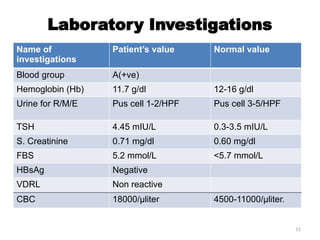
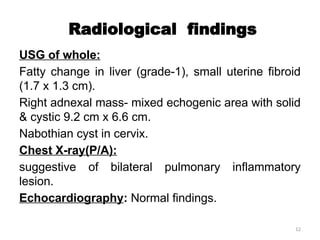
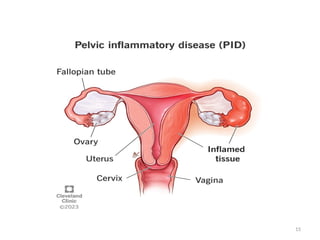
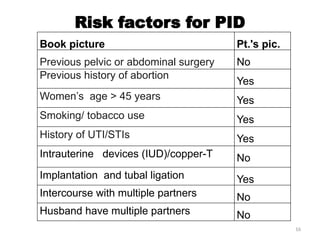
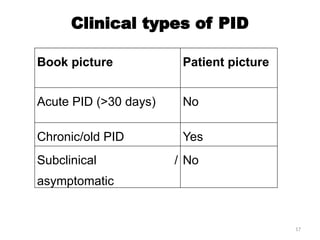
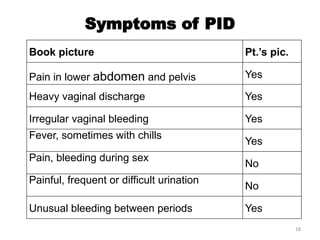
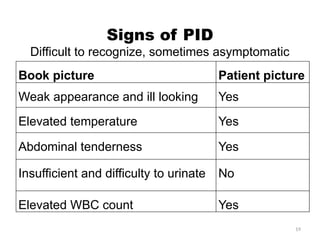
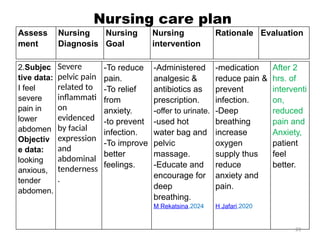
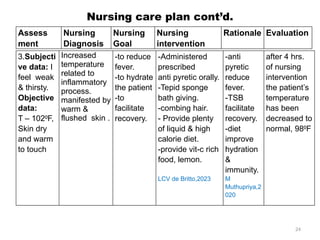
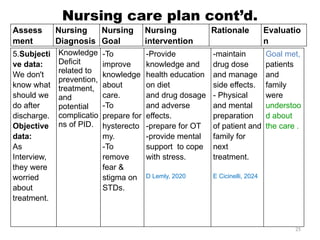
The document details a clinical conference on pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), focusing on a case study of a 47-year-old female patient with various symptoms leading to a PID diagnosis. It outlines objectives for enhancing clinical reasoning, nursing care plans, treatment options, diagnostic findings, and the importance of education regarding prevention and management of PID. The conference emphasizes the necessity of addressing both the medical and psychological aspects of patient care.