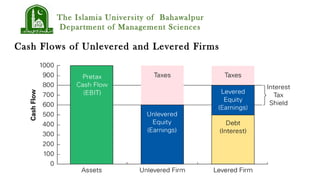
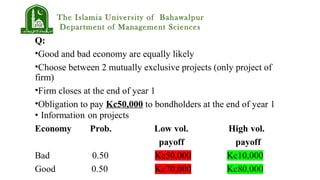
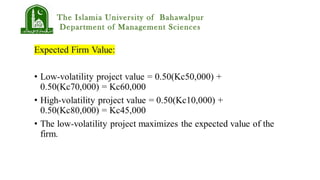
Bondholders could offer the stockholders a side payment equal to the difference in equity values between the two projects conditional on the good state occurring. This would align the incentives of stockholders with the maximization of total firm value.