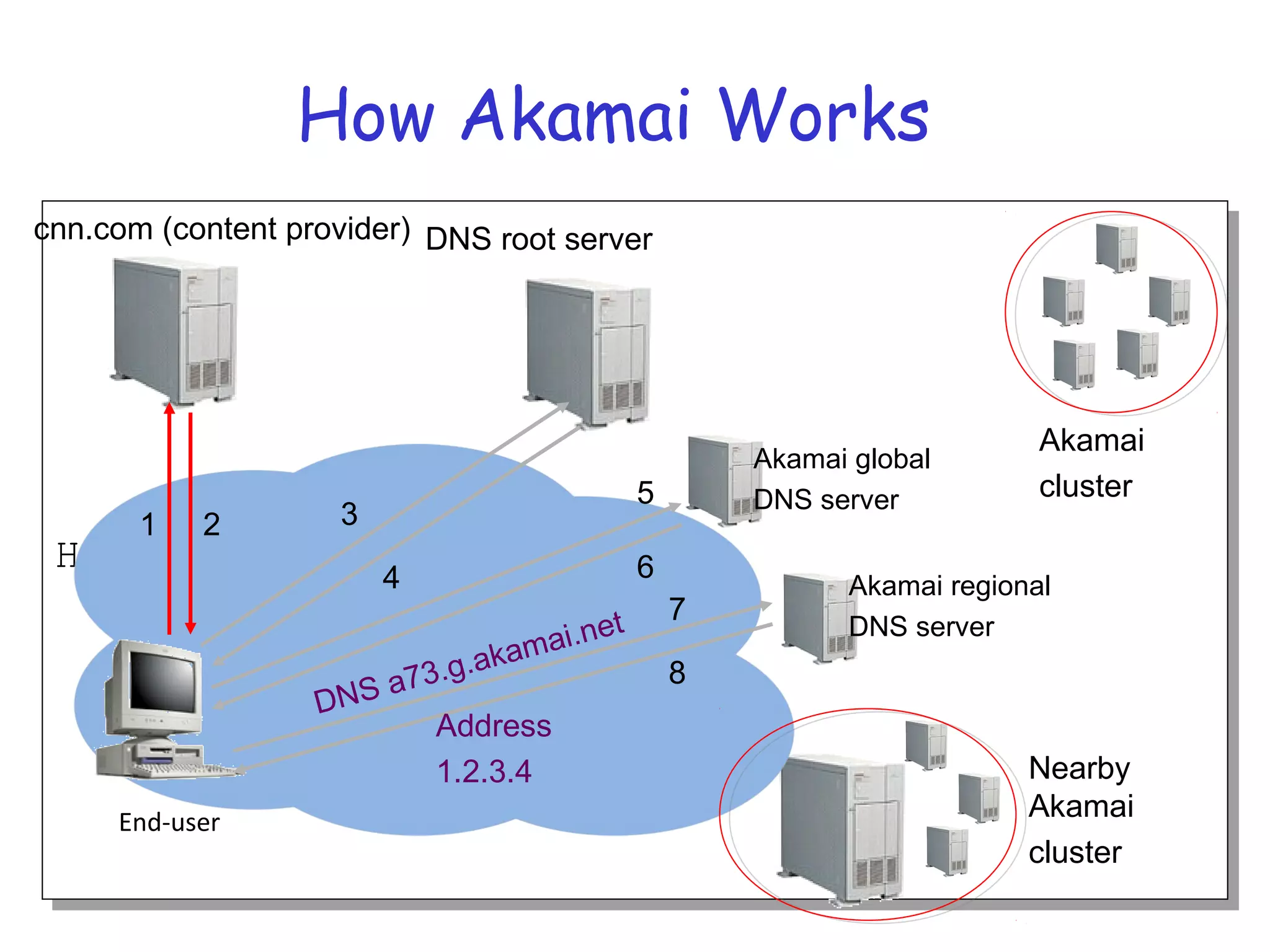
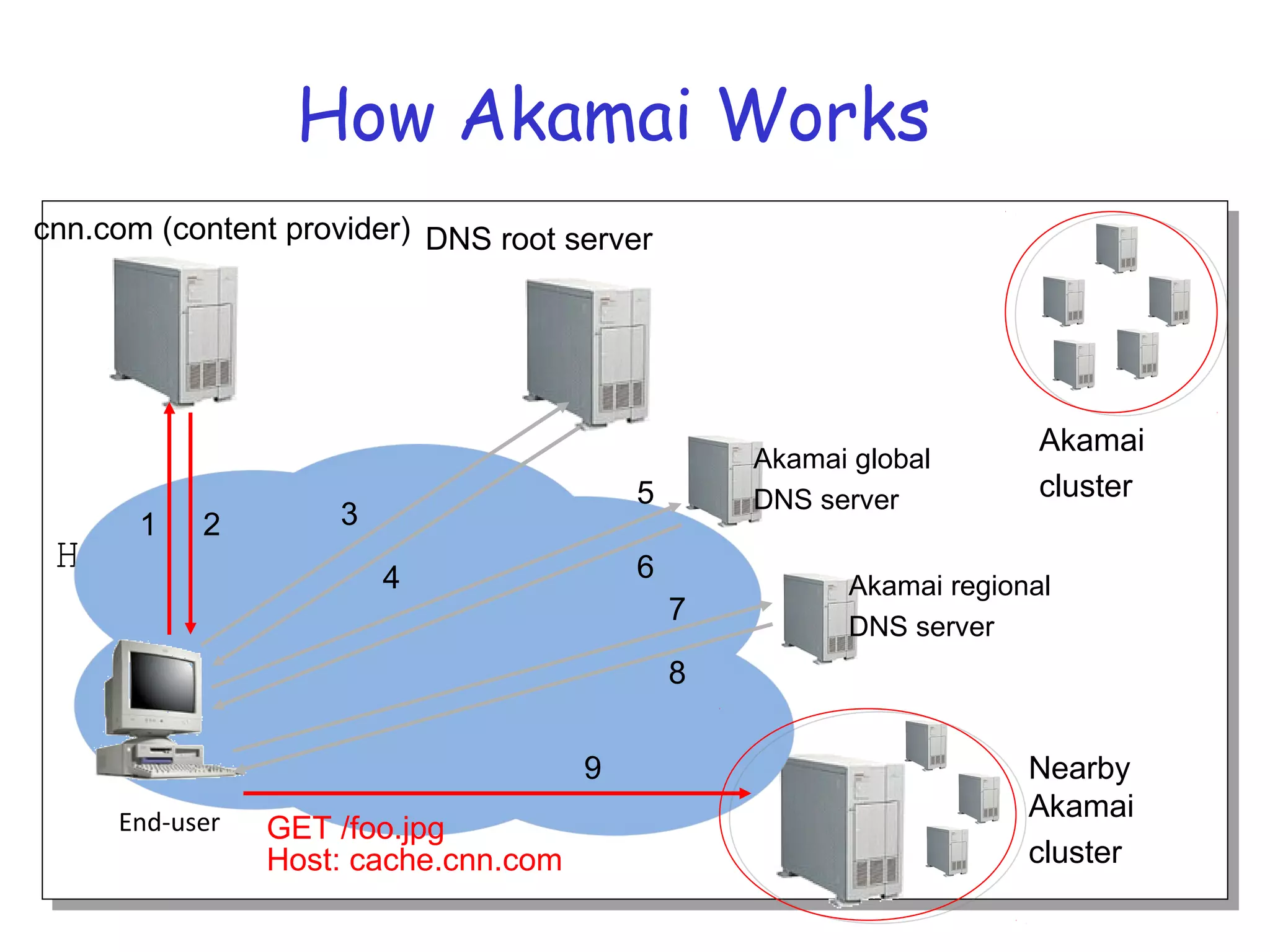
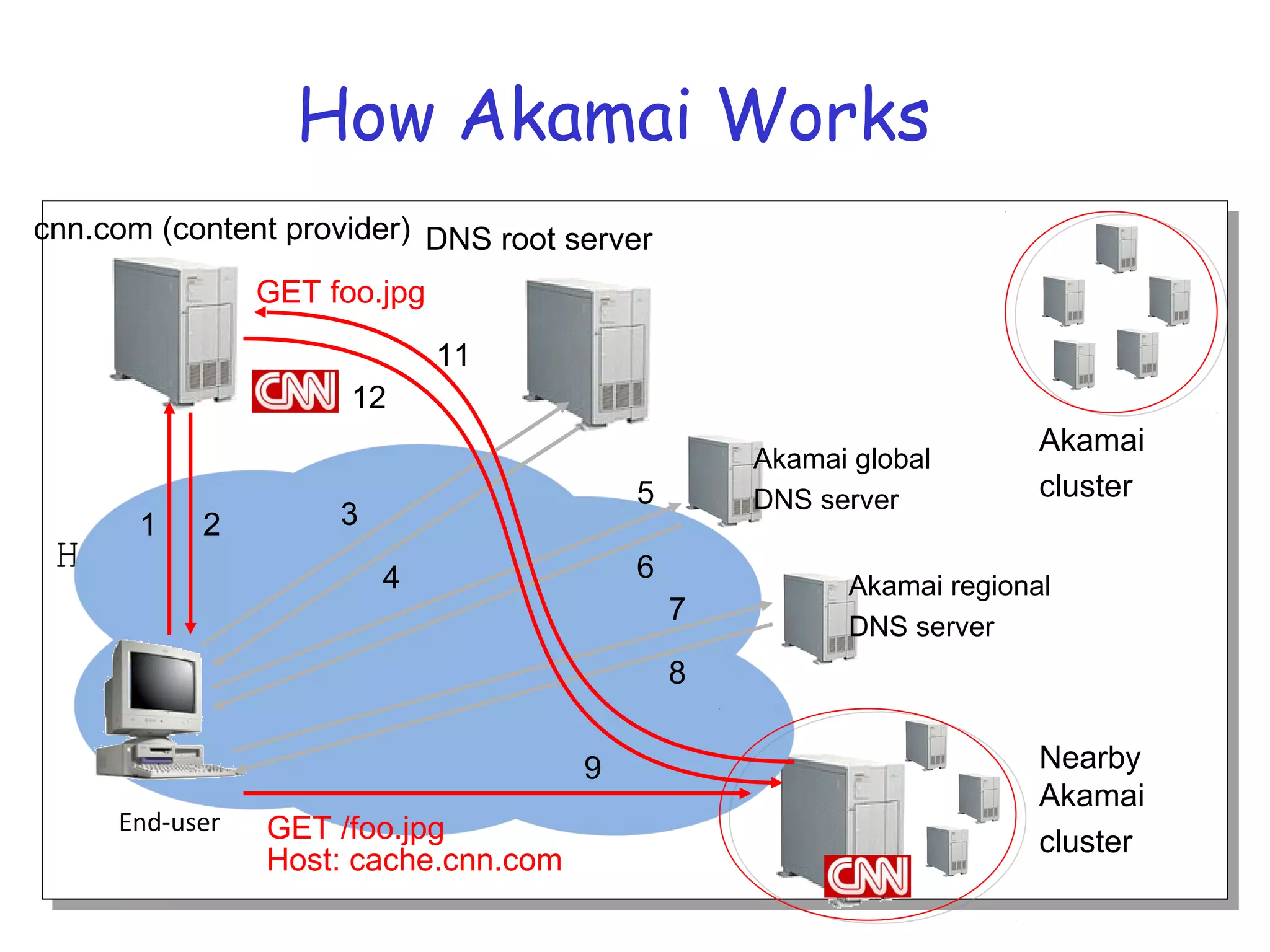
Web caching and content distribution networks aim to improve performance and reduce bandwidth usage. Caching stores previously requested content for future use. Proxies and CDNs place cached content on edge servers near users. When a request is made, the user is redirected to the closest cached copy to minimize latency. CDNs use DNS to map requests to nearby surrogate servers that hold replicated content. This allows the content to be served locally instead of traveling over long distances to the origin server.