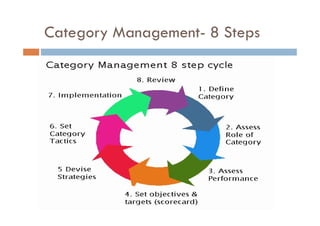
Category management is a strategic approach in retailing that organizes products into related groups to enhance customer satisfaction and increase sales. It involves defining categories, setting objectives, and continuously reviewing performance, often led by a 'category captain' supplier. The process aims to maximize profitability, reduce inventory issues, and improve customer relations.



![Category Management- Definition
4
Category management is a process that involves
managing product categories as business units and
customizing them [on a store by store basis] to satisfy
customer needs- Nielsen
The strategic management of product groups through
trade partnerships which aims to maximize sales and
profit by satisfying consumer and shopper needs-
Institute of Grocery Distribution](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/categorymanagement-definitionand8stepprocess-230717075752-2d793280/85/Category-Management-Definition-and-8-step-process-pdf-4-320.jpg)