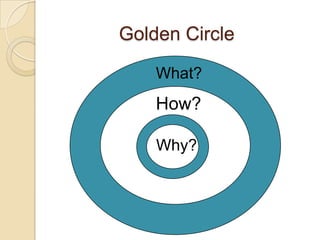
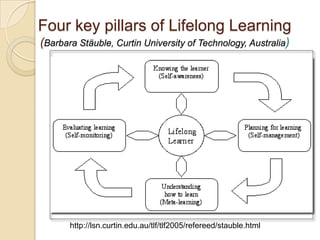
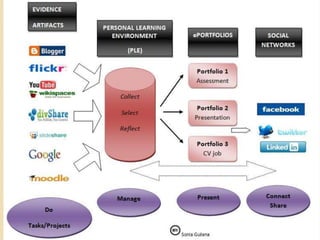
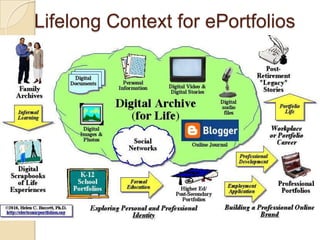
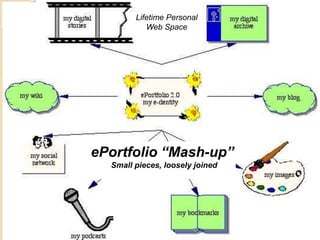
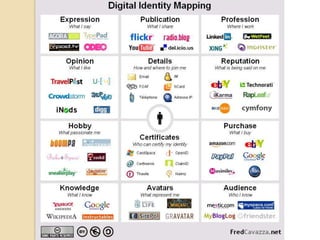
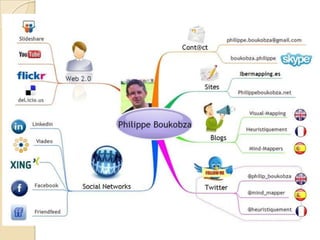
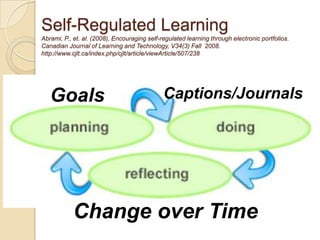
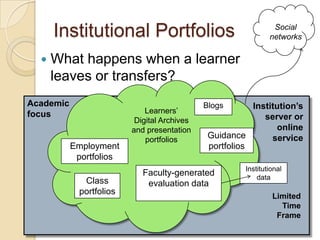
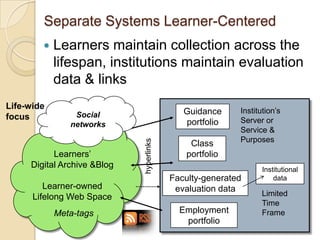
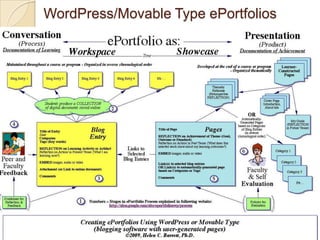
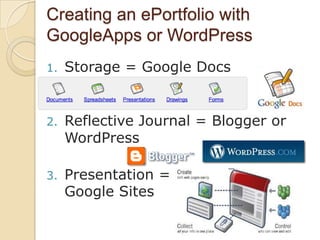
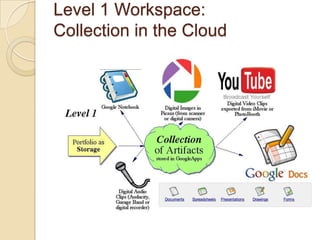
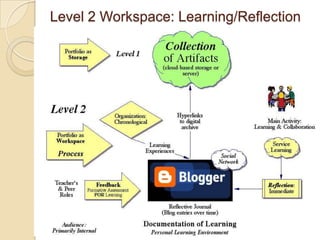
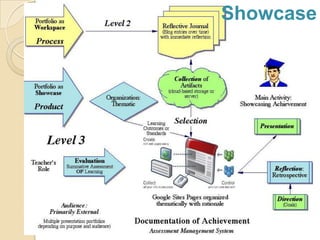
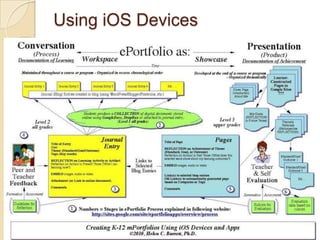
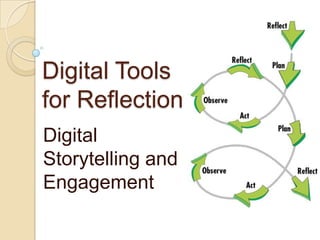
This document discusses teacher professional development portfolios and how they can serve as a lifelong personal and professional learning environment. It defines electronic portfolios and discusses how they can be used across one's lifespan for purposes like reflection, identity development, and career management. The document provides examples of how to create ePortfolios using tools like blogs, Google Apps, and WordPress to showcase work, develop themes, and engage in reflective practice. It argues that ePortfolios and digital tools can support lifelong, self-regulated learning when integrated with social networking strategies.