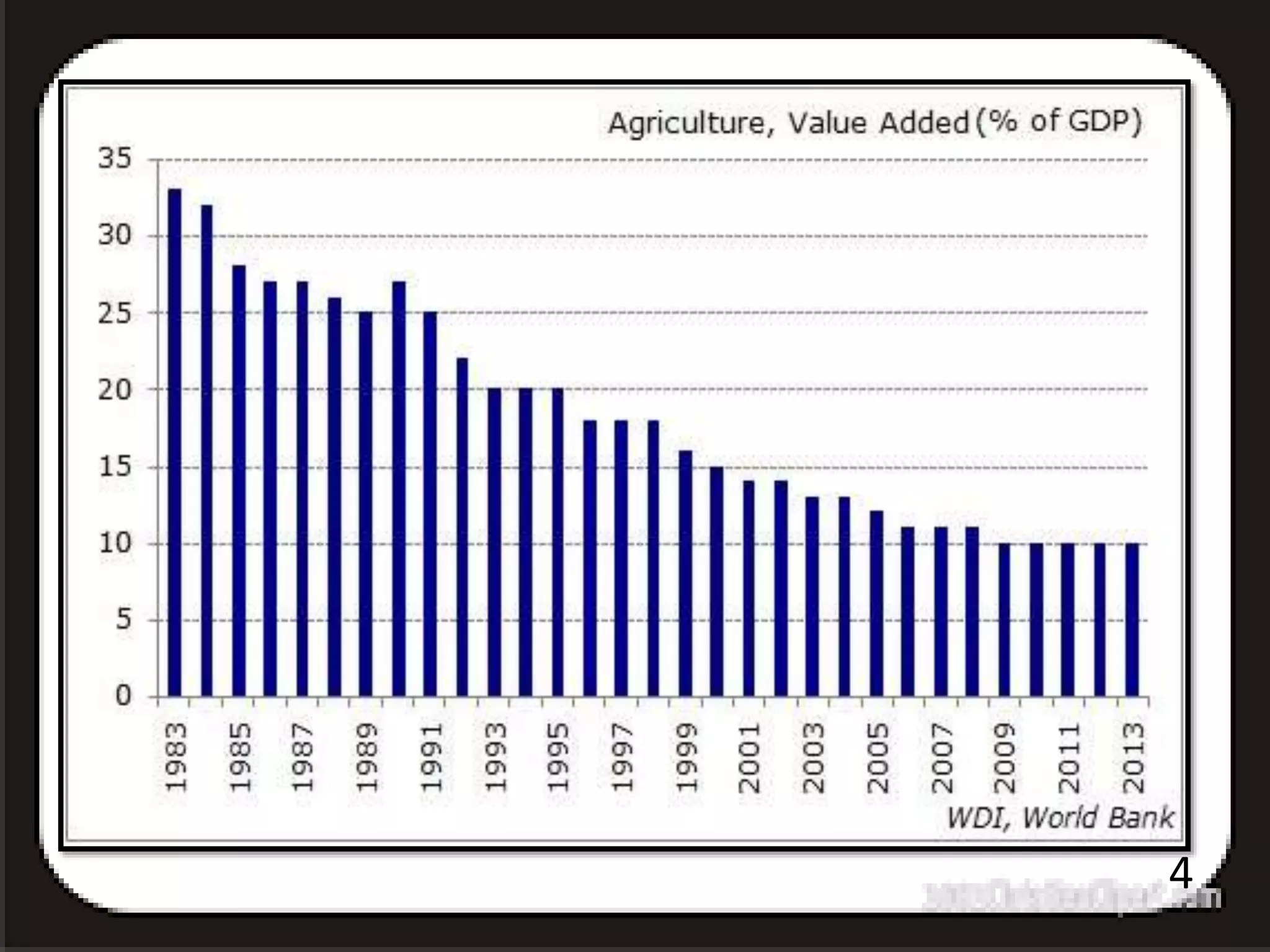
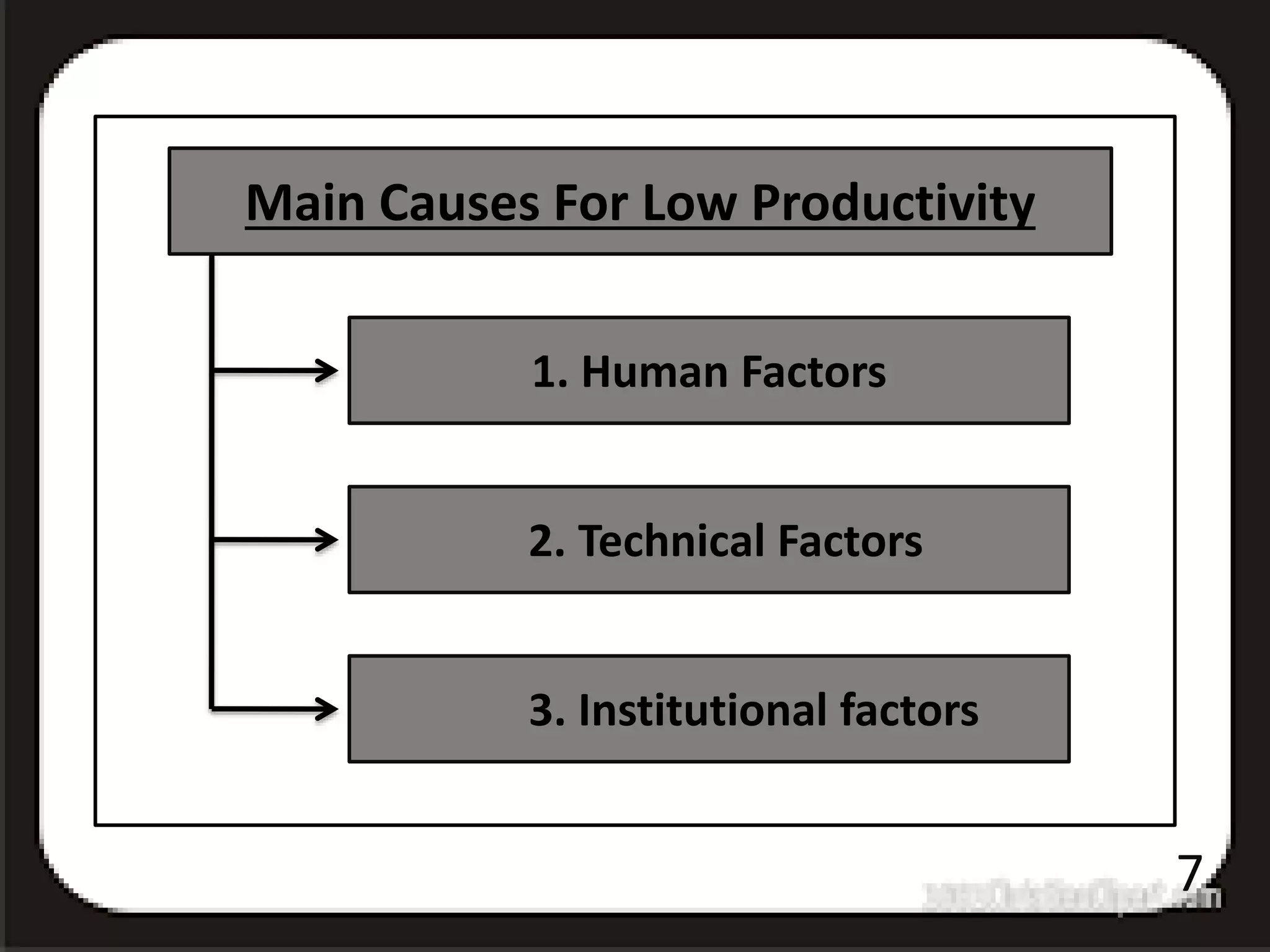
1) Low agricultural productivity in India is caused by human, technical, and institutional factors. Human factors include an unsupportive social atmosphere and high population pressure on limited land resources.
2) Technical factors involve traditional cultivation methods, outdated farm implements, insufficient irrigation, soil problems, pest and disease issues, weak cattle, lack of credit access, underuse of high-yield seeds, and improper marketing.
3) Institutional challenges are small farm sizes, fragmented land holdings, and a defective land tenure system that previously discouraged investment in agriculture. These interrelated issues have collectively constrained productivity growth.