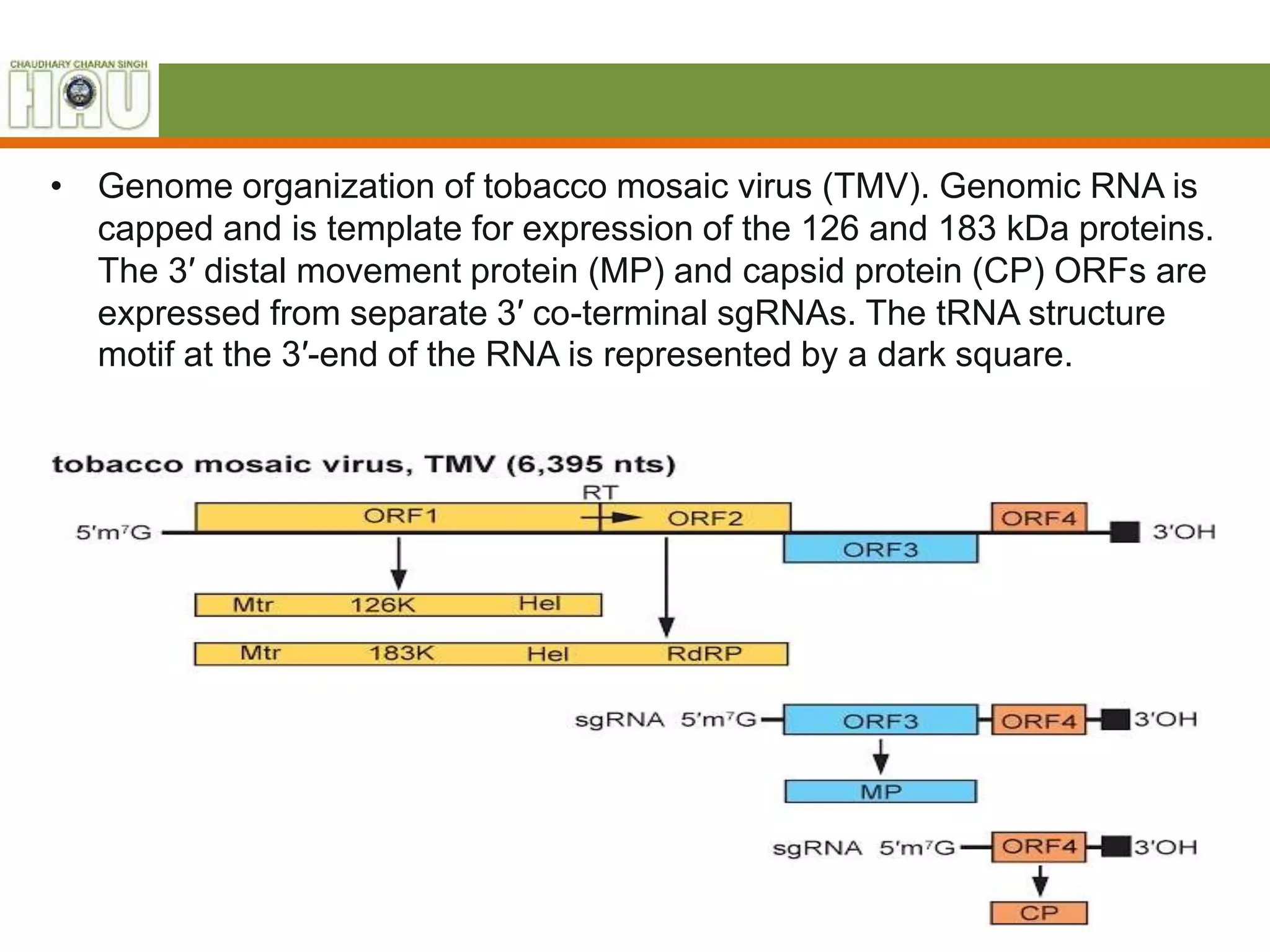
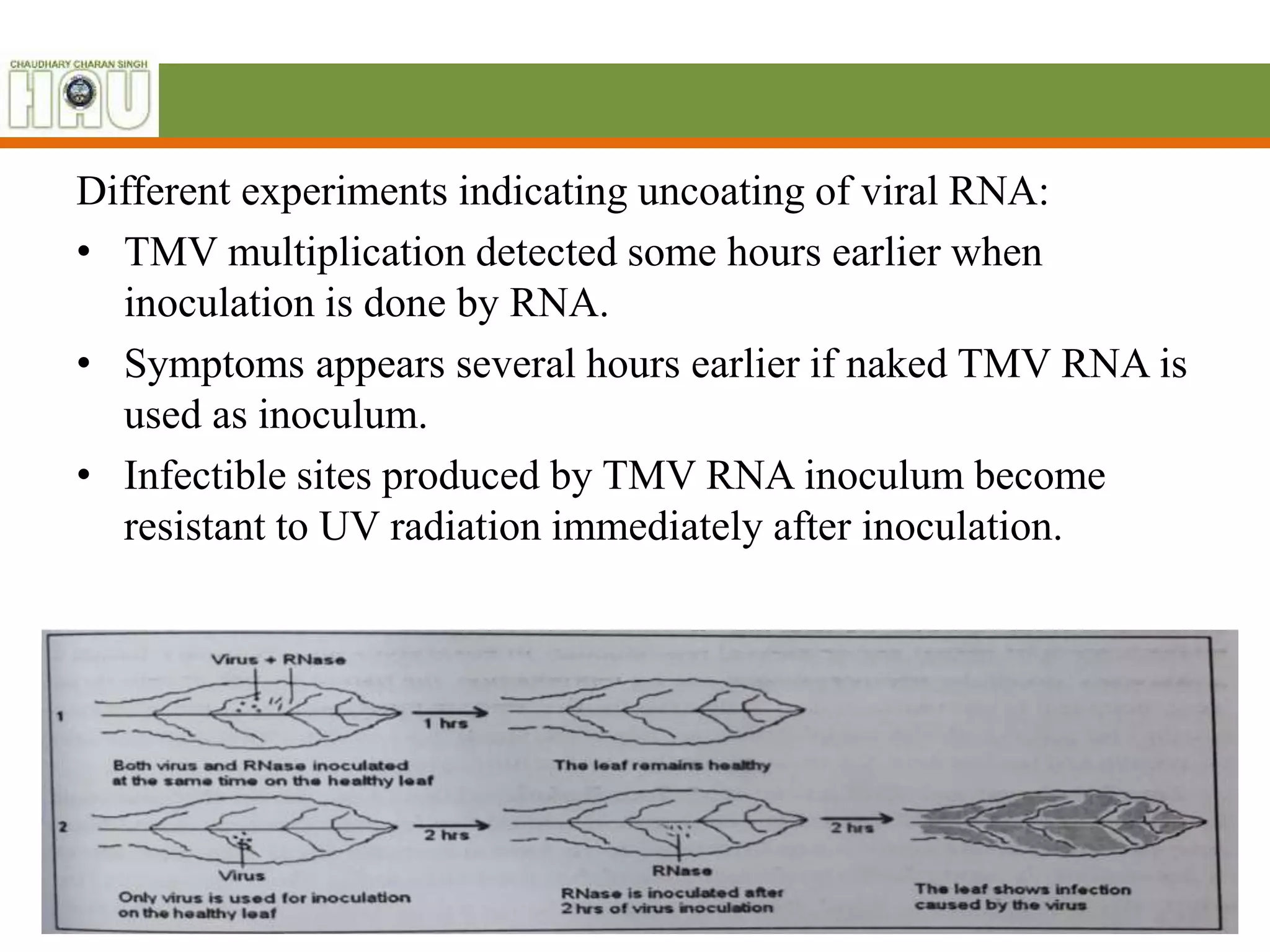
The document summarizes key aspects of Tobamovirus (TMV). It notes that TMV has a non-segmented genome and encodes a 30K movement protein. It has virions that are 18nm in diameter and 300-310nm in length. The genomic RNA encodes at least four proteins, including replication proteins of 124-132kDa and 181-189kDa. TMV enters plants through wounds or openings and its replication involves uncoating, replication of the viral genome and proteins, assembly of new virions, and movement within plant tissues.