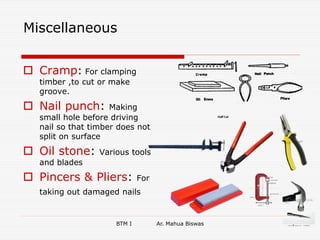
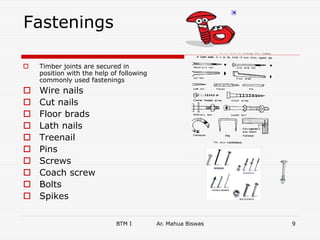
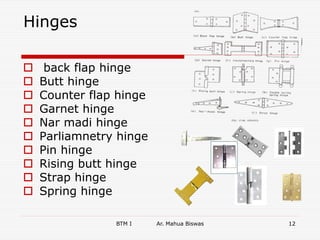
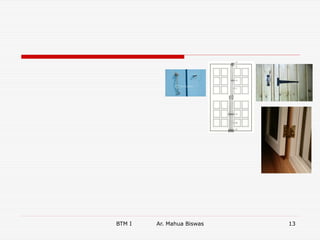
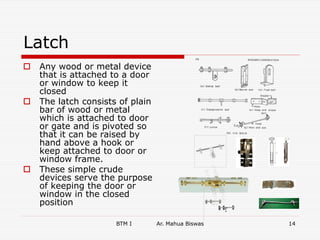
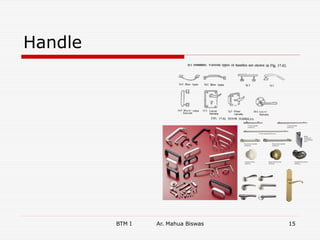
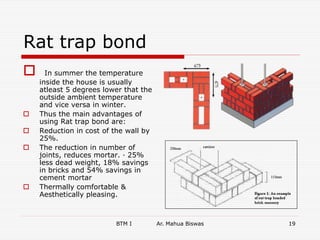
The document discusses various carpentry tools classified into 7 categories: marking and setting out, cutting, boring, planing, hammers and screw drivers, cramping and holding, and miscellaneous. It provides examples of common tools for each category such as squares, saws, braces, and planes. It also covers fastenings like nails, screws, and bolts used to secure timber joints. Fixtures and fastenings including hinges, handles, latches, and locks are described along with examples for each type. The final sections discuss rat trap bond, a cost-effective masonry technique using bricks placed on edge.