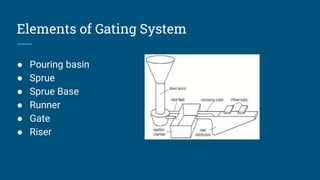
This document provides an overview of the basics of the casting manufacturing process. It discusses the use of patterns and cores to form mold cavities, the various types of patterns and cores, allowances provided in patterns to account for shrinkage and other factors, common casting defects, and key elements of gating systems used to feed molten metal into molds. Moulding processes are also summarized, including the constituents of moulding sand and its important properties.