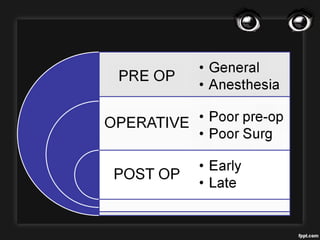
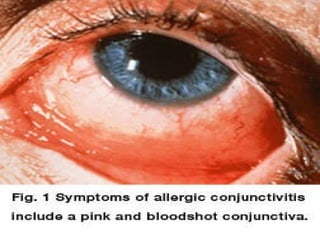
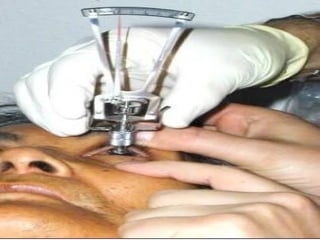
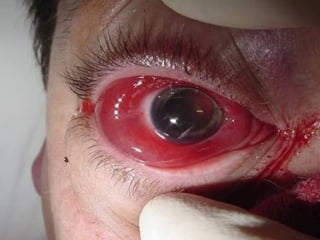
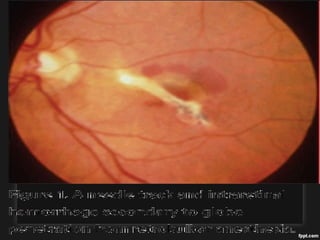
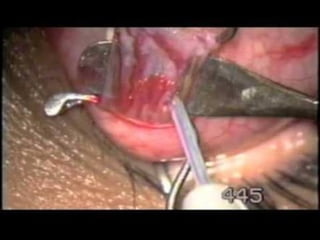
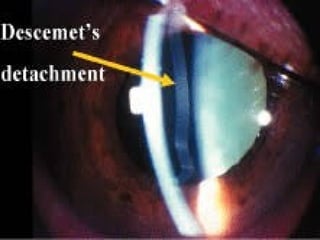
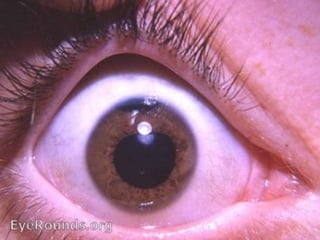
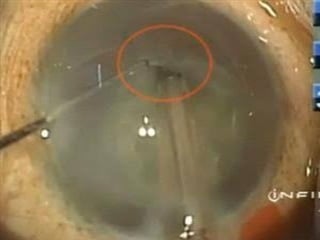
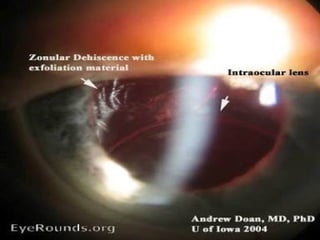
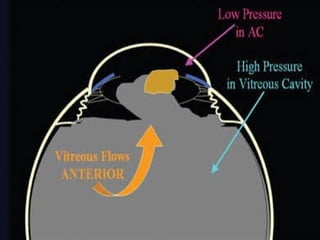
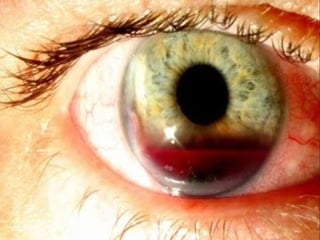
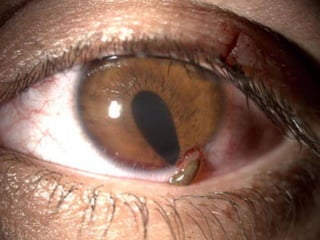
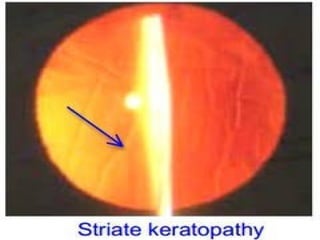
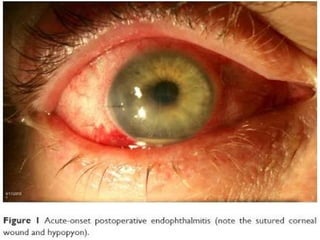
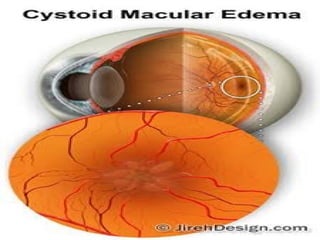
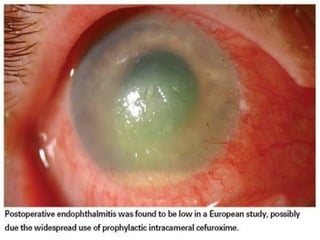
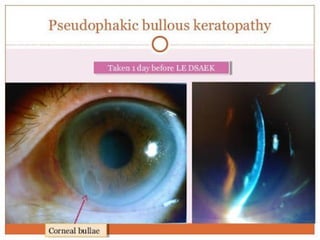
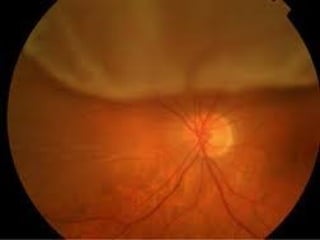
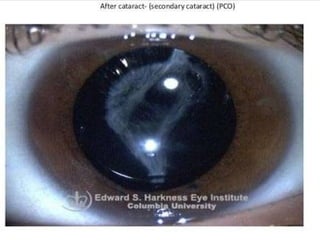
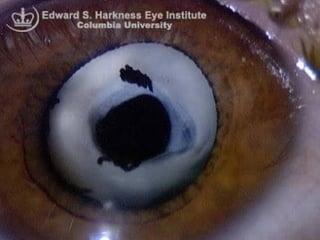
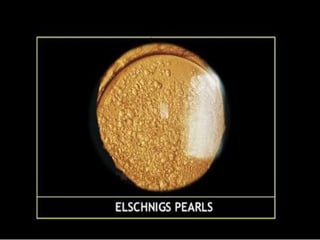
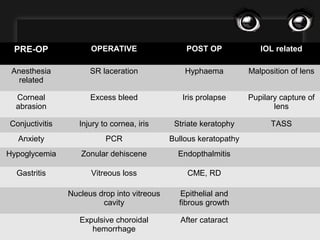
The document outlines various complications associated with cataract surgeries, including pre-operative anxiety, anesthesia risks, and multiple potential post-operative issues such as vitreous loss, endophthalmitis, and secondary cataract. It discusses treatment approaches for these complications and emphasizes the importance of careful surgical technique to minimize risks. Specific causes, symptoms, and appropriate management strategies for each complication are also detailed.