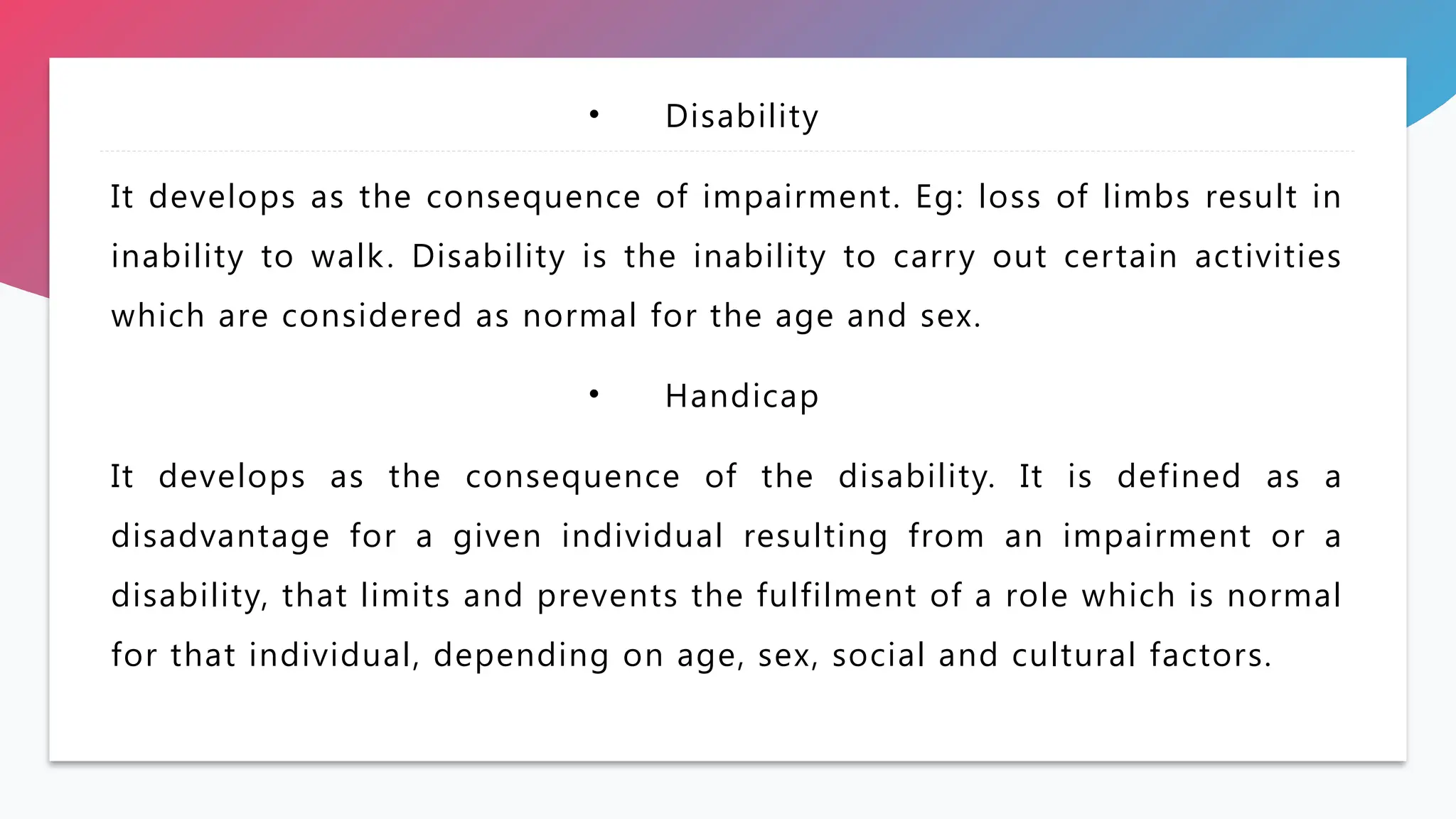
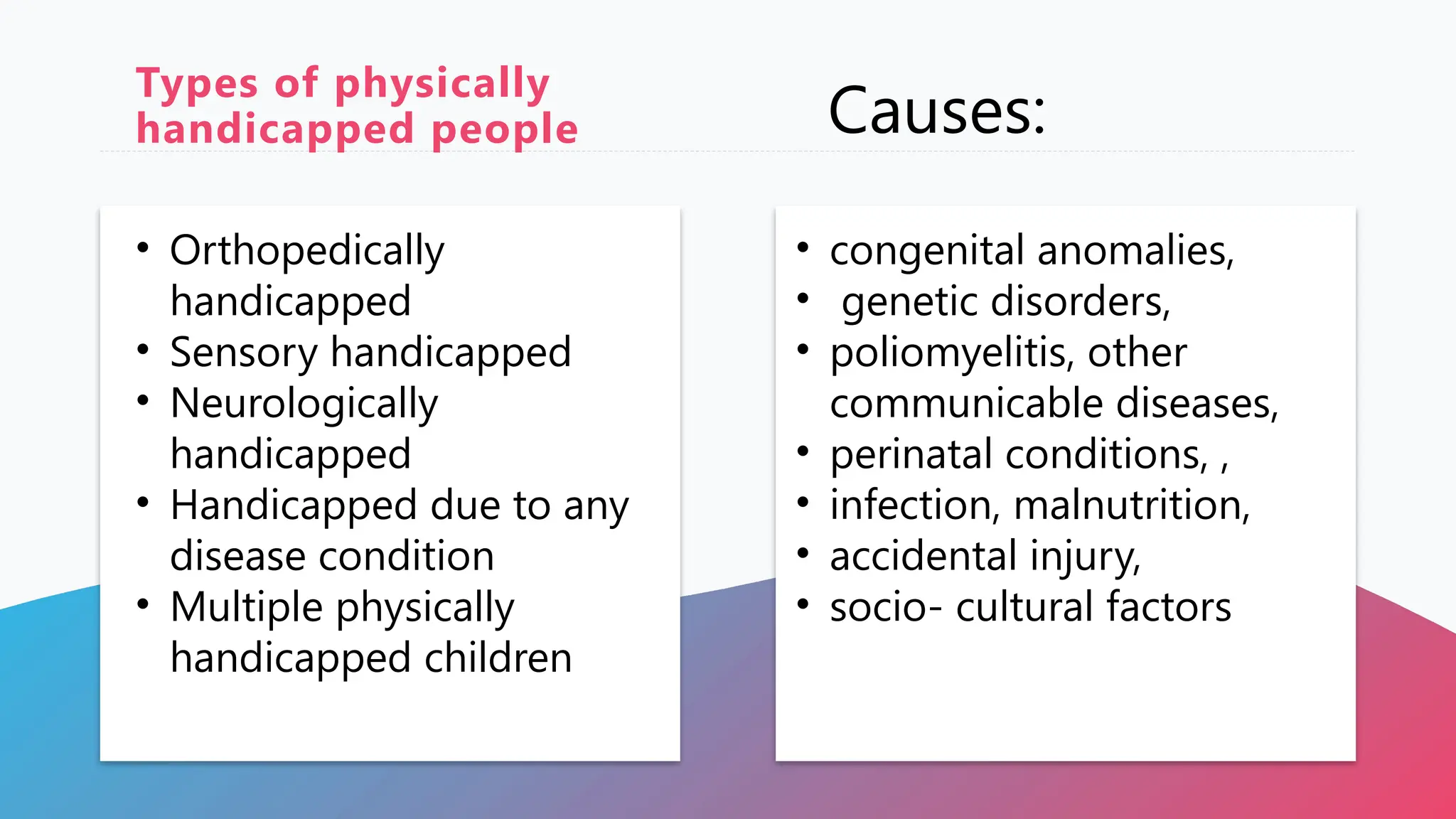
The document discusses the care of physically and mentally challenged children, defining conditions like impairment, disability, and handicap, along with their causes, prevention strategies, management approaches, and the importance of early diagnosis. It highlights the need for a multi-disciplinary approach to treatment, including medical and rehabilitation services, and emphasizes the role of legislation and support in facilitating rehabilitation. Mental retardation is also addressed, detailing its characteristics, signs, and the impact on cognitive and adaptive functioning.