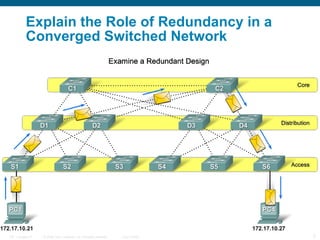
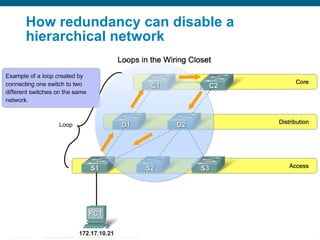
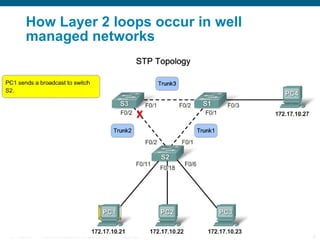
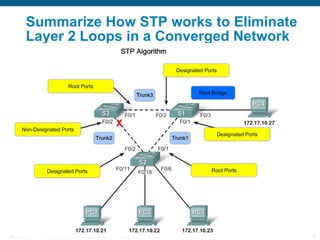
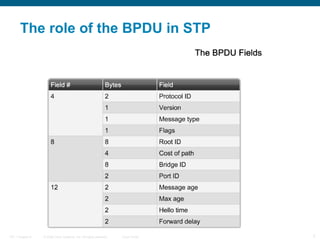
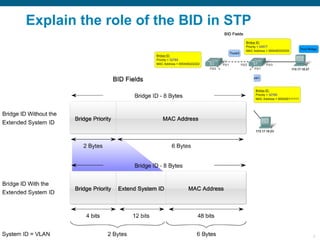
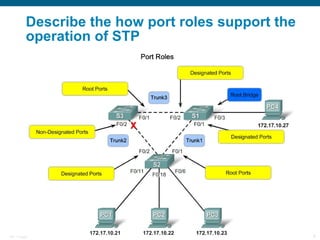
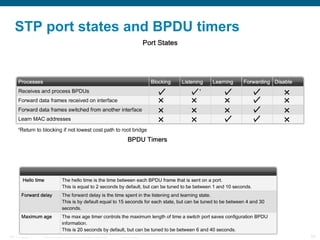
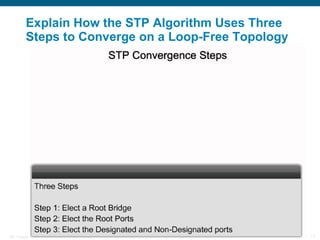
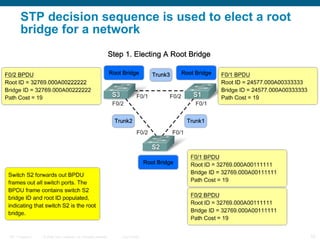
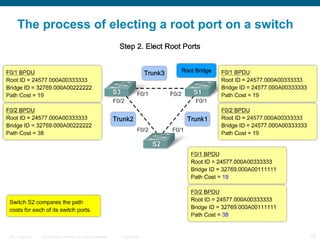
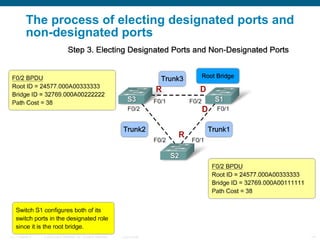
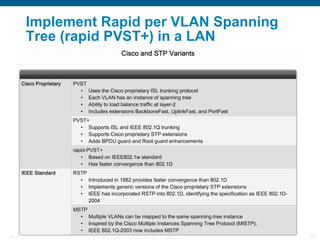
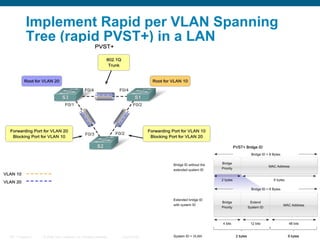
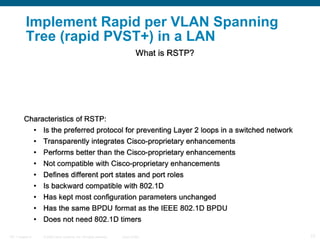
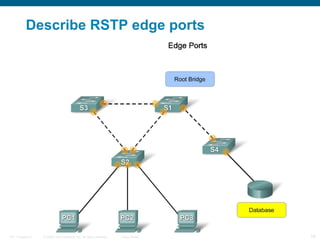
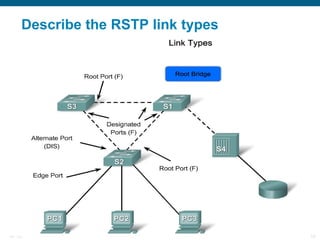
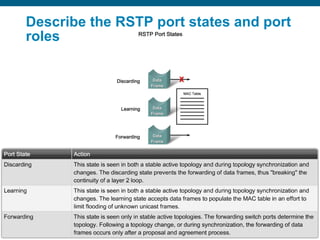
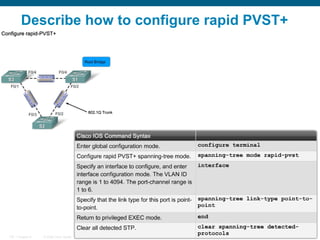
This document discusses spanning tree protocols (STP) which are used to prevent loops from forming on redundant networks. It explains that STP uses port states and timers logically prevent loops by electing a root bridge and designating root ports. Rapid per VLAN spanning tree (rapid PVST+) was developed to improve upon STP by adding VLAN support and significantly faster convergence times of around 6 seconds compared to STP's 50 seconds. The document provides objectives around explaining STP, how it works, and how to implement rapid PVST+ in a LAN network.