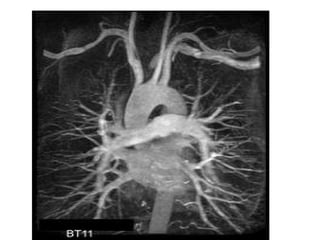
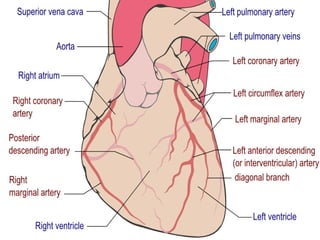
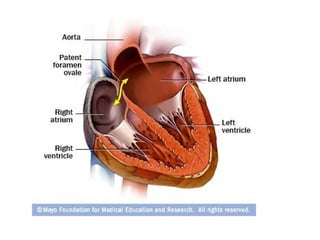
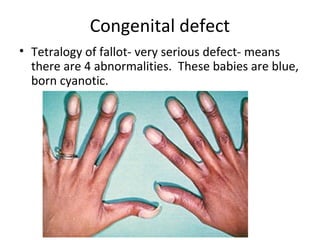
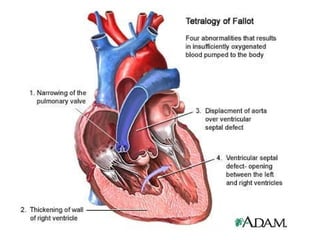
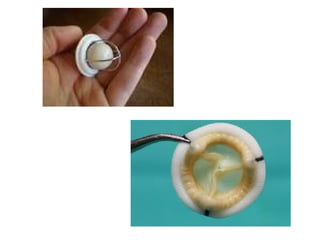
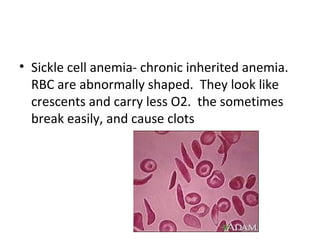
This document discusses several cardiac pathologies including coronary artery disease, hypertensive heart disease, congenital heart defects, valve diseases, heart infections, anemia, and sickle cell anemia. Coronary artery disease is caused by a buildup of plaque in the coronary arteries which can lead to chest pain, heart attack, and death. Congenital defects like tetralogy of fallot involve multiple abnormalities present from birth that cause symptoms like shortness of breath. Valve diseases can involve stenosis where valves are too narrow or insufficiency where valves allow backflow of blood. Rheumatic fever can cause scarring of heart valves. Infections like endocarditis involve inflammation of the inner heart lining. Anem