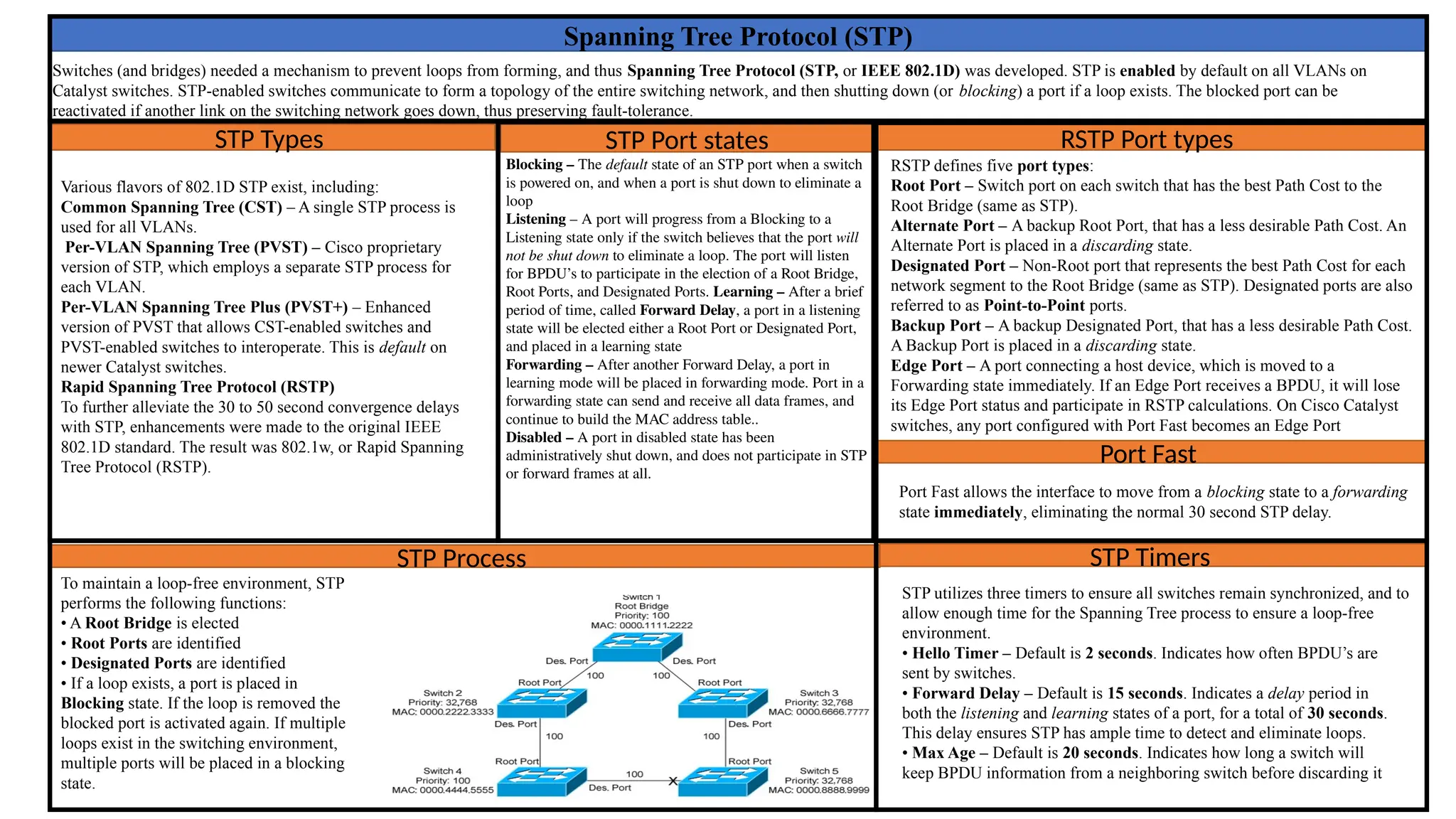
The document explains the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) and its importance in preventing loops in networks of switches and bridges. It details various types of STP, including Common Spanning Tree (CST), Per-VLAN Spanning Tree (PVST), and Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP), as well as the different port types and states crucial for maintaining a loop-free network environment. Additionally, it describes the timers used by STP to synchronize switches and facilitate the elimination of loops.