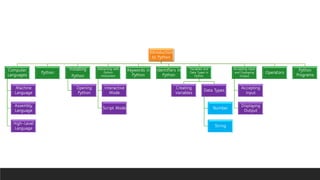
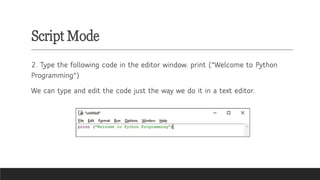
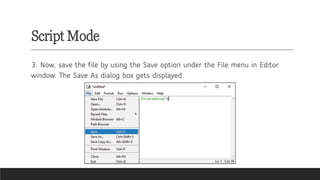
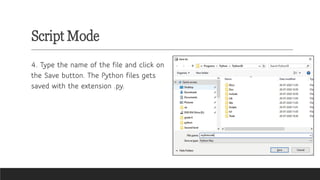
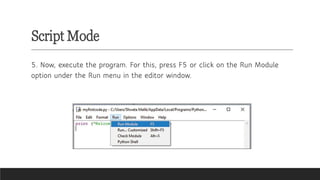
A mind map for Introduction to Python in CBSE Grade 6 Computer Science covers key concepts like:
- Python Basics: High-level programming language created by Guido van Rossum.
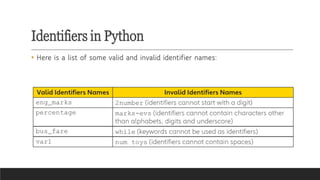
- Variables: Named storage locations holding different data types.
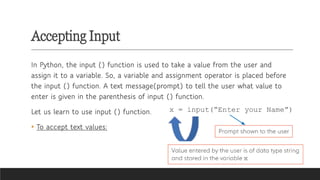
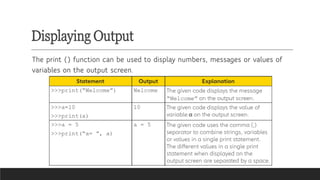
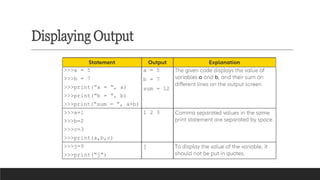
- Input/Output Functions: input() for user input, print() for displaying output.
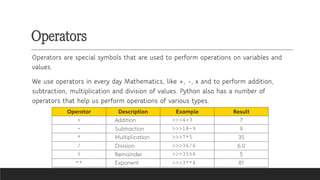
- Data Types: Understanding standard data types Python supports.
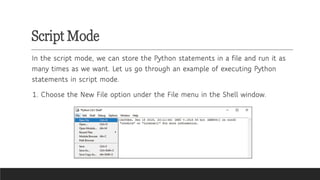
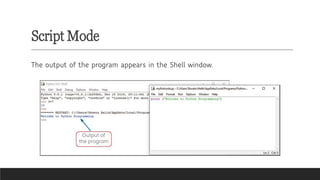
- Interactive Mode: Testing code snippets with immediate feedback.
- Indentation: Crucial for defining code structure and blocks.
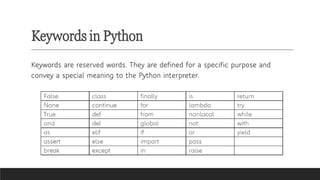
- Comments: Enhancing code readability with explanations.
This mind map aids quick revision and understanding of Python fundamentals.