This document presents a case of Eagle syndrome. Key points:
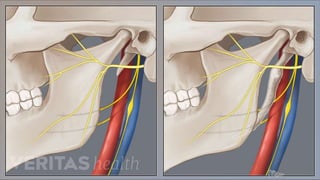
- Eagle syndrome is a rare condition caused by an elongated styloid process or calcified stylohyoid ligament, causing pain in the face and throat.
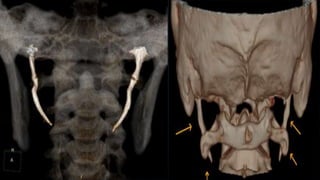
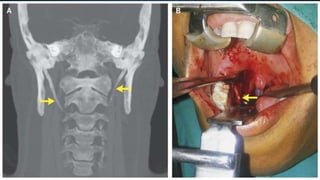
- A 28-year-old female patient presented with jaw and ear pain for 4 months and difficulty swallowing. CT scan revealed elongated styloid processes measuring over 4 cm bilaterally.
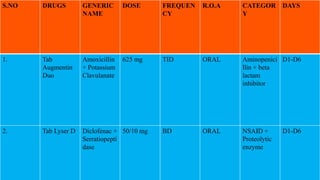
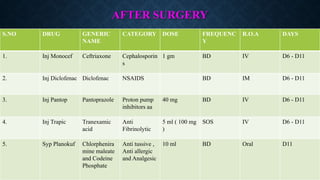
- The patient underwent bilateral tonsillectomy and styloidectomy. Post-surgery, she was treated with antibiotics, analgesics, and proton pump inhibitors and showed improvement in symptoms.


![CAUSES
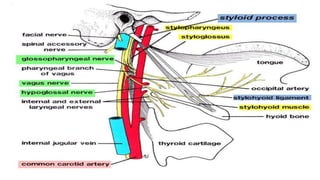
• It is usually caused by the elongated styloid bone or by the calcified stylohyoid ligament
• The styloid process is a short pointy bone just below your ear and the stylohyoid ligament
connects to the hyoid bone in the neck
• According to GARD [ Genetic And Rare Diseases Information Center ] about 4 percent of
population will have this long styloid process
• Other causes may be like tonsillectomy
• It is mostly bilateral [ Both Sides ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/casepresentationoneaglesyndrome-230714014152-b1feced1/85/Case-presentation-on-eagle-syndrome-pptx-4-320.jpg)


![SYMPTOMS
• Pain usually on 1 side of neck or face [ Especially at Jaw ]
• Pain when swallowing or turning the head to 1 side
• Globus hystericus
• Tinnitus
• Sore throat
• Ear ache
• Headache etc.,](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/casepresentationoneaglesyndrome-230714014152-b1feced1/85/Case-presentation-on-eagle-syndrome-pptx-8-320.jpg)








![ASSESSMENT
• Provisional diagnosis :- Globus hystericus
• Final diagnosis :- Based on subjective data & objective data [ CT scan of neck ]
obtained from the patient is assessed to have " Eagle's Syndrome "](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/casepresentationoneaglesyndrome-230714014152-b1feced1/85/Case-presentation-on-eagle-syndrome-pptx-19-320.jpg)


![S.NO VITALS DAY 1 DAY 2 DAY 3 DAY 4
1. Temperature [ in
degree fahrenheit ]
98.6 98.6 98.6 98.6
2. BP [ mm/Hg ] 100/70 110/70 110/80 120/80 , 100/60
3. PR [ bpm ] 70 72 67 84 , 86 , 66 , 65
4. SPO2 [ % ] 99 99 99 99 , 98 ( RR – 22
cpm , 18 )
5. RBS , FBS [ mg/dL
]
107 91 91 108 , 100 , 101 ,
111 , 91 , 105 , 77 ,
75](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/casepresentationoneaglesyndrome-230714014152-b1feced1/85/Case-presentation-on-eagle-syndrome-pptx-22-320.jpg)

![• Ct scan of neck :-
1. Mucosal thickening of b/l maxillary sinus with obliterated right osteomeatal
complex
2. Elongated styloid process b/l [ Right – 4.48 cm , Left – 4.41 cm ]
• Hb – 11.4 , 10.8 gm % [ 12-16 ]
• TRBC – 3.72 , 3.22 millions [ 4 – 6.2 ]
• PCV – 31.6 % ( 34 – 52 )
• CRP – 28.4 , 41.8 mg/l ( Upto 6 )
• X-ray etc.,](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/casepresentationoneaglesyndrome-230714014152-b1feced1/85/Case-presentation-on-eagle-syndrome-pptx-26-320.jpg)
