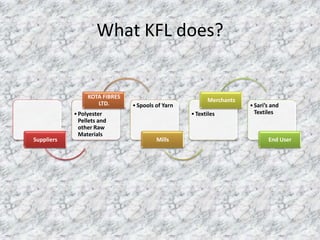
Kota Fibres Ltd. is facing a liquidity crunch and needs to raise cash. It produces textiles and has grown sales 18% annually. However, it now has high inventory, long receivable periods, and pays large dividends. To address this, the presentation recommends: adopting just-in-time practices to lower inventory levels; reducing the credit period to collect receivables faster; lowering dividend payouts; and implementing level production to increase profits and steady cash flow. These changes would improve Kota Fibres' financial ratios and solve its short-term cash needs.