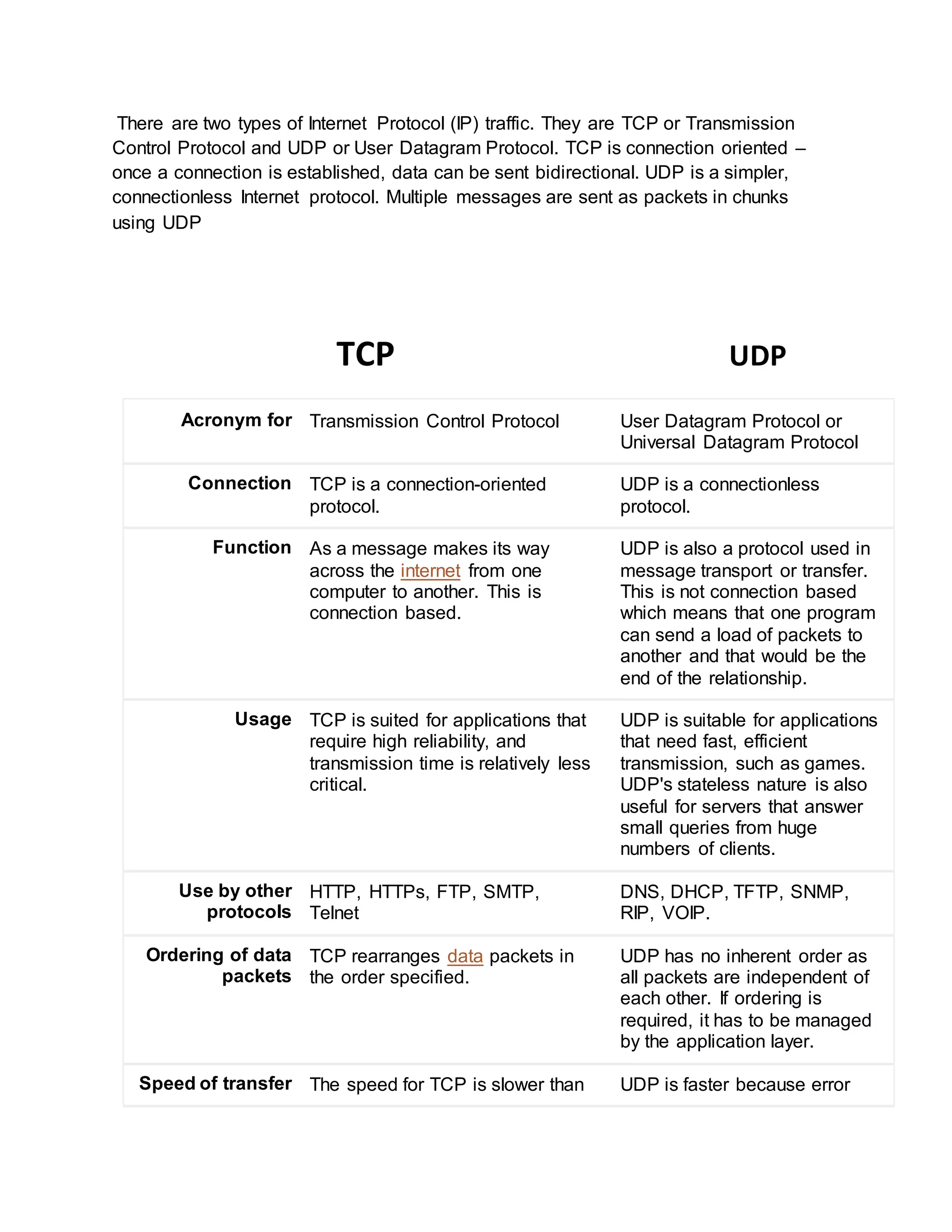
TCP and UDP are the main Internet protocols for transporting data.
TCP is connection-oriented, reliable, and ensures packets are delivered in order. UDP is simpler and connectionless, meaning it does not ensure delivery or order of packets.
While TCP is slower but reliable, UDP is faster but does not guarantee delivery of packets.