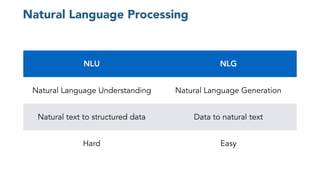
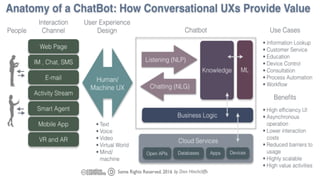
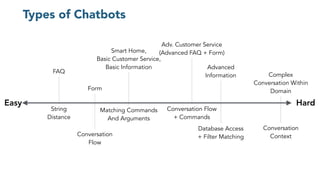
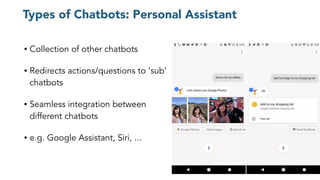
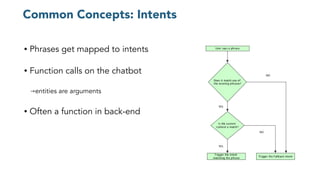
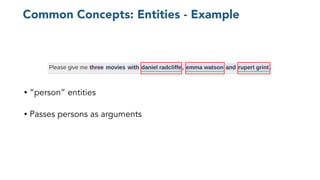
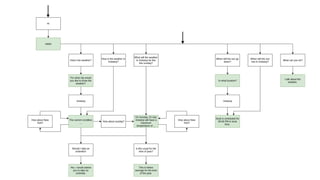
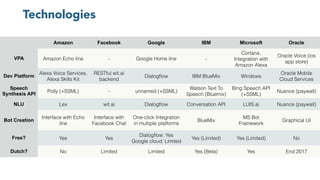
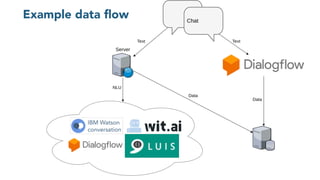
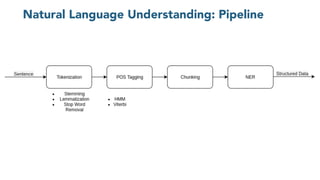
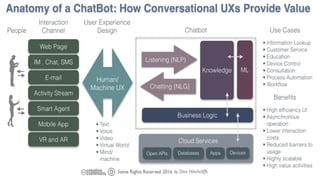
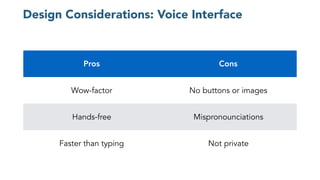
The document discusses chatbots, highlighting their benefits, such as user accessibility and natural language interfaces, along with their drawbacks, including user dissatisfaction after poor experiences. Various types of chatbots and their functionalities are detailed, alongside key concepts such as intents, entities, and conversation context. The future of chatbots is projected to focus on improving natural language understanding (NLU) speed and accuracy, with increasing acceptance and usage in businesses.


![The Good of Chatbots
Message platforms are everywhere
Simple, known interface
Applicable to many situations
63% of the people are willing to communicate through chatbots[1]
[1]: https://venturebeat.com/2017/06/17/the-good-the-bad-and-the-ugly-of-chatbots/
avaamo.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chatbots-201712-171220163052/85/Chatbots-4-320.jpg)
![Introduction: the Bad of Chatbots
73% won’t use the chatbot again after a bad experience[1]
75% want to know it is a bot[1]
50% are disturbed when a bot pretends to be human[1]
Not all languages are equally supported
[1]: https://venturebeat.com/2017/06/17/the-good-the-bad-and-the-ugly-of-chatbots/
steemit.com/@resteemitnow](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chatbots-201712-171220163052/85/Chatbots-5-320.jpg)